Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BFS (Breadth First Search)
Uploaded by
raveendrababup0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views5 pagesBFS (Breadth First Search) is an algorithm that produces a spanning tree by traversing a graph in layers, starting with the starting node's neighbors, then the neighbors' neighbors, and so on. It uses a queue data structure containing vertices, processing the earliest added vertex first. The steps are to initialize a queue, add the starting vertex, visit its unvisited neighbors and add them to the queue, remove the current vertex from the queue when its neighbors have all been visited, and repeat until the queue is empty.
Original Description:
Original Title
BFS EXAMPLE.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBFS (Breadth First Search) is an algorithm that produces a spanning tree by traversing a graph in layers, starting with the starting node's neighbors, then the neighbors' neighbors, and so on. It uses a queue data structure containing vertices, processing the earliest added vertex first. The steps are to initialize a queue, add the starting vertex, visit its unvisited neighbors and add them to the queue, remove the current vertex from the queue when its neighbors have all been visited, and repeat until the queue is empty.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views5 pagesBFS (Breadth First Search)
Uploaded by
raveendrababupBFS (Breadth First Search) is an algorithm that produces a spanning tree by traversing a graph in layers, starting with the starting node's neighbors, then the neighbors' neighbors, and so on. It uses a queue data structure containing vertices, processing the earliest added vertex first. The steps are to initialize a queue, add the starting vertex, visit its unvisited neighbors and add them to the queue, remove the current vertex from the queue when its neighbors have all been visited, and repeat until the queue is empty.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
BFS EXAMPLE :
BFS (Breadth First Search)
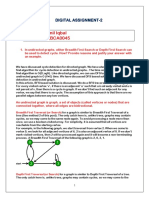
BFS traversal of a graph produces a spanning tree as
final result. Spanning Tree is a graph without loops.
We use Queue data structure with maximum size of
total number of vertices in the graph to implement BFS
traversal.
Step 1 - Define a Queue of size total number of
vertices in the graph.
Step 2 - Select any vertex as starting point for
traversal. Visit that vertex and insert it into the
Queue.
Step 3 - Visit all the non-visited adjacent vertices
of the vertex which is at front of the Queue and
insert them into the Queue.
Step 4 - When there is no new vertex to be visited
from the vertex which is at front of the Queue then
delete that vertex.
Step 5 - Repeat steps 3 and 4 until queue becomes
empty.
Step 6 - When queue becomes empty, then produce
final spanning tree by removing unused edges from
the graph
One more example for BFS
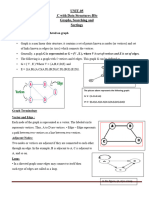
DFS (Depth First Search)
DFS traversal of a graph produces a spanning tree as
final result. Spanning Tree is a graph without loops.
We use Stack data structure with maximum size of
total number of vertices in the graph to implement DFS
traversal.
We use the following steps to implement DFS
traversal...
Step 1 - Define a Stack of size total number of
vertices in the graph.
Step 2 - Select any vertex as starting point for
traversal. Visit that vertex and push it on to the
Stack.
You might also like
- DFS and BFS AlgorithmDocument11 pagesDFS and BFS AlgorithmRohan Chavan100% (1)
- Electrical Circuits LabDocument64 pagesElectrical Circuits LabraveendrababupNo ratings yet
- Graph TraversalDocument38 pagesGraph TraversalJeremy CabudbudNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 10 Implement Graph Traversal Techniques: A) Depth First Search B) Breadth First SearchDocument12 pagesExperiment No.: 10 Implement Graph Traversal Techniques: A) Depth First Search B) Breadth First SearchHarsh AlashiNo ratings yet
- Graph Traversal 1Document40 pagesGraph Traversal 1Sania NazNo ratings yet
- Graph TraversalsDocument11 pagesGraph TraversalsAnandhaSilambarasan DNo ratings yet
- Graph Traversal - DFS & BFSDocument42 pagesGraph Traversal - DFS & BFSKishan100% (1)
- Graph Traversal: 1. DFS (Depth First Search) 2. BFS (Breadth First Search)Document4 pagesGraph Traversal: 1. DFS (Depth First Search) 2. BFS (Breadth First Search)21CS035 Namya ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dsunit 5Document14 pagesDsunit 5venkata rajeshNo ratings yet
- Graph Traversals - Data StructuresDocument4 pagesGraph Traversals - Data Structurescompiler&automataNo ratings yet
- BCA2060 Exercise 6-SLMDocument3 pagesBCA2060 Exercise 6-SLMaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- GraphsDocument7 pagesGraphsEklavya SudanNo ratings yet
- Experiment-2: AIM: WAP To Implement Depth First Search and Breadth Search Algorithms. TheoryDocument3 pagesExperiment-2: AIM: WAP To Implement Depth First Search and Breadth Search Algorithms. Theoryakshat sharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithm: GraphsDocument28 pagesData Structures and Algorithm: GraphsAman BazeNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: Exploring GraphsDocument77 pagesUnit-5: Exploring GraphsHACKER SPACENo ratings yet
- Undirected GraphsDocument33 pagesUndirected GraphsAbdurezak ShifaNo ratings yet
- Ds Unit 5 (Graphs)Document35 pagesDs Unit 5 (Graphs)ashishmohan625No ratings yet
- Breadth First Search-BFSDocument24 pagesBreadth First Search-BFShiremathsuvarna6No ratings yet
- Trees and Graphs3Document13 pagesTrees and Graphs3Ria thanickaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Breadth First SearchDocument6 pages4.2 Breadth First Searchpunithavel132No ratings yet
- CS 611 Slides 2Document28 pagesCS 611 Slides 2Ahmad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- AI Lab ManualDocument37 pagesAI Lab ManualNeha KardileNo ratings yet
- DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS - Unit 5Document35 pagesDATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS - Unit 5BOMMA SRI MUKHINo ratings yet
- AI TheoryDocument4 pagesAI TheorySumedh SumedhNo ratings yet
- Search Algorithms in AI6Document17 pagesSearch Algorithms in AI6jhn75070No ratings yet
- Graphs: by Sonia SoansDocument18 pagesGraphs: by Sonia SoanstvsnNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment Theory 18bca0045Document16 pagesDigital Assignment Theory 18bca0045Shamil IqbalNo ratings yet
- Geeks GraphDocument107 pagesGeeks GraphBHARAT SINGH RAJPUROHITNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument26 pagesGraphgabnarag2No ratings yet
- Implicit: Something Is Being Done For You Automatically. Explicit: You've Written Something in The Source Code To Indicate What You Want To HappenDocument4 pagesImplicit: Something Is Being Done For You Automatically. Explicit: You've Written Something in The Source Code To Indicate What You Want To HappenShubham waghuleNo ratings yet
- DS 3Document45 pagesDS 3Sreehari ENo ratings yet
- Introduction To DFSDocument9 pagesIntroduction To DFSawaz mustafaNo ratings yet
- GRAPHSDocument4 pagesGRAPHSNaseer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Daa Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesDaa Lab ActivityYashwanth gowdaNo ratings yet
- Traversing Graphs:: A Journey Through Connected DataDocument19 pagesTraversing Graphs:: A Journey Through Connected DataSandeep Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Graph Based Algorithms - NotesDocument5 pagesGraph Based Algorithms - Notessathwik vaguNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs in Data StructuresDocument18 pagesTypes of Graphs in Data StructuresJahangir AliNo ratings yet
- Advance Data StructureDocument6 pagesAdvance Data StructureNeha RaiNo ratings yet
- FA20-BCS-133 (AI Lab Assignment#2)Document4 pagesFA20-BCS-133 (AI Lab Assignment#2)ghazanfarhussain2686No ratings yet
- Discrete Structure PresentationDocument34 pagesDiscrete Structure PresentationFᴀsᴇᴇʜ̶ ʜ̶ᴀʀᴏᴏɴNo ratings yet
- cs3304 Discussion Unit 3Document3 pagescs3304 Discussion Unit 3Mobolaji ANo ratings yet
- GeorgiaTech CS-6515: Graduate Algorithms: Graph Algorithms Flashcards by Yang Hu - BrainscapeDocument4 pagesGeorgiaTech CS-6515: Graduate Algorithms: Graph Algorithms Flashcards by Yang Hu - BrainscapeJan_SuNo ratings yet
- Depth First Search Breath First SearchDocument19 pagesDepth First Search Breath First SearchThanakrit NupimNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Uninformed Search Techniques (BFS, DFS, 8-Puzzle Problem)Document12 pagesArtificial Intelligence Uninformed Search Techniques (BFS, DFS, 8-Puzzle Problem)Ammara HaiderNo ratings yet
- Register No: 1108201040 Name:: CS8381 - Data Structure Laboratory Page NoDocument3 pagesRegister No: 1108201040 Name:: CS8381 - Data Structure Laboratory Page NoVairamuthu MNo ratings yet
- 4.5 BFS-DFS-SCC-Counting SortDocument17 pages4.5 BFS-DFS-SCC-Counting SortVivek PandeyNo ratings yet
- I008 - Khemal - Experiment - PAI - 2Document10 pagesI008 - Khemal - Experiment - PAI - 2Khemal DesaiNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT2Document6 pagesEXPERIMENT2guy977867No ratings yet
- BFS and DFSDocument20 pagesBFS and DFSarshiya khanNo ratings yet
- Register No: 1108201040 Name:: CS8381 - Data Structure Laboratory Page NoDocument4 pagesRegister No: 1108201040 Name:: CS8381 - Data Structure Laboratory Page NoVairamuthu MNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Uninformed SearchDocument9 pagesLab 4 Uninformed SearchMohsin ArifNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5Document34 pagesUnit - 5Sanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - DSDocument67 pagesChapter 6 - DSpruthvirajdesai204No ratings yet
- GraphsDocument49 pagesGraphssocekay372No ratings yet
- Unit 05 DSDocument27 pagesUnit 05 DSPavaniNo ratings yet
- Graph 2Document22 pagesGraph 2manudev8924No ratings yet
- GRAPHSDocument38 pagesGRAPHSasdNo ratings yet
- c3 Chapter 2.3Document13 pagesc3 Chapter 2.3rohitdatyal911No ratings yet
- TheoryDocument82 pagesTheoryNibedan PalNo ratings yet
- T21-86 AI Exp4Document5 pagesT21-86 AI Exp4Gaurang PatyaneNo ratings yet
- Fast and Secure Group Key Dissemination Scheme For Out-of-Range V2I CommunicationDocument11 pagesFast and Secure Group Key Dissemination Scheme For Out-of-Range V2I CommunicationraveendrababupNo ratings yet
- A Novel Passwordless Authentication Sche PDFDocument17 pagesA Novel Passwordless Authentication Sche PDFraveendrababupNo ratings yet
- Student Data FormDocument3 pagesStudent Data FormraveendrababupNo ratings yet