Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eye and Orbit: Conjunctiva
Uploaded by
kaplan abateOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye and Orbit: Conjunctiva
Uploaded by
kaplan abateCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye and Orbit
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Conjunctiva:
External infections: Trachoma (Chlamydia trachomatis) remains the leading cause of
preventable blindness in the world: some 85 mio people have active trachoma (infective stage)
and 7.8 mio people have blinding stage. In AA conjunctivitis caused by staph. aureus, str.
pneumoniae, coagulase-negative staphylococci is prevalent.
Squamous cell carcinoma: most arise from actinic keratosis in the interpalpebral fissure of
the limbal conjunctiva and grow slowly in an exophytic, sometimes papillary manner. Neglected
tumors invade into the eye and posteriorly into the orbit.
Retina:
Retinoblastoma:
- the most common eye tumor in childhood
- molecular genetics: the result of a single gene mutation [Rb gene, chromosome 13, tumor
suppressor gene]
- hereditary form: germline mutation
- non-hereditary form: initial mutation in a somatic retinal cell
in both: the loss of both allelic wild-type copies of the Rb gene is the key step in malignant
transformation
- he retina is a derivative of the brain retinoblastoma is an example of a poorly differentiated
(embryonal) neoplasia
- dissemination through choroid vessels or/and through optic nerve
- advanced: even through the sclera orbit preauaricular lymph nodes
- metastasis: CNS, skull, other bones, lymph nodes
Uvea:
Uvea includes: iris, ciliary body, choroid
Uveitis:
o in HIV/AIDS: pneumocystis carinii, toxoplasma Gondii, CMV
o systemic: sarcoidosis
o autoimmune: sympathetic ophthalmia
Uveal melanoma:
- rare, but the most common primary intraocular maligant tumor in adults
- 8-fold risk for white race compared with blacks
- the tumor arises from melanocytes located in these structures (not from the pigment epithel of
retina, iris and ciliary body)
- spread: hematogenous and preferentially to the liver
Orbit:
- in general inflammatory diseases are more common than primary tumors (infections spreading
from the surrounding sinuses [mucor, diabetes])
- most lesions increase the volume of the orbital content exophthalmus, proptosis
Thyroid ophthalmia (Graves orbitopathy)
- is the most common cause of exophthalmus (more than 50% in adults)
- autoimmune-based inflammation (inflammatory infiltrate restricted to the muscle bellies of extracellular
muscle consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells, scattered mast cells)
Rhabdomyosarcoma
- the most common primary malignant orbital tumor in childhood (mean age: 7 years)
Lymphoid tumors: non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- most: low-grade B-cell lymphomas
- older patients (rare in children)
Optic nerve glioma
- nearly always low-grade astrocytoma
- first decades, 50% have neurofibromatosis type I
Optic nerve meningioma
You might also like
- Brain TumorsDocument72 pagesBrain Tumorsmo_mibNo ratings yet
- MCQS CNS PathologyDocument14 pagesMCQS CNS PathologyFourth YearNo ratings yet
- Patho Cns Lung ThyroidDocument5 pagesPatho Cns Lung ThyroidYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Masquerade SyndromeDocument69 pagesMasquerade Syndromerohitaswa100% (1)
- MnemonicS in OphthaDocument22 pagesMnemonicS in Ophthaabuahmed&janaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Epithelial Non-Odontogenic Tumors 2Document11 pagesMalignant Epithelial Non-Odontogenic Tumors 2samamustafa.2003No ratings yet
- Eye Pathology: Dr. Jusuf FantoniDocument8 pagesEye Pathology: Dr. Jusuf Fantonitutor tujuhNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument78 pagesBrain Tumorsnarswiponshistoryan100% (3)
- CNS Flash PointsDocument3 pagesCNS Flash PointsAbdul MannanNo ratings yet
- DR - Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument19 pagesDR - Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKuyesNo ratings yet
- Neuropathology: Dr. Siddaganga S MDocument29 pagesNeuropathology: Dr. Siddaganga S Msiddaganga sigiNo ratings yet
- Meningomyelocele (Spina Bifida) : Bony Neural Arch Not Completely ClosedDocument33 pagesMeningomyelocele (Spina Bifida) : Bony Neural Arch Not Completely Closedlindelle elijahNo ratings yet
- Sol IntracranialDocument76 pagesSol IntracranialPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- SalivaryDocument42 pagesSalivaryElgilani zaherNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Diagnosis: Neck LumpDocument36 pagesAn Approach To Diagnosis: Neck LumpTracy WheelerNo ratings yet
- Marek's DiseaseDocument55 pagesMarek's Diseasehhes8116No ratings yet
- Neuropathology: FK UisuDocument28 pagesNeuropathology: FK UisuAnggi WahyuNo ratings yet
- EM Male Genital Tract RGDocument25 pagesEM Male Genital Tract RGPrakashNo ratings yet
- PROPTOSISDocument26 pagesPROPTOSISAhmad fayazNo ratings yet
- Oculars TumorDocument109 pagesOculars TumorNovita EmyNo ratings yet
- Male Genital System - Pathology (Lect 10-12)Document83 pagesMale Genital System - Pathology (Lect 10-12)Farahh ArshadNo ratings yet
- TUMOR MATA FX TranslateDocument34 pagesTUMOR MATA FX TranslateAisyahNo ratings yet
- Metastatic TumorsDocument43 pagesMetastatic TumorsRadio ResidentNo ratings yet
- Eye TermsDocument16 pagesEye TermsTa Thuy LinhNo ratings yet
- Neet StuffDocument26 pagesNeet StuffBalasubrahmanya K. R.No ratings yet
- GIT, AlemDocument224 pagesGIT, Alemmex GbrekorkosNo ratings yet
- Tumors of Auditory Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesTumors of Auditory Nervous SystemgitengeorgeNo ratings yet
- You May Find Useful Some of My Pathology Notes. Markos Greece. You May Find Useful Some of My Pathology Notes. Markos Greece. (10557)Document3 pagesYou May Find Useful Some of My Pathology Notes. Markos Greece. You May Find Useful Some of My Pathology Notes. Markos Greece. (10557)Shawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- Adult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistDocument39 pagesAdult Brain Tumours: DR M.P. Okemwa PathologistSalman MajidNo ratings yet
- Tumors of Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesTumors of Nervous SystemNininghrNo ratings yet
- LEUKOKORIADocument3 pagesLEUKOKORIAFahlevie EpinNo ratings yet
- ApanuchDocument35 pagesApanuchannisa fauzia rahmaNo ratings yet
- L75 - Pathology of CNS TumorsDocument73 pagesL75 - Pathology of CNS Tumorsb deepthiNo ratings yet
- 03 - OMF PathDocument29 pages03 - OMF Pathlabasgrazuoli0% (2)
- Brain Lectures CollectionDocument171 pagesBrain Lectures CollectionSourabh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Nada's GI Path ReviewDocument44 pagesNada's GI Path ReviewNada Much100% (2)
- Pediatric Tumors of The Eye and OrbitDocument60 pagesPediatric Tumors of The Eye and OrbitDMdewiNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument22 pagesIlovepdf MergedSRO oONo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument1 pageBrain Tumorskaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The CNSDocument26 pagesTumors of The CNSShailendra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Pediatric TumorsDocument25 pagesPediatric Tumorswiwit adeNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck: Salivary Gland Tumors: An OverviewDocument12 pagesHead and Neck: Salivary Gland Tumors: An OverviewVanessa MordiNo ratings yet
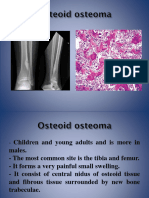
- Bone 2Document43 pagesBone 2kazelio2017No ratings yet
- 6 - Oral Epithelial TumorsDocument12 pages6 - Oral Epithelial TumorsPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Aruns PL - Ade FinalDocument9 pagesAruns PL - Ade FinaldrarunsinghNo ratings yet
- LymphadenopathyDocument12 pagesLymphadenopathyErikha Chairil100% (1)
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Rhabdomyosarcoma Retinoblastoma: by Derrota, Keith Angelo CDocument39 pagesNon-Hodgkin Lymphoma Rhabdomyosarcoma Retinoblastoma: by Derrota, Keith Angelo CKeith Angelo Canete DerrotaNo ratings yet
- Non-Pathogenic Amoeba - Free LivingDocument42 pagesNon-Pathogenic Amoeba - Free Livingمحمد رحيم حسن محمودNo ratings yet
- SDL 8 Intracranial Space Occupying LesionDocument5 pagesSDL 8 Intracranial Space Occupying LesionJonathan YeohNo ratings yet
- Brainstem and Cerebellum Lesions in Adults: Pearls To The Diagnosis With MRIDocument48 pagesBrainstem and Cerebellum Lesions in Adults: Pearls To The Diagnosis With MRIradiologirsckNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAli KhanNo ratings yet
- OPHTHALMOPLEGIADocument58 pagesOPHTHALMOPLEGIAAryo Handoko SitorusNo ratings yet
- Head and Nexck - PPTXDocument80 pagesHead and Nexck - PPTXVijay SudhaNo ratings yet
- THE PAROTID GLAND Anatomy MMDocument5 pagesTHE PAROTID GLAND Anatomy MMmahmoodNo ratings yet
- Brain CancerDocument24 pagesBrain CancerJohn Lester FernandezNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System Pathology: Presented byDocument70 pagesCentral Nervous System Pathology: Presented byNicholasNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant Brain Tumor - Systematic Approach PDFDocument29 pagesThe Radiology Assistant Brain Tumor - Systematic Approach PDFMichael DeanNo ratings yet
- MedscapeDocument12 pagesMedscapeRissa WatlolyNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Mendelian Rules: Second Filial Generation (F2 Generation)Document1 pageThe Mendelian Rules: Second Filial Generation (F2 Generation)kaplan abateNo ratings yet
- The Nine SaintsDocument1 pageThe Nine Saintskaplan abate67% (3)
- Types of ComputerDocument19 pagesTypes of Computerkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Blood Type ThingDocument1 pageBlood Type Thingkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Sos Hermann Gmeiner School Hawassa: Department of Natural ScienceDocument34 pagesSos Hermann Gmeiner School Hawassa: Department of Natural Sciencekaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DevelopmentDocument46 pagesCognitive Developmentkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Aptitude TestDocument1 pageAptitude Testkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism: Kaplan AbateDocument1 pageHyperthyroidism: Kaplan Abatekaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Holy GrailDocument2 pagesHoly Grailkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Some Home Remedies: Asthma AttackDocument2 pagesSome Home Remedies: Asthma Attackkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Cryopreservation: I Freeze People To Cheat Death': by Rose Eveleth 22 Aug 2014Document1 pageCryopreservation: I Freeze People To Cheat Death': by Rose Eveleth 22 Aug 2014kaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Eight (8) Things We All Want and Need:: by Dan AuitoDocument1 pageEight (8) Things We All Want and Need:: by Dan Auitokaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument1 pageBrain Tumorskaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Our Third ExamDocument6 pagesOur Third Examkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Our Fourth ExamDocument12 pagesOur Fourth Examkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Our Second ExamDocument8 pagesOur Second Examkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- s13014 015 0495 4Document6 pagess13014 015 0495 4produxing 101No ratings yet
- Case Report: Multiple Skeletal Metastases From A Giant Cell Tumour of The Distal Fibula With Fatal OucomeDocument28 pagesCase Report: Multiple Skeletal Metastases From A Giant Cell Tumour of The Distal Fibula With Fatal OucomeWaskitho NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer in Pakistan - Awareness and Early DetectionDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer in Pakistan - Awareness and Early DetectionMurk NiazNo ratings yet
- Art Cancer Gastrico PDFDocument8 pagesArt Cancer Gastrico PDFvane_vane_tatyNo ratings yet
- TataDocument2 pagesTatavamsi NathNo ratings yet
- 7 08 Ristic RDocument13 pages7 08 Ristic RsucrooNo ratings yet
- Breast Case ProformaDocument2 pagesBreast Case ProformaSyed FirdozNo ratings yet
- HER2 Targeted Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast CancerDocument58 pagesHER2 Targeted Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast Cancerreny hartikasariNo ratings yet
- Stase Gastro - Multiple Nodul HeparDocument13 pagesStase Gastro - Multiple Nodul HeparRozen RyuhaNo ratings yet
- Go Wyoming (Fall 2023)Document32 pagesGo Wyoming (Fall 2023)The Livingston County NewsNo ratings yet
- Fibroids PowerpointDocument27 pagesFibroids Powerpointteritohaha100% (3)
- ThyroidDocument43 pagesThyroidchowhan04No ratings yet
- Kanker Ovarium: Dr. Dino Rinaldy, SP - OG (K) Onk RSUD Dr. H. Abdul MoeloekDocument16 pagesKanker Ovarium: Dr. Dino Rinaldy, SP - OG (K) Onk RSUD Dr. H. Abdul MoeloekIlham HarsyaNo ratings yet
- UROLOGYDocument3 pagesUROLOGYNoneNo ratings yet
- American Cancer SocietyDocument56 pagesAmerican Cancer SocietyranaNo ratings yet
- Iq2wjqjhfkkby1lyhkyd5z3iDocument2 pagesIq2wjqjhfkkby1lyhkyd5z3iSubham RajputNo ratings yet
- Moleculer Basis of NeoplasiaDocument33 pagesMoleculer Basis of NeoplasiahudaNo ratings yet
- Full Tanzania Assessment ReportDocument62 pagesFull Tanzania Assessment ReportPatrickLnanduNo ratings yet
- Nrg-Gi002 Protocol PresentationDocument16 pagesNrg-Gi002 Protocol Presentationapi-508897697No ratings yet
- Jadwal Pir MalangDocument4 pagesJadwal Pir MalangAbraham BayuNo ratings yet
- Radiology ConferenceDocument8 pagesRadiology ConferenceLisa SmithNo ratings yet
- Peprah 2018Document7 pagesPeprah 2018Dewa OkaNo ratings yet
- Anorectal Contouring GuidelinesDocument10 pagesAnorectal Contouring GuidelinescoyeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Oral Cancer Clinical Practice GuidelineDocument8 pagesOral Cancer Clinical Practice GuidelineSheila JuddNo ratings yet
- 1.1.0.0.rel CapcpDocument15 pages1.1.0.0.rel CapcpkarimahihdaNo ratings yet
- NephroblastomaDocument26 pagesNephroblastomaRahul Dhaker100% (3)
- CisplatinDocument15 pagesCisplatinJaya Semara PutraNo ratings yet
- Cancer Localizari Mamar Chimio 1Document135 pagesCancer Localizari Mamar Chimio 1Alexandra TeodorescuNo ratings yet
- A10v61n6 PDFDocument6 pagesA10v61n6 PDFSipkhotunWindayaniNo ratings yet
- Example Clinical Lab 04.21.2022 PDFDocument4 pagesExample Clinical Lab 04.21.2022 PDFBenziy JijyNo ratings yet