Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document
Uploaded by
Calvin Dante BarrientosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document
Uploaded by
Calvin Dante BarrientosCopyright:
Available Formats
Pneumonia (from the Greek pneuma, “breath”) is a potentially fatal infection and
inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (i.e., bronchioles and alveoli) this can be
characterised by collection of puss and other fluids on the lungs. Lung air sacs are
structures that help in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Collection of pus in
them makes breathing difficult.Pneumonia can be caused by many kinds of micro
organisms including bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. When an infected individual
coughs or sneezes, these organisms get into the air and breathing in of this air leads to
contraction of the illness. It is thus a contagious disease.The condition varies from mild
to severe depending on the type of organism involved, age and the underlying health of
the individual. Pneumonia can be categorized as: community-acquired, hospital-
acquired and pneumonia occuring in Immunocompromised individuals (individuals with
weakened immune system).
Pneumonia is usually caused due to an infection with a bacteria, virus, fungi or parasite.
In adults it is mostly caused by bacteria whereas in children and infants it is commonly
due to viruses. Physical or chemical injury to the lungs can also result in the condition.
Individuals who smoke, who are hospitalized and have long-term illness such as
asthma, heart disease, cancer, lung diseases or diabetes are at a higher risk of
developing pneumonia.
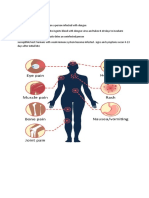
Sign and symptoms of pneumonia can be sudden or slowly progressive. In most cases
the symptoms of pneumonia mimics that of flu or other common lung infections such as
bronchitis.The main signs and symptoms of pneumonia are: cough that produces
phlegm (sputum) which is either yellow, blood-stained or rust coloured, chest pain,
difficulty in breathing, chills, fever, headache, excessive sweating, weight loss, loss of
appetite, muscle pain, weakness and tiredness.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- People V Madrigal GonzalesDocument2 pagesPeople V Madrigal GonzalesCalvin Dante Barrientos100% (2)
- Letter of Complaint and Reply To Complaint - PDFDocument2 pagesLetter of Complaint and Reply To Complaint - PDFCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Dear Dean AgdonDocument3 pagesDear Dean AgdonCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Literature: Scroll Top&Needaccess TrueDocument3 pagesLiterature: Scroll Top&Needaccess TrueCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Topic For ResearchDocument2 pagesTopic For ResearchCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Basic Webpage Design: Understanding Web Technologies and ApplicationsDocument40 pagesBasic Webpage Design: Understanding Web Technologies and ApplicationsCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Servant Leadership Overview of TheDocument3 pagesModule 1: Servant Leadership Overview of TheCalvin Dante Barrientos100% (1)
- Cultural and Spiritual Aspect of Geriatric CareDocument2 pagesCultural and Spiritual Aspect of Geriatric CareCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Excel Formulas3 PDFDocument44 pagesExcel Formulas3 PDFCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Impact of Online Classes On Undergraduate Degree CompletionDocument15 pagesInvestigating The Impact of Online Classes On Undergraduate Degree CompletionCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Advocacy Message Development 1Document2 pagesAdvocacy Message Development 1Calvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Barrientos Case StudyDocument6 pagesBarrientos Case StudyCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Intro Leuk DengDocument4 pagesIntro Leuk DengCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- ReservoirDocument1 pageReservoirCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Savemore Sikatuna To Monas Bakery Then Follow The DirectionsDocument1 pageSavemore Sikatuna To Monas Bakery Then Follow The DirectionsCalvin Dante BarrientosNo ratings yet