Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin B12 role metabolism assignment
Uploaded by
Aneeza Ahmad100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
42 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Biochem- Vit.B12 role in metabolism
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
42 views3 pagesVitamin B12 role metabolism assignment
Uploaded by
Aneeza AhmadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Biochemistry Assignment
Submitted to:
Dr. Muhammad Ijaz
Submitted by:
Aneeza Ahmad FA19-PHM-023
Dua ul Aruj FA19-PHM-004
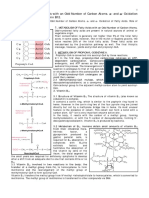
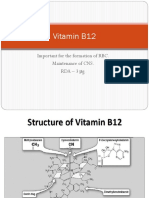
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Role in Metabolism
Vitamin b12 also known as Cobalamin is a water-soluble
vitamin. It works as a coenzyme, so it is used in enzyme
catalyzed reactions. Following are the three classes of enzymes
that require B12 to function:
• Methyltransferases
• Isomerases
• Dehydrogenases
Vitamin B12 is used by the body in two forms, either as
methylcobalamin or 5-deoxyadenosyl cobalamin. The enzyme
methionine synthase needs methylcobalamin as a cofactor. This
enzyme is normally involved in the conversion of the amino acid
homocysteine into methionine. 5-Deoxyadenosyl cobalamin is a
cofactor needed by the enzyme that converts l-methylmalonyl CoA to
succinyl CoA. This conversion is an important step in the extraction of
energy from proteins and fats. In addition, succinyl CoA is necessary to
produce hemoglobin which is the substance that carries oxygen in red
blood cells.
Methionine Cycle:
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) plays an important role in the conversion of
homocysteine to methionine in methionine cycle, as it takes the methyl group
from 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate (folic acid) and forms methyl cobalamin which
then releases this methyl group in order to convert homocysteine into
methionine. Moreover, cobalamin is needed in the conversion of the methionine
to homocysteine, where methionine is converted to SAM (S-adenosyl methionine)
product in the presence of ATP by methionine adenosyl transferase. In case of
deficiency of vitamin B12, the body does not have the ability to produce
methionine, which can cause many problems.
Conversion of Methylmalonyl coenzyme A (CoA) to succinyl
CoA:
Two molecules of adenosyl cobalamin are required to convert methylmalonyl CoA
to succinyl CoA, which is a TCA cycle intermediate, through methylmalonyl CoA
mutase enzyme, while propionyl CoA is converted to d-methylmalonyl CoA. In
case of vitamin B12 deficiency, methylmalonyl CoA mutase activity is impaired
and there is accumulation of methylmalonic acid inside the body. These
impairments lead to many problems and issues. The body loses its ability to
produce the TCA cycle intermediate, succinyl CoA, which will lead to an
impairment of TCA cycle as there is reduced conversion of succinate to fumarate,
malate, and to the end product of the cycle, which is responsible for providing
small amount of energy before going to electron transport chain which is
responsible of high energy production. There is also an impairment in
gluconeogenesis, which is the metabolic pathway responsible for generating
glucose from non-carbohydrate substances.
You might also like
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Englec 29 Fa Odd 2021Document3 pagesEnglec 29 Fa Odd 2021Yannick fokaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document31 pagesVitamin B12DR JIJIN J UNo ratings yet
- Materi V - Vitamin B12Document35 pagesMateri V - Vitamin B12Salwa Kamilia100% (1)
- Amino AcidsDocument21 pagesAmino AcidsArbin PanjaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Metabolisme Vitamin B12 B9 CDocument49 pages3 - Metabolisme Vitamin B12 B9 CPaulinNo ratings yet
- Functions of GlycogenDocument11 pagesFunctions of GlycogenBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Lec. B12Document94 pagesLec. B12Arshad Mehmood MinhasNo ratings yet
- Vitamins As Coenzymes & CofactorsDocument6 pagesVitamins As Coenzymes & CofactorsCalcium QuèNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lec.2 (Vitamins 2)Document6 pagesChemistry Lec.2 (Vitamins 2)Muhammed AbdulsamadNo ratings yet
- 6.megaloblastic AnaemiasDocument34 pages6.megaloblastic AnaemiasWissam AlwazaniNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated and Odd-Chain Fatty Acid Catabolism: March 24, 2003Document7 pagesUnsaturated and Odd-Chain Fatty Acid Catabolism: March 24, 2003Sheila HoraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12: Essential for RBC Formation and CNS MaintenanceDocument19 pagesVitamin B12: Essential for RBC Formation and CNS MaintenanceHari PrasathNo ratings yet
- Agents Used in Anemias 2Document25 pagesAgents Used in Anemias 2Raboha TawilNo ratings yet
- Chap139 PDFDocument3 pagesChap139 PDFvivianNo ratings yet
- BCH242-BCH252 2021 Lipid MetabDocument37 pagesBCH242-BCH252 2021 Lipid MetabEmmanuella OffiongNo ratings yet
- Fatty acid metabolism pathwaysDocument7 pagesFatty acid metabolism pathwayslucienneNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument15 pagesAmino Acid Metabolismshanto.tn98No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document4 pagesVitamin B12Thirunavukkarasu ANo ratings yet
- Amino Acids BiosynthesisDocument56 pagesAmino Acids BiosynthesisDeea LobonțiuNo ratings yet
- Beta oxidationDocument26 pagesBeta oxidationShivanand MaliNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Lipid MetabolismDocument19 pagesAn Overview of Lipid Metabolismshanto.tn98No ratings yet
- Digestion and Metabolism of ProteinDocument12 pagesDigestion and Metabolism of ProteinvjtfkNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Synthesis & DegradationDocument49 pagesAmino Acid Synthesis & DegradationMuhammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Medical Biochemistry (Week-16)Document7 pagesMedical Biochemistry (Week-16)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12, Folic Acid, and TheDocument4 pagesVitamin b12, Folic Acid, and TheFAZRI MONo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Anemia 4Document27 pagesTopic 9 - Anemia 4Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Vitamins As Coenzymes CofactorsDocument5 pagesVitamins As Coenzymes CofactorssharenNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument46 pagesOxidation of Fatty AcidsRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Metabolism in TissuesDocument19 pagesIntegrated Metabolism in TissuesMarielle TomesNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument10 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismatifzeaNo ratings yet
- Cobalamin: A Critical Vitamin in The ElderlyDocument11 pagesCobalamin: A Critical Vitamin in The ElderlyLuis ÓnidasNo ratings yet
- Chemistrry AllDocument7 pagesChemistrry AllTHARSHANA JERUSALEMNo ratings yet
- Lipid 3 Energy Production From Lipid 2023Document36 pagesLipid 3 Energy Production From Lipid 2023M. Ilham Ramadhan AsihNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 Properties and MetabolismDocument7 pagesVitamin B12 Properties and Metabolismkalaiarasi ravichandranNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Wajid: Institute of Pharmacy Gulab Devi Educational Complex, LahoreDocument36 pagesMuhammad Wajid: Institute of Pharmacy Gulab Devi Educational Complex, LahoreAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- General Biochemistry Functions Deficiency Diseases: Vitamins B and BDocument34 pagesGeneral Biochemistry Functions Deficiency Diseases: Vitamins B and Bsajjad khanNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism (III) - Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesLipid Metabolism (III) - Fatty Acid Oxidationlightning proNo ratings yet
- Activation of Fatty Acids: Beta Oxidation Is The Process by WhichDocument5 pagesActivation of Fatty Acids: Beta Oxidation Is The Process by WhichAriel RezaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism 4 D Hopeless :) : RemindersDocument22 pagesMetabolism 4 D Hopeless :) : RemindersAina BautistaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 CoenzymeDocument19 pagesVitamin B12 Coenzymeprabhu100% (2)
- Workineh Case Studyy 1Document17 pagesWorkineh Case Studyy 1HABTAMU MOLLANo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic Anaemia Lecture 1Document6 pagesMegaloblastic Anaemia Lecture 1Nauzaina IjazNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids OverviewDocument30 pagesAmino Acids OverviewbrownhazelNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Lipids (2) NewDocument64 pagesMetabolism of Lipids (2) NewLyra Get100% (1)
- Lecture Lipid 1Document35 pagesLecture Lipid 1Achraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Essential and Non-Essential Amino AcidsDocument15 pagesMetabolism of Essential and Non-Essential Amino AcidsMrs SalimNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument25 pagesBeta OxidationManoj SigdelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short Course: Fatty Acid DegradationDocument22 pagesBiochemistry: A Short Course: Fatty Acid DegradationEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument11 pagesBeta OxidationMUTHONI IRERINo ratings yet
- Metabolism of ProteinDocument6 pagesMetabolism of ProteinSrijanNo ratings yet
- Lipids MetabolismDocument19 pagesLipids MetabolismOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Activation and Transport into the Mitochondria for Energy ProductionDocument10 pagesFatty Acid Activation and Transport into the Mitochondria for Energy ProductionKarl Torres Uganiza RmtNo ratings yet
- Subjective QuestionsDocument5 pagesSubjective QuestionsAgustina MandasariNo ratings yet
- Glycerol Metabolism Fatty Acid Metabolism Interrelationship of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism Ketosis, Acidosis, and DehydrationDocument32 pagesGlycerol Metabolism Fatty Acid Metabolism Interrelationship of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism Ketosis, Acidosis, and DehydrationJanella Marie EspinoNo ratings yet
- BioChemistry ExplainationDocument6 pagesBioChemistry ExplainationVichhaiJacksonNo ratings yet
- CH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Document4 pagesCH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Nhân TrầnNo ratings yet
- L15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and KetogenesisDocument50 pagesL15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Ketogenesisyebadem228No ratings yet
- Vitamin B: Chapter OutlineDocument18 pagesVitamin B: Chapter OutlineCỏPhongSươngNo ratings yet
- Immunology First Exam..Document7 pagesImmunology First Exam..Abdallah Essam Al-Zireeni100% (1)
- Albert Et Al., 2014 PDFDocument19 pagesAlbert Et Al., 2014 PDFIndrani BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Mutation 23-11Document22 pagesLecture 6 Mutation 23-11Saif MohamedNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document1 pageReport 1api-549182101No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Classified - Part 2 FinalDocument153 pagesUnit 4 Classified - Part 2 Finalp8q4jkz4p5No ratings yet
- Virology The Study of VirusesDocument45 pagesVirology The Study of Virusesdawoodabdullah56100% (2)
- AP Bio Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Bio Cram Chart 2021Evangeline YaoNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualDocument26 pagesBiology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualGeorge EskandarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Demo MutationDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Demo Mutationmary graceNo ratings yet
- 6 Cell CycleDocument31 pages6 Cell CycleaprilNo ratings yet
- Pulse Chase ExperimentDocument7 pagesPulse Chase ExperimentNikhil Govind Bharambe50% (2)
- ANTIBODYDocument22 pagesANTIBODYapi-19916399100% (1)
- 1 SMDocument55 pages1 SMCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Erick Flesch - DNA-Replication-Overview-and-ReviewDocument2 pagesKami Export - Erick Flesch - DNA-Replication-Overview-and-ReviewFuckyouNo ratings yet
- Plant Sciences Ii Class - Assignment # 2: Semester IiiDocument3 pagesPlant Sciences Ii Class - Assignment # 2: Semester IiiTHE LIGHT AND NIGHTNo ratings yet
- Poultry and Pig Nutrition, Challenges of The 21st Century (VetBooks - Ir)Document431 pagesPoultry and Pig Nutrition, Challenges of The 21st Century (VetBooks - Ir)amamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- 21cloningsimulation EditedDocument4 pages21cloningsimulation EditedPrakriti AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Worthington Enzyme ManualDocument2 pagesWorthington Enzyme ManualAdi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Summaries 1-30 ReviewedDocument53 pagesMicrobiology Summaries 1-30 ReviewedyepNo ratings yet
- In Situ Click ChemistryDocument2 pagesIn Situ Click ChemistryClara CarreraNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton Molecular Motors: Structures and Their Functions in NeuronDocument10 pagesCytoskeleton Molecular Motors: Structures and Their Functions in NeuronnadaNo ratings yet
- Chemico-Biological InteractionsDocument7 pagesChemico-Biological InteractionskisnantoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton PRESENTATIONDocument36 pagesCytoskeleton PRESENTATIONChaudryNomiNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Pathophysiology of Parkinson S DiseaseDocument552 pagesEtiology and Pathophysiology of Parkinson S DiseaseAstrid Figueroa100% (2)
- Tugas Imunologi Dasar Fast TrackDocument23 pagesTugas Imunologi Dasar Fast TrackAnditri WeningtyasNo ratings yet
- Prescotts Microbiology 9th Edition Willey Test Bank 1Document34 pagesPrescotts Microbiology 9th Edition Willey Test Bank 1nancy100% (54)
- PPP QuestionsDocument3 pagesPPP QuestionsHarun MohamedNo ratings yet
- Three Pillars of Drug Development Case StudyDocument2 pagesThree Pillars of Drug Development Case StudyVVBNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument176 pagesBiochemistryaggoodNo ratings yet
- Sel Dan JaringanDocument1 pageSel Dan JaringanBakhitah Nurul100% (1)