Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handouts in Busfin
Uploaded by
Aimelenne Jay Aninion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesOriginal Title
handouts in busfin
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesHandouts in Busfin
Uploaded by
Aimelenne Jay AninionCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
What is Finance?
• Finance is the art & science of managing 'MONEY'.
• Finance is the life blood of Business (funds).
• “Finance v/s Money”
Nature of Financial Management
Financial management is mainly concerned with the proper management of funds.
The financial manager must see that the funds are procured in a manner that there is risk, cost and control considerations are properly
balanced in a given situation and there is optimum utilization of funds.
Financial institution- Is an organization that handles financial transactions for individuals, groups and other organization – profit, non profit, private
or government owned.
Transactions like saving and borrowing money, sending or receiving money to or from overseas, and exchanging currencies are all done
through financial institutions.
Most common examples of financial institutions and the ones you are most familiar with are banks and insurance companies
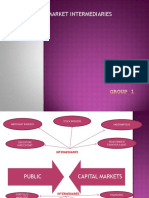
FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS are also referred to as FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES
Financial intermediaries are called as such because at times, they facilitate the flow of funds between the savers and demanders of funds
in an economy or a financial system.
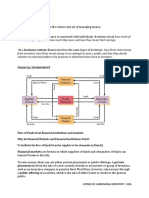
FINANCIAL PRODUCTS are called as FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Financial products are signified by instruments when individuals and organizations alike deal with each other in completing financial transactions.
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS?
a document which signifies a legal or binding agreement between the 2 parties.
It has a monetary values
- Ex: personal check ( it has monetary value: once it is dated, written or payee, signed by the person who issued or
his/her legal representative.
- Ex: stock certificate ( once issued to the purchaser of the stock certificate, legally it means that the person or
organization owns stocks of a business enterprise)
Depository institution & non depository institution
a. Depository institution - manages money that is deposited by individuals and organizations.
Examples: banks, credit unions and savings and loan associations
b. Non depository institution – does not handle deposits. Instead, such institutions serve as intermediaries between savers and demanders of
funds, individuals, households and other businesses who need additional funds to support personal needs or business operations.
Examples: mutual funds, hedge funds, brokerage, and investment firms.
* Hedge funds (a limited partnership of investors that uses high risk methods, such as investing with borrowed money, in hopes of realizing large
capital gains)
TYPES OF FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
• Commercial Banks
o Accepts deposits from individuals and organizations that have
excess funds and provide them loans to those who need or want to borrow money.
o Savings and loans have been the focus or services that commercial
banks provide to their customers
Credit Unions
o are normally associated with cooperatives
o the interest rates offered by this are generally higher or lower on certain types of loans compared to what most
banks will offer.
o this is done to encourage more people to become members
o However, it is not open to general public
o Only members are serviced by this
o There is usually a profit sharing between members every at the end of fiscal yr
Investment Bank
o they do not have any dealings with the general public
o they facilitate buying and selling of stocks
Insurance Companies
o provide individuals and organizations a way to manage risk
o they operate on the principle of pooling of risks wherein premiums are collected from clients.
Brokerage
o a financial institution that earns through commissions
o they facilitate buying and selling of securities
o it can either be a discount or full service
*Discount brokerage firms – allow their clients to do their own research about investment options.
*Full service brokerage firms – provides clients advice and help them manage their investment portfolio
-> Investment portfolio – a collection of financial products owned by a single investor – either individual or an organization
Investment Companies
o wherein individuals and other organizations invest in investment portfolios that are managed by professionals who are tasked to
keep track of market trends and the performance of different financial product or instruments.
o Investors pool their funds together and combined funds then placed by the company in different investment options
Example: mutual funds
FINANCIAL MARKET
Financial institutions operate in the financial market
Financial Market – means for the buying and selling of stocks, bonds and other financial instruments.
STOCKS – shares of a corporation sold to investors
BONDS - are a form of debt that the issuing entity promises to repay at some point in the future
MONEY MARKET & CAPITAL MARKET
Money markets = are the markets where transactions involving short term debt securities take place.
SHORT TERM DEBT – just like in accounting, is one that is due or demandable within one year or less
Ex: treasury bills, commercial paper
CAPITAL MARKET
- Capital markets = are the markets where transactions involving long term debt maturing in more than one year. The buying and selling of
stocks issued by corporations also takes place here.
2 types of markets of financial transactions within the capital market:
1. Primary market – new issues of securities are traded. Source of new securities for the secondary market
2. Secondary market – where previously issued securities are traded
MOST COMMON FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
1. Savings
2. Loans
3. Bonds
4. Security
5. Treasury bills
6. Insurance products
7. Mutual funds
CAREERS IN FINANCE
1. Investment Banker
2. Insurance Broker/Agent
3. Financial Advisor
4. Stockbroker
5. Fund Manager
6. Academe
7. Corporate Consultants
8. Country Manage
9. CFO
10. Corporate Finance Manager
You might also like
- Mutual Funds - The Mutual Fund Retirement Plan For Long - Term Wealth BuildingFrom EverandMutual Funds - The Mutual Fund Retirement Plan For Long - Term Wealth BuildingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Self AssessmentRimuruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1mark sanadNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument4 pagesFinancial InstitutionsCrisha Diane GalvezNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument6 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsFarrah Jane BitacNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Financial InstitutionsDocument58 pagesBusiness Finance Financial InstitutionsCristabelle RussellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsWill De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Financial EnvironmentDocument30 pagesFinancial EnvironmentIan TattaoNo ratings yet
- Investment BankingDocument12 pagesInvestment BankingmehnazzNo ratings yet
- Economic Functions of The Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesEconomic Functions of The Financial InstitutionsKemotherapy LifesucksNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3Safh SalazarNo ratings yet
- What Is A Financial IntermediaryDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Financial IntermediaryYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions 1Document29 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions 1Hamza Iqbal100% (1)
- The Domestic and International Financial Market_Alfinda and AbionDocument9 pagesThe Domestic and International Financial Market_Alfinda and Abionspp9g6qg6cNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions TheoryDocument4 pagesFinancial Institutions TheorySandeep Singh SikerwarNo ratings yet
- (Asc) Financial Markets HandoutDocument13 pages(Asc) Financial Markets HandoutRENZ ALFRED ASTRERONo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document54 pagesChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagementJherica Grace FloresNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument49 pagesNotesMatthew MullalyNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsAdriana Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- 2 Financial Assets and MarketsDocument42 pages2 Financial Assets and MarketsM-Faheem AslamNo ratings yet
- Banking and Financial Institution 1ST Term MT ReviewerDocument16 pagesBanking and Financial Institution 1ST Term MT ReviewerAly JoNo ratings yet
- Financial Market ReviewerDocument9 pagesFinancial Market ReviewerBryan NograNo ratings yet
- Money Banking Chapter 5Document12 pagesMoney Banking Chapter 5ebsa ahmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsKurt Anne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Capital Market IntermediariesDocument15 pagesCapital Market IntermediariesSebin SebastianNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument31 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionsqueen estevesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Financial MarketsDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 2 Financial MarketsAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Financial InstitutionsDocument35 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Financial Institutionsteshome dagne100% (2)
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1Shivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Christiene P. Schwandner: Financial Sector DefinedDocument4 pagesChristiene P. Schwandner: Financial Sector DefinedGladys Gaccion OpitzNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of FinancialDocument4 pagesFinancial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of Financialsheinamae quelnatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, 2, 3, 4 Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management SSSSSSDocument12 pagesChapter 1, 2, 3, 4 Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management SSSSSSSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Specialty CorporationDocument171 pagesSpecialty CorporationAdrian Steven Claude CosicoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Finance BasicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Finance Basicsnatalie clyde matesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementMikaella Adriana GoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business FinanceDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Business FinanceHennessy Shania Gallera ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFBuzon Kyle BluNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument8 pagesFinancial Marketshahid3454No ratings yet
- Investment and Portfolio Management - PrelimDocument6 pagesInvestment and Portfolio Management - PrelimTrisha TarucNo ratings yet
- Question 1) Briefly Explain Capital Allocation Process With The Help of Diagram?Document7 pagesQuestion 1) Briefly Explain Capital Allocation Process With The Help of Diagram?Usama KhanNo ratings yet
- Branches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsDocument6 pagesBranches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsBernadette D. PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides ForDocument56 pagesFinancial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides Forsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Learn key financial conceptsDocument14 pagesLearn key financial conceptsCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- Finmar NotesDocument5 pagesFinmar NotesariannejonesmNo ratings yet
- Financial IntermediaryDocument4 pagesFinancial IntermediaryValerie Mae AbuyenNo ratings yet
- SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY Faculty of Accounting and finance Financial market and institution assignment oneDocument10 pagesSAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY Faculty of Accounting and finance Financial market and institution assignment oneruhamaNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's University Faculty of Accounting and Finance Financial Market and Institution Assignment OneDocument10 pagesSaint Mary's University Faculty of Accounting and Finance Financial Market and Institution Assignment OneruhamaNo ratings yet
- Vidhu Khatri Sorav Sharma Manali Mathur Atul Kesharwani Rahul SanvariyaDocument13 pagesVidhu Khatri Sorav Sharma Manali Mathur Atul Kesharwani Rahul SanvariyaSorav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Business and The Financial Markets Chapter 03Document50 pagesBusiness and The Financial Markets Chapter 03James KuruvalakaNo ratings yet
- The Financial EnvironmentDocument16 pagesThe Financial EnvironmentJason Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionDocument17 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionDELOS SANTOS, APRIL JOY E.No ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial InstitutionsDocument45 pagesIntroduction to Financial InstitutionsSofoniyas GashawNo ratings yet
- Unit ThreeDocument22 pagesUnit ThreeEYOB AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Financial InstitutionsDocument4 pagesFinancial InstitutionsTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- Understand Key Financial Concepts and Terms in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesUnderstand Key Financial Concepts and Terms in 40 CharactersGil TeodosipNo ratings yet
- Branches of Finance: Department of Ducation - Bureau of Curriculum DevelopmentDocument44 pagesBranches of Finance: Department of Ducation - Bureau of Curriculum DevelopmentRaquel Sibal RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions GuideDocument48 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions GuideJun AdajarNo ratings yet
- Fin Market and InstitutionDocument3 pagesFin Market and Institutionzeus manNo ratings yet
- Investment Banks: Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesInvestment Banks: Financial Institutionsruthmae bumanglagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 (Who Will Be Like Jesus)Document1 pageLesson 2 (Who Will Be Like Jesus)Aimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao Adventist Academy: Date Program Speaker Theme SponsorDocument2 pagesWestern Mindanao Adventist Academy: Date Program Speaker Theme SponsorAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Create A Financial Statement: Ipt OutputDocument2 pagesCreate A Financial Statement: Ipt OutputAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao Adventist AcademyDocument1 pageWestern Mindanao Adventist AcademyAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao Adventist Academy "The School For Better Future" 7028 Dumingag, Zamboanga Del Sur PhilippinesDocument1 pageWestern Mindanao Adventist Academy "The School For Better Future" 7028 Dumingag, Zamboanga Del Sur PhilippinesAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Managing Organizational Change and Development: 1. External ForcesDocument8 pagesChapter 13: Managing Organizational Change and Development: 1. External ForcesAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Letter Requesting Permission for Research Study on Anti-Drug Abuse CampaignDocument2 pagesLetter Requesting Permission for Research Study on Anti-Drug Abuse CampaignAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Semi FinalDocument2 pagesApplied Economics Semi FinalAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Arts 7: Western Mindanao Adventist Academy "The School For Better Future" 7028 Dumingag, Zamboanga Del Sur PhilippinesDocument1 pageArts 7: Western Mindanao Adventist Academy "The School For Better Future" 7028 Dumingag, Zamboanga Del Sur PhilippinesAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Group DynamicsDocument2 pagesChapter 12 - Group DynamicsAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- General Principles of ManagementDocument5 pagesGeneral Principles of ManagementAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Floriculture Is Profitable Business To Venture in When Planned ProperlyDocument2 pagesFloriculture Is Profitable Business To Venture in When Planned ProperlyAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Executive SummaryDocument10 pages1.0 Executive SummaryAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- V's Tea Bar Business PlanDocument20 pagesV's Tea Bar Business PlanAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Matching accounting terms and creating a personal cash flow statementDocument1 pageMatching accounting terms and creating a personal cash flow statementAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- V's Tea Bar Business PlanDocument20 pagesV's Tea Bar Business PlanAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- The Hierarchy of AuthorityDocument1 pageThe Hierarchy of AuthorityAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- SMC Group of Companies Payroll Report For The Month of March 2019Document1 pageSMC Group of Companies Payroll Report For The Month of March 2019Aimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Itinerary For Educational Tour at Cagayan de Oro CityDocument1 pageItinerary For Educational Tour at Cagayan de Oro CityAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- SMC Group of Companies Payroll Report For The Month of March 2019Document1 pageSMC Group of Companies Payroll Report For The Month of March 2019Aimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12 - Table 1Document2 pagesExercise 12 - Table 1Aimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Letter Requesting Permission for Research Study on Anti-Drug Abuse CampaignDocument2 pagesLetter Requesting Permission for Research Study on Anti-Drug Abuse CampaignAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document2 pagesExercise 3Aimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10 - Total Quarterly EnrolmentDocument1 pageExercise 10 - Total Quarterly EnrolmentAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Hot Dog Cart Business PlanDocument18 pagesHot Dog Cart Business PlanAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageExercise 4 - Schematic DiagramAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9 - Final GradesDocument1 pageExercise 9 - Final GradesAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 - Grading SystemDocument2 pagesExercise 13 - Grading SystemAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12 - Table 1Document2 pagesExercise 12 - Table 1Aimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Search For Miss SMC 2018: Criteria Sheet For Production Number and Best in Cheer Dance AttireDocument6 pagesSearch For Miss SMC 2018: Criteria Sheet For Production Number and Best in Cheer Dance AttireAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Competitor Analysis On Banks CBE's Case Study - FinalsDocument25 pagesCompetitor Analysis On Banks CBE's Case Study - FinalsAbel JacobNo ratings yet
- ABL Online Banking Facilities and ATM ServicesDocument150 pagesABL Online Banking Facilities and ATM ServicesTabeena NoorNo ratings yet
- A New Window Final Self CorrectionDocument342 pagesA New Window Final Self CorrectionGbenro AdegbolaNo ratings yet
- Atm Cum Debit Card Application FormDocument2 pagesAtm Cum Debit Card Application FormImran AhmadNo ratings yet
- House Hearing, 109TH Congress - Financial Services Regulatory Relief: The Regulators' ViewsDocument301 pagesHouse Hearing, 109TH Congress - Financial Services Regulatory Relief: The Regulators' ViewsScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Certificate in Commercial Credit IndiaDocument4 pagesCertificate in Commercial Credit Indiaskumarites100% (1)
- 1.1. Origin and Meaning of BankDocument15 pages1.1. Origin and Meaning of BankSuneeta KarkiNo ratings yet
- HHRG 117 Ba00 Wstate Hsum 20210519Document14 pagesHHRG 117 Ba00 Wstate Hsum 20210519ForkLogNo ratings yet
- ESCRA - Spouses - Panlilio - v. - Citibank - N.A.20181016-5466-sjgrxpDocument32 pagesESCRA - Spouses - Panlilio - v. - Citibank - N.A.20181016-5466-sjgrxpMHERITZ LYN LIM MAYOLANo ratings yet
- Financial Market Short Notes & QuestionsDocument12 pagesFinancial Market Short Notes & QuestionssyedmerajaliNo ratings yet
- Meezan Bank HR: Roles, Planning and Recruitment ProcessDocument33 pagesMeezan Bank HR: Roles, Planning and Recruitment ProcessAsad0% (1)
- Industry Analysis AXIS BANKDocument13 pagesIndustry Analysis AXIS BANKEric D'souza0% (1)
- Introduction To Asset Liability and Risk MGMTDocument147 pagesIntroduction To Asset Liability and Risk MGMTMani ManandharNo ratings yet
- Ssci 122 - Ethics Think Sheet 1 Solving ProblemsDocument2 pagesSsci 122 - Ethics Think Sheet 1 Solving ProblemsClass&dayNo ratings yet
- Weekly FinDocument6 pagesWeekly FinInternational Business TimesNo ratings yet
- Leo Wanta Official Biography: Americans: Wanta Be Free - Chapter OneDocument23 pagesLeo Wanta Official Biography: Americans: Wanta Be Free - Chapter Oneenerchi1111No ratings yet
- Central Bank Vs FloresDocument3 pagesCentral Bank Vs FloreschrystelNo ratings yet
- Checkbook Register: Date Num Payee / Description Category R BalanceDocument8 pagesCheckbook Register: Date Num Payee / Description Category R BalanceRubeel KhatibNo ratings yet
- BarclayDocument4 pagesBarclayDeedra ColeNo ratings yet
- The Fuller Method Learn To Grow Your Money Exponentially - V8.1 013120 PDFDocument44 pagesThe Fuller Method Learn To Grow Your Money Exponentially - V8.1 013120 PDFJulius Mark Carinhay TolitolNo ratings yet
- Addis Print 2Document49 pagesAddis Print 2Addishiwot seifuNo ratings yet
- HBLDocument42 pagesHBLsamiNo ratings yet
- 5 6084915055709651012Document8 pages5 6084915055709651012Ajit Yadav100% (1)
- Economics For Managers: Unit 17 Inflation 1-14Document90 pagesEconomics For Managers: Unit 17 Inflation 1-14Radhakrishnan PNo ratings yet
- Rosbank Moscow issues 250M euro bank guaranteeDocument1 pageRosbank Moscow issues 250M euro bank guaranteeUlrich Maria Baltzer0% (1)
- Distressed Property Investing: A Foreclosure and REO Tutorial For New and Intermediate Real Estate InvestorsDocument93 pagesDistressed Property Investing: A Foreclosure and REO Tutorial For New and Intermediate Real Estate Investorsnorthpoint100% (21)
- Monetary Policy of PakistanDocument6 pagesMonetary Policy of Pakistanbravo.naumanNo ratings yet
- Harry BennettDocument1 pageHarry BennettEmannuel Ontario33% (3)
- Test dated 22.05.2017 CBS menu optionsDocument8 pagesTest dated 22.05.2017 CBS menu optionsAditya KaushalNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (97)
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerFrom EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Disloyal: A Memoir: The True Story of the Former Personal Attorney to President Donald J. TrumpFrom EverandDisloyal: A Memoir: The True Story of the Former Personal Attorney to President Donald J. TrumpRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (214)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistFrom EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Introduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsFrom EverandIntroduction to Negotiable Instruments: As per Indian LawsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Getting Through: Cold Calling Techniques To Get Your Foot In The DoorFrom EverandGetting Through: Cold Calling Techniques To Get Your Foot In The DoorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (63)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- Product-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfFrom EverandProduct-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Note Brokering for Profit: Your Complete Work At Home Success ManualFrom EverandNote Brokering for Profit: Your Complete Work At Home Success ManualNo ratings yet
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessFrom EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityFrom EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Ready, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successFrom EverandReady, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)From EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Business Legal Lifecycle US Edition: How To Successfully Navigate Your Way From Start Up To SuccessFrom EverandThe Business Legal Lifecycle US Edition: How To Successfully Navigate Your Way From Start Up To SuccessNo ratings yet
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialFrom EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialNo ratings yet
- Angel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000From EverandAngel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (86)
- IFRS 9 and CECL Credit Risk Modelling and Validation: A Practical Guide with Examples Worked in R and SASFrom EverandIFRS 9 and CECL Credit Risk Modelling and Validation: A Practical Guide with Examples Worked in R and SASRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)