Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Che-12 CH-01 E-07,08,09,10,11
Uploaded by
Ridhima Rathor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesThe document discusses different types of solids and crystal structures. It describes covalent or network solids where atoms are connected by covalent bonds forming giant molecules. Examples given are diamond, silicon carbide, and silica. It also discusses the properties of diamond and graphite. Graphite has layers of carbon atoms bonded within each layer, but the layers can slide, making graphite soft. The document then covers crystal lattices as regular arrangements of points that make up unit cells, the smallest repeating portion that generates the crystal structure. There are 14 possible lattice types and characteristics of unit cells like particle positions and edge lengths are discussed.
Original Description:
Original Title
che-12 CH-01 E-07,08,09,10,11 (4)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of solids and crystal structures. It describes covalent or network solids where atoms are connected by covalent bonds forming giant molecules. Examples given are diamond, silicon carbide, and silica. It also discusses the properties of diamond and graphite. Graphite has layers of carbon atoms bonded within each layer, but the layers can slide, making graphite soft. The document then covers crystal lattices as regular arrangements of points that make up unit cells, the smallest repeating portion that generates the crystal structure. There are 14 possible lattice types and characteristics of unit cells like particle positions and edge lengths are discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesChe-12 CH-01 E-07,08,09,10,11
Uploaded by
Ridhima RathorThe document discusses different types of solids and crystal structures. It describes covalent or network solids where atoms are connected by covalent bonds forming giant molecules. Examples given are diamond, silicon carbide, and silica. It also discusses the properties of diamond and graphite. Graphite has layers of carbon atoms bonded within each layer, but the layers can slide, making graphite soft. The document then covers crystal lattices as regular arrangements of points that make up unit cells, the smallest repeating portion that generates the crystal structure. There are 14 possible lattice types and characteristics of unit cells like particle positions and edge lengths are discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Scientific coaching centre class -12 chemistry unit- 0 1 E-07
4 )Covalent or Network solids:-
● In this type of Solids the constituent particles are atoms of Same or different
elements connected to each other by covalent bond network .
● They are called giant molecules
Examples: diamond , silicon,carbide,silica,etc.
Characteristics of covalent or network solids
i) They are very hard and brittle.Diamond is the hardest su
ii) They have very high melting points.
iii) They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
iv) They have high enthalpies of fusion .
Characteristics of diamond
i) Diamond is the hardest substance in nature
ii) It is an insulator
Characteristics and structure of graphite
● Graphite is soft.
● It is a conductor of electricity.
Structure of graphite
Carbon atoms are arranged in different layers and each atom is covalently bonded to three of its neighbouring
atoms in the same layer. The fourth valence electron of each atom is present between different layers and is free
to move about. This free electrons make graphite a good conductor of electricity different layers can slide one
over the other .This makes graphite a soft solid and a good solid lubric
Scientific coaching centre class -12 chemistry unit- 0 1 E-08
Fig: Structure of graphite
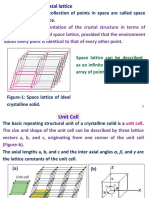
Crystal lattices and unit cells
Crystal lattice:A regular three dimensional arrangement of points in space is called a
crystal lattice .
➔ There are only 14 possible three dimensional lattices . They are called Bravais
lattices.
Characteristics of a crystal lattice
(a)Each point in a lattice is called lattice point or lattice site.
Scientific coaching centre class -12 chemistry unit- 0 1 E-o9
(b) Each point in a crystal lattice represents one constituent particles which may be an
atom ,molecule or an Ion.
(c)Lattice points are joined by straight lines to bring out the geometry of the lattice
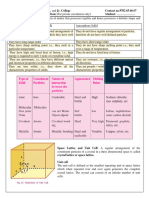
Unit cell :-Unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice which , when repeated in
different directions, generates the entire lattice .
Characteristics of a unit cell
I. Its dimensions along the three edges a, b and c .These edges may or may not be
mutually perpendicular .
II. Angle between the edges, (between b and c) (between a and c) and (between a and
b).Thus,a Unit cell is characterized by six parameters a,b,c, , , and .
Types of unit cells
(a) Primitive unit cells or simple unit cells
(b)Centered unit cells
(a)Primitive unit cells :-Unit cells in which the constituent particles are present only at the
corners are called primitive unit cells
(b)Centred unit cells:- When a unit cell contains one or more constituent particles
present at position other than corners in addition to those at corners, it is called a centred unit
cell
Scientific coaching centre class -12 chemistry unit- 0 1 E-10
Types of centred unit cell
i) Body-centred unit cell-In a body centred unit cell each corner is occupied by a Point and one Point
occupies t he the centre of the body of the unit cell
ii) Face centred unit cell- This unit cell Contains one constituent particle present at the centre of each face,
besides the ones that are at its corners
iii) End- centred unit cell-I n End- centred unit cell 8 lattice points are on the corners and one lattice point is
present at the centre of any two opposite faces.
seven primitive unit cells and their possible variations as Centred unit cells
Calculation of atoms in a unit cell
Scientific coaching centre class -12 chemistry unit- 0 1 E-11
No.of atoms in a simple cubic unit cell=8 × ( corner atoms ) × 1
8
atom per unit cell=1atom
No.of atoms in a body- centred cubic unit cell=8 × ( corner atoms ) × 1
8
atom per unit cell +1(body center atom)
=1+1=2
No.of atoms in a face centred cubic unit cell=8 × ( corner atoms ) × 1
8
atom per unit cell +6(face atom)
1
× 2
atom per unit cell =1+3=4
You might also like
- Unit-6 Solid State 2021Document12 pagesUnit-6 Solid State 2021jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Solid State 2Document19 pagesSolid State 2Kaustubh PurohitNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Document21 pagesElectrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Nur Mohammad AkramNo ratings yet
- ch3 p1Document42 pagesch3 p1Sary KilanyNo ratings yet
- EPM - Mid - Lecture - 02 - Chapt - 1 CompressDocument24 pagesEPM - Mid - Lecture - 02 - Chapt - 1 CompressPartho Protim MondolNo ratings yet
- Solids: Xii Science Chemistry Notes Unit 1 Solid StateDocument3 pagesSolids: Xii Science Chemistry Notes Unit 1 Solid StateRaashiNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument16 pagesSolid StateAman DeepNo ratings yet
- Solid State NotesDocument10 pagesSolid State NotesLesedi mmabatho MashabelaNo ratings yet
- Chm361-Chapter 3 SolidDocument60 pagesChm361-Chapter 3 Solidfatin harrisNo ratings yet
- 7 Crystalline & Solid StateDocument37 pages7 Crystalline & Solid StateNazmi LatifNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2013 - Chemistry CBSE - Hand Out - 1 - Solid StatesDocument6 pagesIIT JEE 2013 - Chemistry CBSE - Hand Out - 1 - Solid Statespedo1972No ratings yet
- SolidstateDocument21 pagesSolidstateAryan SaiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Document28 pagesElectrical Properties of Materials: Chap 1Shuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet
- 2-1. Review On Crystal Structure and Quantum Physics BandsDocument49 pages2-1. Review On Crystal Structure and Quantum Physics BandsStevie AdrielNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Part 1: Free Electron TheoryDocument43 pagesCourse Outline: Part 1: Free Electron TheorySabar AliNo ratings yet
- MME M1 Ktunotes - inDocument76 pagesMME M1 Ktunotes - inkannanNo ratings yet
- SMER1Document80 pagesSMER1Supreeth PremkumarNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document32 pagesCH 3Hasan AliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State PhysicsDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Solid State PhysicsRahmat KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Solid State: Multiple Choice Questions (1 Mark)Document149 pagesSolid State: Multiple Choice Questions (1 Mark)arun dapNo ratings yet
- Class7 Handout Mtse 5010 2019Document17 pagesClass7 Handout Mtse 5010 2019PPSwainNo ratings yet
- Topper Guidance Academy: Whole Chemistry by - DR - C.K.RaiDocument12 pagesTopper Guidance Academy: Whole Chemistry by - DR - C.K.Raikumar PraveenNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry Chapter 1 (The Solid State) Important Solved QuestionsDocument14 pagesClass 12th Chemistry Chapter 1 (The Solid State) Important Solved Questionsshamiksha dNo ratings yet
- MSE8013 Chapter01 Structure and Symmetry of CrystalDocument57 pagesMSE8013 Chapter01 Structure and Symmetry of CrystalJie GanNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Classes of Engineering Materials & Conducting MaterialsDocument18 pagesUnit - I: Classes of Engineering Materials & Conducting MaterialsDeependra SinghNo ratings yet
- Solid State Note 02Document47 pagesSolid State Note 02YudusterNo ratings yet
- "Crystal Physics": Submitted By:-Roll No.: - ClassDocument29 pages"Crystal Physics": Submitted By:-Roll No.: - Classsabitri beheraNo ratings yet
- Crystal LatticeDocument9 pagesCrystal LatticeShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Solid State Questions: 12th StandardDocument7 pagesSolid State Questions: 12th StandardShriya RameshNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Solid State 2023Document15 pagesUnit-6 Solid State 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- MEC208 Unit 1 2015-1Document125 pagesMEC208 Unit 1 2015-1KAMAL PATINo ratings yet
- BMT ManualDocument23 pagesBMT ManualAsheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Semiconductor Device Theory: Lecture 4: Space Lattice, Unit Cells, and Types Dr. Awais Gul MemonDocument18 pagesAdvanced Semiconductor Device Theory: Lecture 4: Space Lattice, Unit Cells, and Types Dr. Awais Gul MemonPDMA SindhNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure of MetalsDocument31 pagesCrystal Structure of MetalsTanzir Musa100% (2)
- Solid State NotesDocument36 pagesSolid State NotesRajeev KaushikNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics CH 1 NotesDocument11 pagesClass 12 Physics CH 1 NotesuvsNo ratings yet
- 2 Crystal SystemsDocument39 pages2 Crystal SystemskimNo ratings yet
- MSE - ChapterDocument42 pagesMSE - ChapterFaisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Solid State 1 MR DavidDocument188 pagesSolid State 1 MR Davidfrank samndomiNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Crystallography 2Document3 pagesX-Ray Crystallography 2Miles NsgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 NTDocument52 pagesLecture 1 NTMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv & V Crystal PhysicsDocument46 pagesUnit - Iv & V Crystal PhysicsParthaSarathyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lecture Manual 2020 CHAPTER 03-3-2 Chemistry of Materials CrystalDocument6 pagesChemistry Lecture Manual 2020 CHAPTER 03-3-2 Chemistry of Materials CrystalPals TripNo ratings yet
- The Solid StateDocument80 pagesThe Solid StateManu NathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document75 pagesChapter 3SAIF ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Nanomaterials: Lecture 02: Structure of MaterialsDocument35 pagesStructural Analysis of Nanomaterials: Lecture 02: Structure of MaterialswinnieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document55 pagesChapter 2Dhurba KarkiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two, The Structure of Crystalline Solids PDFDocument23 pagesChapter Two, The Structure of Crystalline Solids PDFOmar Abu MahfouthNo ratings yet
- CHEM3115 Inorganic Materials Lec-4Document19 pagesCHEM3115 Inorganic Materials Lec-4نیاز اشرفNo ratings yet
- Cryatal Structure FundamentalDocument30 pagesCryatal Structure FundamentalMd Mehrab Alam ShayikhNo ratings yet
- Material Science and MetallurgyDocument43 pagesMaterial Science and MetallurgySanjay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Solid StateDocument22 pagesChemistry: Solid StatePranjul singhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Solid StateDocument17 pagesUnit 1 The Solid StateSuresh DasaraddiNo ratings yet
- Slides 01Document29 pagesSlides 01Anudwaipaon AntuNo ratings yet
- CE 241 Materials Science: States of Aggregation (Of Atoms)Document35 pagesCE 241 Materials Science: States of Aggregation (Of Atoms)yasin yttNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 2Document25 pagesAssignment No 2Samama FahimNo ratings yet
- Solids and Modern Materials: Lecture PresentationDocument44 pagesSolids and Modern Materials: Lecture PresentationlaraNo ratings yet
- Scientific Coaching Centre 47Document3 pagesScientific Coaching Centre 47Ridhima RathorNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument4 pagesUntitled Document PDFRidhima RathorNo ratings yet
- Go Grammar Solution Class-7Document4 pagesGo Grammar Solution Class-7Ridhima RathorNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument10 pagesUntitled Document PDFRidhima RathorNo ratings yet
- राम आज अनुपस्थित है (b) वह बीमार है (c) तुमने एक बाघ देखा है (d) वह आ रहा है (d) हमलोग खेलते हैं (e) तुम ववद्यालय जाते होDocument1 pageराम आज अनुपस्थित है (b) वह बीमार है (c) तुमने एक बाघ देखा है (d) वह आ रहा है (d) हमलोग खेलते हैं (e) तुम ववद्यालय जाते होRidhima RathorNo ratings yet
- Bio-12 CH-2 8, 9 PDFDocument3 pagesBio-12 CH-2 8, 9 PDFRidhima RathorNo ratings yet
- Jessica Watkins Motion For ReleaseDocument20 pagesJessica Watkins Motion For ReleaseThe Columbus DispatchNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Consumer Preferences: AcknowledgmentDocument14 pagesUnderstanding The Consumer Preferences: AcknowledgmentfareedahsanNo ratings yet
- Accompanist WebinarDocument17 pagesAccompanist WebinarzramarioNo ratings yet
- M C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 145Document2 pagesM C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 145Nor Kamarul AshikinNo ratings yet
- Educational Philosophies of Filipino EducatorsDocument32 pagesEducational Philosophies of Filipino EducatorsRonard Denopol100% (3)
- Steps of Cable SplicingDocument2 pagesSteps of Cable SplicingAndrea ramirezNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall Design - Error in Type BDocument1 pageShear Wall Design - Error in Type Brey0% (1)
- Comprehensive Review Module For MyGateDocument39 pagesComprehensive Review Module For MyGatePrateek Jena (PGDM 18-20)No ratings yet
- Valentine's DayDocument6 pagesValentine's Dayabbyreader07No ratings yet
- MBA Revised Syllabus 2008Document60 pagesMBA Revised Syllabus 2008Pinak GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Alice Parker - Hark The Herald Angels Sing - SATBDocument5 pagesAlice Parker - Hark The Herald Angels Sing - SATBAlfirson BakarbessyNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Theories of Social Stratification.Document6 pagesPaper 1 Theories of Social Stratification.Abhijeet Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Anti-Spam Filter Based On Naïve Bayes, SVM, and KNN ModelDocument5 pagesAnti-Spam Filter Based On Naïve Bayes, SVM, and KNN ModelEdgar MarcaNo ratings yet
- Computer Based Examination: A Project Report ONDocument7 pagesComputer Based Examination: A Project Report ONSalman RazaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Gas PressureDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Gas Pressurefarrahlaily0% (1)
- Bio 110 Lab Manual Spring 2011Document97 pagesBio 110 Lab Manual Spring 2011Thom_mccaffNo ratings yet
- Arraignment For Practice CourtDocument3 pagesArraignment For Practice CourtSCSC BIRNo ratings yet
- Cwa 16926-11Document31 pagesCwa 16926-11richard2017No ratings yet
- A Little Bit of Everything Chords (Ver 3) by Dawestabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveDocument3 pagesA Little Bit of Everything Chords (Ver 3) by Dawestabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveldvierteNo ratings yet
- Formula": To Be + Past Participle (Verb) Am/Is/Are + Fed/Watered/Used/Cooked/Thrown/BoughtDocument7 pagesFormula": To Be + Past Participle (Verb) Am/Is/Are + Fed/Watered/Used/Cooked/Thrown/BoughtDanielli HladkiNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Keamanan PengobatanDocument39 pagesPrinsip Keamanan PengobatanAnastasia Yovita SariNo ratings yet
- Sansad Adarsh Gram YojanaDocument40 pagesSansad Adarsh Gram YojanaJagan RathodNo ratings yet
- Gottlieb SubtitlingDocument12 pagesGottlieb SubtitlingJimmy Abdillah100% (1)
- Intro QM ChemDocument47 pagesIntro QM Chemiinanc_1No ratings yet
- Interpretasi MeaningDocument136 pagesInterpretasi Meaningkaryna91No ratings yet
- Traditional Food Eaten During Chinese New Year: Chūnjié Qíjiān Chī de Chuántǒng ShíwùDocument4 pagesTraditional Food Eaten During Chinese New Year: Chūnjié Qíjiān Chī de Chuántǒng ShíwùVashaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Linus Pauling Heart Protocol (Pauling Therapy) With 12 Grams of Vitamin C and 6 Grams of LysineDocument3 pagesDr. Linus Pauling Heart Protocol (Pauling Therapy) With 12 Grams of Vitamin C and 6 Grams of LysineEbook PdfNo ratings yet
- Evening Street Review Number 29Document181 pagesEvening Street Review Number 29Barbara BergmannNo ratings yet
- PBR-005-HandoutC - FillableDocument2 pagesPBR-005-HandoutC - FillableMollyanna StephensNo ratings yet
- SAC Review: Omic' Technologies: Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics and MetabolomicsDocument7 pagesSAC Review: Omic' Technologies: Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics and MetabolomicsandreaNo ratings yet