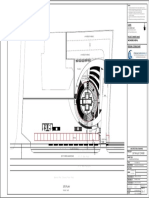
Review on Multi-Level Car Park
Radhika A. Dahane * Dr. P. S. Pajgade
Final year, M.E. (structures) Professor
PRMI&TR, Badnera, Department of Civil Engg
Amravati – 444701 PRMI&TR, Badnera,
radhika.dahane666@gmail.com Amravati – 444701
Abstract: Problems of parking space in urban towns and in all places of large congregation is
becoming a common issue around the world. Over the years engineers and architects have come
up with a lot of solutions finding a way to create more parking spaces within minimum size of land
by the design and construction of multi-storey car parks. This is line with the trend in modern
cities all over the world of developing high-rise buildings as to overcome the challenges of urban
over population, for optimal use of scarce land resources, as status symbol, etc. Standing on the
advances made so far and the frequent problematics verified on existing Multi-storey car parks,
this research present the design of a multi-storey car park for the mitigation of traffic challenges
in public areas using various case studies.
Keywords: Design, Multi-storey car park, Structural analysis, traffic challenges, Urbanization.
1.0 INTRODUCTION parking takes place. It is essentially a stacked
parking lot that has multiple access and exit
T he population of the world is continuously on
the increase and towns and cities have grown
up around their public transport system. The
system to avoid traffic congestion in and out. Car
parking systems have been around almost since
the time cars were invented. There are car parking
increasing population and expanding urban systems in most areas where there is significant
centers has been accomplished by increasing car amount of traffic. Car parking systems and the
ownership and increasing demand for movement accompanying technologies have increased and
for various purposes. Regardless of income or diversified over the years. Car parking systems
social status, the conditions under which people were developed in the early 20th century in
travel have become more and more difficult and response to the need for storage space for
sometimes absolutely intolerable. Demand for vehicles.
transport and travel intensity tends to increase
sharply with the growing size of a city and town Multi-storey car park is used virtually in every
especially when the city center or major centers of advanced nation. It is called parking structure and
activity continues to grow in terms of both size and is used in the United States especially when it is
employment . Parking in public areas can be very necessary to distinguish the structure from the
tasking with little or no form of security because it garage in a house. Architects and civil engineers
is fraught with all sorts of hazards created by usually call it a parking structure due to the nature
either humans or lack of parking structures. In of their work. The earliest known multi-storey car
order to reduce the stress of parking and any form park was built in 1918 for Hotel La Salle at West
of danger or insecurity to cars and owners, Washington Street in the West Loop area of
adequate parking facilities must be provided to downtown Chicago, Illinois. It was designed by
meet up for the demand of parking. Holabird and Roche. Today, a lot of innovation has
been done on parking system, ranging from
Over the years engineers and architects have providing services of man power to help in parking
found a way to create more parking spaces within automobiles to the use of machines and robots.
minimum size of land by the design and The design of a car park involves various process
construction of multi-storey car parks. Multi-storey and specifications. A lot of car park design
car park also known as a parking garage or a guidance document have been made and are still
parking structure is a building designed for car in the making up till now but the very first one was
parking with a number of floors or levels on which prepared in 1970’s and updated in 1980’s.
* Corresponding Author
� Multi-level parking has come with a number the highest supported level to the foundations. As
of reliefs since they come with a number of the height of a building becomes much, horizontal
advantages such as optimal utilization of spaces, deflections must be computed with greater
for comfort for drivers since the stress of struggling accuracy. The deflected shapes of individual
for parking space is taken off, more security and structural members should be taken into account
environmental harmony. in the final analysis of tall slender structures.
1.1 Literature Review 1.2 Success Stories
Multi-storey car parks have a number of ( Ref : “Pre feasibility report for development of
unique features that distinguish them from other multi-level car park facilities on PPP format in
buildings or structures. A lack of understanding cities of Karnataka” 6th October, 2009 by KSIIDC-
and recognition of these distinct characteristics by IL&FS Project Development Company (KIPDC)
designers and those responsible for inspection
and maintenance is believed to be the major 1.3 Case Studies
cause of many of the common problems identified
Project summary sheets of the Multi level Car
in these structures.
Parking Projects which are successfully
Parking structures are generally classified as implemented across India are provided below.
either “static” or “automated.” The automated
Sector 17 – Chandigarh
parking are more common in Europe while static is
the most prevalent type of parking structure in the
United States. The two types of ramps that can be Parameters Details
used are straight ramp and curve ramp. Five types Developer SPML
of layout that can be used in traditional parking Mun.Corporation
structure includes parallel packing, perpendicular/ Client
o o o o
Chandigarh
angle 90 , angle 60 , angle 45 and angle 30 . The Capacity (ECS) 1200
floor level system can be flat on the same floor,
Height G+3 + 2 basement
can be split level or staggered floor systems or
Combination (Manual,
sloping floor systems. For the design aspect, there Technology / Type
are numerous configurations of multi-storey car semi‐Automatic)
parks featuring different arrangements of deck and Land area 6996 sqm
ramp. The final selection of the configuration will Approx Cost 3.50 lac / ECS (2007)
be determined by the overall size of the car park, Upto 2 Hour ‐ Rs 10
the shape of the site and the use for which the car For 2 to 5 Hour ‐ Rs 15
Parking Charges
park is intended. Starting from the planning For > 5 Hour ‐ Rs 20
dimensions, you consider the bay width, aisle Monthly ‐ Rs 500
width, ramp dimensions, planning grid, alignment Occupancy Under implementation
paths to exit barriers, means of escape distances, 9% of floor area +
travel distances from the car to the destination, Commercial Facility Advertising inside
security, visibility, space allowances, lift provision premises)
and payment system among other things.
Implementation Str. BOT
In structural design, a building that is at least Concession Period 9 yrs 11 months
three storey in height must be framed. The loads
from the occupants are transmitted through the Many factors influence whether a user will
slab, beam and column and to the foundation and find the car park easy to use and be comfortable in
therefore each element of the frame must be the car park. The most important elements are
designed to effectively handle its own dead load outlined below:
and the load being transferred to it. For the
• size of car park and ease of circulation
idealization of the actual structure, the structural
model should relate the actual behavior to material • layout in terms of column spacing, ability to find
properties, structural details, and loading and available spaces easily, aisle and ramp widths,
boundary conditions as accurately as it is headroom and ramp gradients.
practicable. The structure should be so designed • safety and security
that adequate means exist to transmit the design
ultimate load, wind and imposed loads safely from • parking angle.
�• level of visibility and lighting car park. For longer-stay car parks, this is not so
critical; therefore the bay Dimensions could be
• quality and style of internal surface finishes
reduced where customers are more familiar with
• clear and concise user information and signage. the parking arrangements such as at office or
station car parks.
New Market – Kolkata
Some structural failures were reported in the
Parameters Details mid-1990s concerning the 1970’s car parks, which
Developer Simpark mainly involved the older stock of car park
structures. Among these incidents was failure of
Kolkate Municipal
Client car park barriers caused by accidental impact that
Corporation
resulted in cars falling onto the lower floors. There
Capacity (ECS) 280
were other well publicized failures, one caused by
Height 1 floor (2nd Basement) concrete degradation with reinforcement corrosion
Technology / Type Fully Automatic in a slab with the structural consequences of a
Land area 4,320 sq m (180 X 24 m) punching shear failure leading to a partial
Approx Cost 10 lac / ECS progressive collapse. The nature and mechanisms
Upto 4 Hour ‐ Rs 10 / hr of this collapse was fragile, with little prior warning
Parking Charges For 4 to 8 Hour ‐ Rs 55 of structural distress. Brittle failures are more likely
Monthly ‐ Rs 1,500 in reinforced concrete structures due to
Occupancy 80% deteriorations of structural members or wrong
Commercial Facility 1st Basement (3800 sqm) choice of materials and bad combination of same.
Implementation Str. BOT Failure to detect this kind of mechanisms leads to
concrete degradation and corrosion to progress
Concession Period 20 yrs (from 2007)
until structural collapse occurs.
O&M 15 min daily
In recognition of the problems affecting
Sambhaji Park – Pune development of car park technology and to allow
the lessons learnt from such failures to be
incorporated into design guidance, review of
Parameters Details institutional guidance began in July 1999. The
Capacity (ECS) 80 review noted that failures in older car parks were
Developer Ram Ratan Group not connected to inadequate design details and
Height 40 mts insufficient understanding of the adverse loading
Technology Automatic (Tower conditions to which the structures could be
Parking) subjected and the poor performance of drainage
Land area 250 sqm and waterproofing systems, which are vital for the
Approx Cost 28 Crs. durability of the structure. The situation was
worsened by the absence of proper monitoring
Parking Charges Normal (10 Rs for two hrs
and 50 for whole day) and adequate maintenance.
Occupancy 50% (no parking Structural health monitoring, inspection and
regulation has not been maintenance of car parks by qualified
enforced) professionals experienced in corrosion, fatigue
Commercial Facility None (only advertisement and structural deterioration are essential for
rights) durable structures including car parking facilities.
Implementation Str. BOT As with any other structure, design details that
Concession Period 5 yrs enhance durability, facilitate proper inspection and
the maintenance of drainage and waterproofing
Parking arrangements should be designed to will significantly extend the life and safety of a car
allow drivers to manoeuvre easily and safely. The park structure. Historically, car parks were
maneuvering ease is a function of aisle and bay designed according to building codes. The review
widths, which also influence the dynamic capacity suggested that durability requirements for closed
of the car park. This is of particular importance for car parks should be similar to those for bridges or
short-stay car parks such as at retail centers marine structures due to vehicular wheel load
where aisle capacities are critical to the operation effects not applicable to building structures.
� ACKNOWLEDGEMENT [5] C. Arya, Design of Structural Elements:
Concrete, Steelwork, Masonry, and Timber
The authors like to thank Prof. P. A. Kadu, Designs to British Standards and Euro codes,
HOD, Department of Civil Engineering P. R. M. I. (3rd Edition; Taylor & Francis, London, 2009).
T & R., Badnera for his encouragement, fullest
cooperation and valuable guidance given by him [6] “Pre feasibility report for development of
to author from time to time. Authors also thanks to multi-level car park facilities on PPP format in
Dr N. W. Kale principal, P. R. M. I. T. & R., cities of Karnataka” 6th October, 2009 by
Badnera for providing him library facilities for KSIIDC-IL&FS Project Development Company
collection of literature. Author also thanks to (KIPDC)
colleagues as well as non teaching staff of Civil
department who directly or indirectly helped in
preparing the manuscript.
References Author’s Biography
[1] International Journal of Innovative Technology
and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE) ISSN: Ms. Radhika A. Dahane is
2278-3075, Volume-4 Issue-10, March 2015 Graduated in Civil Engineering
and presently pursuing her PG in
[2] D. Pike, C.K. Jolly, M. Pundsack, J.N. Stewart Structural Engineering from Sant
and W. Whapples, Design recommendations Gadge Baba Amravati University,
for multi-storey and underground car parks; Amravati (Maharashtra).
Published by the Institution of Structural
Engineers; 4th Edition London, UK, (2011).
Prof. P.S.Pajgade obtained PG
[3] M.D. Khairunnur, L. Nuur L, Multi-storey Car (Earthquake Engineering.) from
Parking; accessed on 2nd Oct, 2013; University of Roorkee, Roorkee
http://www.scribd.com/mobile/ doc/2194924? and doctoral degree from
Width. Amravati University, Amravati. His
area of specialization is Structural
[4] K. Milton, Steel-framed Car Parks; Published Dynamics .He is working with
by Corus Construction & Industrial; P.R.M.I.T & R, Badnera. He has a teaching
Scunthorpe, North Lincolnshire, 2004 experience of 29 years