Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AK96 Error Code 350 PDF
AK96 Error Code 350 PDF
Uploaded by
vikas bansal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageAn array is a block of computer memory that stores elements which are accessed by their index numbers. The document discusses how the AK 96 simulation software uses arrays to store and organize variables of different types related to the variables of interest. It provides an example of the FRI array which stores integer variables from fluid control systems, with the variable names indicating the source, memory type, variable type, and index within the array.
Original Description:
Original Title
413124301-AK96-Error-Code-350.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn array is a block of computer memory that stores elements which are accessed by their index numbers. The document discusses how the AK 96 simulation software uses arrays to store and organize variables of different types related to the variables of interest. It provides an example of the FRI array which stores integer variables from fluid control systems, with the variable names indicating the source, memory type, variable type, and index within the array.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views1 pageAK96 Error Code 350 PDF
AK96 Error Code 350 PDF
Uploaded by
vikas bansalAn array is a block of computer memory that stores elements which are accessed by their index numbers. The document discusses how the AK 96 simulation software uses arrays to store and organize variables of different types related to the variables of interest. It provides an example of the FRI array which stores integer variables from fluid control systems, with the variable names indicating the source, memory type, variable type, and index within the array.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
About...
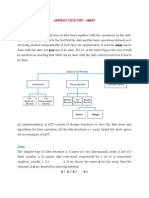
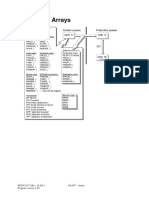
Arrays
An array is a defined block of computer memory. It consists of elements, and the number of
elements determine the array size. The elements are accessed by their index numbers. The
index number is placed in parenthesis after the array name, e.g. ArrayName(99). This array
consists of 100 elements (0-99):
In the AK 96, all variables of interest are placed in arrays. The array names refer to the type
of variables stored in the arrary. An example: the FRI-array stores variables from the fluid
control.
The key to the variables:
ex. FRI(FI_DEGASS$PRESS)
F is source TRACO name
R is RAM
I is the type of the variable, in this case an integer
(FI_DEGASS$PRESS) is the index in the FRI array
Source TRACO names
B: Blood
F: Fluid
O: Operator's
C: Common
AK 96® - Arrays HCEN12371 Rev. 10.2011
Program version 3.50
You might also like
- Data Structures and Algorithms in Swift: Implement Stacks, Queues, Dictionaries, and Lists in Your AppsFrom EverandData Structures and Algorithms in Swift: Implement Stacks, Queues, Dictionaries, and Lists in Your AppsNo ratings yet
- John W. Schaum Piano Course Pre A-The Green Book - 22Document1 pageJohn W. Schaum Piano Course Pre A-The Green Book - 22vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- ARRAYSDocument4 pagesARRAYSOluwamodupe EstherNo ratings yet
- 16 Arrays: L L L LDocument17 pages16 Arrays: L L L LroselathikaNo ratings yet
- LAB 01 One-Dimensional ArraysDocument12 pagesLAB 01 One-Dimensional ArraysNina RicciNo ratings yet
- C Arrays: - A Collection of Same Type Data, 1D, 2DDocument27 pagesC Arrays: - A Collection of Same Type Data, 1D, 2DSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Array:-: Data - Type Variable - Name (Size of The Array)Document5 pagesArray:-: Data - Type Variable - Name (Size of The Array)Sai DeepNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Unit 2Document116 pagesLecture Notes - Unit 2Kanagaraj SubramaniNo ratings yet
- C Arrays: - A Collection of Same Type Data, 1D, 2DDocument25 pagesC Arrays: - A Collection of Same Type Data, 1D, 2DZakirNo ratings yet
- Array: (Problem Solving of C')Document10 pagesArray: (Problem Solving of C')Akash RavNo ratings yet
- Sharad DocumentDocument3 pagesSharad Documentme0906840029No ratings yet
- SAS Advance-3-1Document14 pagesSAS Advance-3-1PremNo ratings yet
- Arrays Strings-Program-NotesDocument46 pagesArrays Strings-Program-NoteskalpanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Arrays and Strings: ArrayDocument22 pagesChapter 3: Arrays and Strings: Arrayafzal_aNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 C ProgrammingDocument37 pagesModule - 3 C ProgrammingSimranNo ratings yet
- Understanding Array by DK Mamonai 09CE37Document17 pagesUnderstanding Array by DK Mamonai 09CE37Darya MemonNo ratings yet
- V Unit PDFDocument7 pagesV Unit PDFChithirai VeniNo ratings yet
- C Programming 7Document21 pagesC Programming 7CarabNo ratings yet
- Assignment For CPLCDocument2 pagesAssignment For CPLCChristine HaliliNo ratings yet
- Arrays in CDocument9 pagesArrays in CLigaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 (C++) - ArraysDocument91 pagesUnit 6 (C++) - ArraysMiley GirmayNo ratings yet
- Summarizing Objects: SEC-2 Ch-4 Data: Descriptive Statistics and TabulationDocument2 pagesSummarizing Objects: SEC-2 Ch-4 Data: Descriptive Statistics and TabulationRahulNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Between Data Type and Data StructuresDocument11 pagesDifferentiate Between Data Type and Data StructureskrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Arrays and PointersDocument32 pagesUnit 6 - Arrays and PointersAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- C Programming Chapter 5Document7 pagesC Programming Chapter 5damner0% (1)
- C Prog Notes All UnitesDocument220 pagesC Prog Notes All UnitesAashiQ ShayarNo ratings yet
- Abstract Data Type-ArrayDocument6 pagesAbstract Data Type-ArrayRajendranbehappyNo ratings yet
- Lecture#4Document11 pagesLecture#4HassanNo ratings yet
- Arrays - Study MaterialDocument3 pagesArrays - Study MaterialDinesh VelNo ratings yet
- Scs1102 Unit IIIDocument76 pagesScs1102 Unit IIIFaiz ShamsNo ratings yet
- ArrayDocument68 pagesArraySRIVARSHIKA SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Macros Explained - Array RoutinesDocument10 pagesMacros Explained - Array RoutinesDamianPanNo ratings yet
- Dimentional ArrayDocument4 pagesDimentional Arrayanon_684505362No ratings yet
- C Programming: Unit 3Document28 pagesC Programming: Unit 3Krupa KrupaNo ratings yet
- R-Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesR-Cheat SheetPrasad Marathe100% (1)
- Arrays: C ProgrammingDocument3 pagesArrays: C Programmingchandan971No ratings yet
- Introduction To Scala 2Document14 pagesIntroduction To Scala 2Avan TennantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ArraysDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Arrayssalman bhaiNo ratings yet
- Document For Programming in JAVADocument3 pagesDocument For Programming in JAVAAngad SoodNo ratings yet
- Array in C'Document17 pagesArray in C'pankajusbNo ratings yet
- VariablesDocument27 pagesVariablesErnest BarreraNo ratings yet
- Creating Arrays - Arrays Are Declared by Using The Array Type Name, Optionally Followed by "Of"Document3 pagesCreating Arrays - Arrays Are Declared by Using The Array Type Name, Optionally Followed by "Of"Iruma KunNo ratings yet
- Matlab Chapter 5Document20 pagesMatlab Chapter 5peprahkofi05No ratings yet
- Math CP Lecture 10.Pptx Filename UTF-8''Math&CP Lecture 10Document14 pagesMath CP Lecture 10.Pptx Filename UTF-8''Math&CP Lecture 10FILZAH HASHMINo ratings yet
- Arrays: Data-Type Array-Name (Array-Size)Document6 pagesArrays: Data-Type Array-Name (Array-Size)Dark AngelNo ratings yet
- The NACA Airfoil SeriesDocument6 pagesThe NACA Airfoil Seriesranjith manuNo ratings yet
- NACA Airfoil SeriesDocument6 pagesNACA Airfoil SeriesMohammad Taha IrfanNo ratings yet
- The NACA Airfoil SeriesDocument6 pagesThe NACA Airfoil SeriesAlberto Gonzales LHNo ratings yet
- ch4 Arrays StringsDocument8 pagesch4 Arrays StringsPetros AbebeNo ratings yet
- Arrays and String: 1. Single Dimension ArrayDocument6 pagesArrays and String: 1. Single Dimension ArrayPriya ShettyNo ratings yet
- Pascal - ArraysDocument3 pagesPascal - ArraysAndrewNo ratings yet
- Note & Programs On ARRAY: Declaration of An ArrayDocument1 pageNote & Programs On ARRAY: Declaration of An Arraybasualok@rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- CS 101 Lecture 6 PDFDocument8 pagesCS 101 Lecture 6 PDFMohammad ArafatNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2012 13 - CP0332 - 28 Aug 2012 - RM01 1Document2 pagesFALLSEM2012 13 - CP0332 - 28 Aug 2012 - RM01 1Thomas VargheseNo ratings yet
- Java Programming Tutorial With Screen Shots & Many Code ExampleFrom EverandJava Programming Tutorial With Screen Shots & Many Code ExampleNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Class3 90Document1 pageClass3 90vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- BSP Page4 PDFDocument1 pageBSP Page4 PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Achievers Section: 950 G 1 KG 225 G 3 KG 725 GDocument1 pageAchievers Section: 950 G 1 KG 225 G 3 KG 725 Gvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- BSP pg6Document1 pageBSP pg6vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- C CC 002, Preset Variable StorageDocument2 pagesC CC 002, Preset Variable Storagevikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Number of Schools: (By School Category - State Level)Document50 pagesNumber of Schools: (By School Category - State Level)vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Of in (A) (C) : Triangles GivenDocument1 pageOf in (A) (C) : Triangles Givenvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Ak95 34Document3 pagesAk95 34vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Ak96 1112 Page PDFDocument2 pagesAk96 1112 Page PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Ak 58 PDFDocument58 pagesAk 58 PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Fresenius For The Exam PDFDocument2 pagesFresenius For The Exam PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Trainning For The ExamDocument5 pagesTrainning For The Examvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Ak96 PDFDocument1 pageAk96 PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- C CB 008, Blood VolumeDocument1 pageC CB 008, Blood Volumevikas bansalNo ratings yet
- C CB 003, Venous PressureDocument1 pageC CB 003, Venous Pressurevikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Ak96 PDFDocument1 pageAk96 PDFvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Meritpathcrmo 2015 Set 2Document1 pageMeritpathcrmo 2015 Set 2vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Index of sl100Document3 pagesIndex of sl100vikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Syllabus 2016-17: ClassDocument2 pagesSample Paper Syllabus 2016-17: Classvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- INMO-2010 Problems and SolutionsDocument5 pagesINMO-2010 Problems and Solutionsvikas bansalNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Home Sewing MachineDocument151 pagesService Manual: Home Sewing Machinevikas bansalNo ratings yet