Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W2. Notes
Uploaded by
Cristelyn Tomas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesThe document defines key terms related to financial markets, institutions, and instruments. It distinguishes financial institutions from financial instruments and markets. It also explains the roles of various financial institutions like commercial banks, insurance companies, and mutual funds. The learning objectives are to define financial markets, institutions, and instruments, and identify types of each. It provides examples of common financial instruments like bonds and stocks.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to financial markets, institutions, and instruments. It distinguishes financial institutions from financial instruments and markets. It also explains the roles of various financial institutions like commercial banks, insurance companies, and mutual funds. The learning objectives are to define financial markets, institutions, and instruments, and identify types of each. It provides examples of common financial instruments like bonds and stocks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesW2. Notes
Uploaded by
Cristelyn TomasThe document defines key terms related to financial markets, institutions, and instruments. It distinguishes financial institutions from financial instruments and markets. It also explains the roles of various financial institutions like commercial banks, insurance companies, and mutual funds. The learning objectives are to define financial markets, institutions, and instruments, and identify types of each. It provides examples of common financial instruments like bonds and stocks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
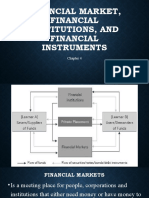
LEARNING COMPETENCIES:
• Distinguish a financial institution from financial
instrument and financial market.
• Enumerate the varied financial institutions and their
corresponding services.
• Compare and contrast the varied financial
instruments.
• Explain the flow of funds within an organization –
through and from the enterprise—and the role of the
financial manager.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
• Prepare a diagram illustrating how the
Financial System works
• Define Financial Markets, Financial Institutions
and Financial Instruments.
• Identify the types of Financial Markets,
Financial Institutions and Financial
Instruments.
PRIVATE PLACEMENTS
• the sale of a new security directly to
an investor or group of investors.
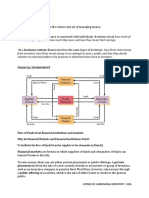
FINANCIAL MARKET
•an organized forum that lets the lender
along with other suppliers of funds,
and Borrower, along with other users
of funds, meet and make transactions.
FINANCIAL INSTITUTION
•intermediaries that channel the savings of
individuals, businesses, and governments
into loans or investments.
FINANCIAL SYSTEM
How transactions between suppliers
and users of funds take place. How
would they prove that there was a
transaction so that the demander
will be able to repay the supplier on
time and at the right amount?
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS is a real or a
virtual document representing a legal
agreement involving some sort-of
monetary value These can be debt
securities like corporate bonds or equity
like shares of stock.
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
• Financial Assets any asset that is cash, equity instrument
of another entity, contractual right to receive cash or
another financial asset from another entity, and
contractual right to exchange instruments with another
entity under conditions that are potentially favorable
• Financial Liabilities is any liability that is a contractual
obligation. To deliver cash or other financial instrument to
another entity, To exchange financial instruments with
another entity under conditions that are potentially
unfavorable,
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Debt Instruments -generally have fixed returns
due to fixed interest rates.
Examples:
• Treasury Bonds and Treasury Bills are issued by
the Philippine government.
• Corporate Bonds are issued by publicly listed
companies.
Equity Instruments-generally have varied returns
based on the performance of the issuing company.
Examples: Preferred and Common Stock
FINANCIAL MARKETS
Primary Market-market where a security is
sold when it is first issued and sold to
investors.
Secondary Market-the market where
subsequent trading takes place and individual
investors trade among themselves
FINANCIAL MARKETS
Money Market-are a venue wherein securities
with short-term maturities (1 year or less) are
sold.
Capital Market-securities with longer-term
maturities
FINANCIAL INSTITUTION
Commercial Banks-Individuals deposit funds at
commercial banks, which use the deposited
funds to provide commercial loans to firms and
personal loans to individuals, and purchase debt
securities issued by firms or government
agencies.
Insurance Companies -iindividuals purchase
insurance (life, property and casualty, and
health) protection with insurance premiums.
FINANCIAL INSTITUTION
Mutual Funds-are owned by investment companies which
enable small investors to enjoy the benefits of investing in a
diversified portfolio of securities purchased on their behalf
by professional investment managers.
Pension Funds-Financial institutions that receive payments
from employees and invest the proceeds on their behalf.
Other financial institutions -Financial institutions that
receive payments from employees and invest the proceeds
on their behalf.
•STEPS IN THE FINANCIAL
PLANNING PROCESS
•ILLUSTRATE THE FORMULA
AND FORMAT IN THE
PREPARARTION OF BUDGETS
AND PROJECTED FS
You might also like
- The Domestic and International Financial Market - Alfinda and AbionDocument9 pagesThe Domestic and International Financial Market - Alfinda and Abionspp9g6qg6cNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsKurt Anne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Let'S Go Back To The Past: Quiz For The Last Lesson DiscussedDocument26 pagesLet'S Go Back To The Past: Quiz For The Last Lesson DiscussedReina Mae Martinez RiegoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3Safh SalazarNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsAdriana Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Financial Markets Inst. and InstrumentsPerbielyn BasinilloNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFDocument19 pagesFinancial Markets - Chapter 1 PDFBuzon Kyle BluNo ratings yet
- Composition of Financial SystemDocument10 pagesComposition of Financial SystemKareen Tapia PublicoNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument3 pagesFinancial MarketsAguit, Queene JoyNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument21 pagesBusiness Finance: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleNOVELYN QUILNATNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument6 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsFarrah Jane BitacNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment - Lecture2Document20 pagesFinancial Environment - Lecture2mehnaz kNo ratings yet
- The Basic Structure of Financial MarketsDocument10 pagesThe Basic Structure of Financial Markets202220012No ratings yet
- Financial EnvironmentDocument30 pagesFinancial EnvironmentIan TattaoNo ratings yet
- BAP 4 Capital Market L1-3Document17 pagesBAP 4 Capital Market L1-3Mabel Jean RambunayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Airra SungaNo ratings yet
- Handouts in BusfinDocument2 pagesHandouts in BusfinAimelenne Jay AninionNo ratings yet
- Overview of Financial Markets and Financial InstitutionsDocument53 pagesOverview of Financial Markets and Financial InstitutionsCharmaine Klaire Agan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document37 pagesCH 1xyzNo ratings yet
- FINAMAN Lecture2 Business Firms and Financial MarketsDocument48 pagesFINAMAN Lecture2 Business Firms and Financial MarketsJun AdajarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BFDocument12 pagesChapter 2 BFJanah MirandaNo ratings yet
- MPCB Module 1 Intro To Financial MarketDocument6 pagesMPCB Module 1 Intro To Financial MarketAlfe PinongpongNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions 1Document29 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions 1Hamza Iqbal100% (1)
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2CjNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Lectures Part 1Document26 pagesCapital Market Lectures Part 1ainlee lataganNo ratings yet
- Q. Is There A Relationship Between Financial Institutions and Financial Markets?Document3 pagesQ. Is There A Relationship Between Financial Institutions and Financial Markets?Zabir Tahzin HassanNo ratings yet
- Branches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsDocument6 pagesBranches of Finance: Financial Markets & Financial InstitutionsBernadette D. PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Financial Market Handout For BSAIS 2Document4 pagesFinancial Market Handout For BSAIS 2Suitzie Anne Villamor TobiasNo ratings yet
- Business and The Financial Markets Chapter 03Document50 pagesBusiness and The Financial Markets Chapter 03James KuruvalakaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesAssignment - Financial MarketsTaruntej Singh100% (3)
- NotesDocument49 pagesNotesMatthew MullalyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsWill De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Fin Market and InstitutionDocument3 pagesFin Market and Institutionzeus manNo ratings yet
- Ch.7 An Overview: Financial MarketDocument23 pagesCh.7 An Overview: Financial MarketArly Kurt TorresNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDocument58 pagesFinancial Markets, Institutions, and InstrumentsDaniela MercadoNo ratings yet
- June 27, 2017 - FINANCIAL MARKETSDocument26 pagesJune 27, 2017 - FINANCIAL MARKETSLaila Mae PiloneoNo ratings yet
- Fim 4Document33 pagesFim 4akshat srivastavaNo ratings yet
- SAPM (Indian Financial System)Document6 pagesSAPM (Indian Financial System)Sharon SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Composition and Characteristics of Financial MarketDocument11 pagesComposition and Characteristics of Financial MarketPoojan KariaNo ratings yet
- Why Study Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument7 pagesWhy Study Financial Markets and InstitutionsMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Some What Solved QB-Financial Mnagement-MBM633Document7 pagesSome What Solved QB-Financial Mnagement-MBM633Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument31 pagesFinancial MarketsCheesca Macabanti - 12 Euclid-Digital ModularNo ratings yet
- 2philippine Financial SystemDocument45 pages2philippine Financial SystemSay SayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Financial System and Its RegulationDocument16 pagesLesson 2 The Financial System and Its RegulationEliza Calixto-SorianososNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1mark sanadNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides ForDocument56 pagesFinancial Institutions, Markets, & Money, 10 Edition: Power Point Slides Forsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Financial System, Markets and ServicesDocument65 pagesFinancial System, Markets and Servicessatya123b8101100% (1)
- Neha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyDocument8 pagesNeha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyArishfa khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Financial SystemDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Financial SystemSimran JainNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument34 pagesFinancial Marketsmouli poliparthiNo ratings yet
- Finman Report Chapter 8Document17 pagesFinman Report Chapter 8Markbenson MarananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument41 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionMuhd Rizzwan0% (1)
- Lecture TwoDocument28 pagesLecture TwoSajed RahmanNo ratings yet
- Economic Functions of The Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesEconomic Functions of The Financial InstitutionsKemotherapy LifesucksNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic Developmentrevathi alekhya80% (10)
- Module 3. Securities (Lecture Notes)Document11 pagesModule 3. Securities (Lecture Notes)course shtsNo ratings yet
- Good DR y If StillDocument26 pagesGood DR y If Stillsantoshmishra5510No ratings yet
- FINANCEDocument5 pagesFINANCEAARTI MaidNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions 1Document32 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions 1Hamza Iqbal100% (1)
- w1 DLL Orgman August 22 24 To 26Document3 pagesw1 DLL Orgman August 22 24 To 26Cristelyn Tomas100% (1)
- w1 DLL Fabm1 August 22 23 To 25 26Document3 pagesw1 DLL Fabm1 August 22 23 To 25 26Cristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- Managing Tools ActivityDocument3 pagesManaging Tools ActivityCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Tools in Managing ReceivablesDocument2 pagesQuiz in Tools in Managing ReceivablesCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- Pre-Immersion PPT ClassDocument14 pagesPre-Immersion PPT ClassCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- W1 NotesDocument2 pagesW1 NotesCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- W4.2BF WorksheetsDocument6 pagesW4.2BF WorksheetsCristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- Name of Applicant: Name of Applicant:: Criteria 1 2 3 4 5 Criteria 1 2 3 4 5Document1 pageName of Applicant: Name of Applicant:: Criteria 1 2 3 4 5 Criteria 1 2 3 4 5Cristelyn TomasNo ratings yet
- Data Pricing Edmund Lee PDFDocument41 pagesData Pricing Edmund Lee PDFAmit Bisai100% (1)
- Muddy Waters Capital LLC: Director of Research: Carson C. BlockDocument34 pagesMuddy Waters Capital LLC: Director of Research: Carson C. BlockYash BhojwaniNo ratings yet
- A Study On Goodwill and Its Treatments in Accounting: Assoc. Prof. Manh Dung TranDocument9 pagesA Study On Goodwill and Its Treatments in Accounting: Assoc. Prof. Manh Dung TranThe IjbmtNo ratings yet
- CEILLI Sample Questions - Set 1 (ENG)Document13 pagesCEILLI Sample Questions - Set 1 (ENG)Premkumar NadarajanNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Principles Real Estate: An Introduction To The ProfessionDocument11 pagesReal Estate Principles Real Estate: An Introduction To The Professiondenden007No ratings yet
- EE40 Homework 1Document2 pagesEE40 Homework 1delacruzrae12No ratings yet
- Unit I - EXIM PolicyDocument30 pagesUnit I - EXIM Policypiyush khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Mock BarDocument3 pagesMock BarAe-cha Nae GukNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Behavioral Finance and Technical Analysis: Problem SetsDocument13 pagesChapter 12: Behavioral Finance and Technical Analysis: Problem SetsBiloni Kadakia100% (1)
- Teaching Accounting Ethics: A Thought ExperimentDocument23 pagesTeaching Accounting Ethics: A Thought ExperimentMuchai PeterNo ratings yet
- SMEDA Fabric Dyeing & Finishing Unit (Knit Fabric)Document27 pagesSMEDA Fabric Dyeing & Finishing Unit (Knit Fabric)Nisar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Prepare A Business PlanDocument36 pagesPrepare A Business PlanDewi Nurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Sap Fico Complete End User ManualDocument374 pagesSap Fico Complete End User ManualAsma Jamshaid100% (3)
- OMI (Actiuni ETF) Tabel de Specificatii - 121020 PDFDocument81 pagesOMI (Actiuni ETF) Tabel de Specificatii - 121020 PDFCiprian AndriciNo ratings yet
- Philippine Real Estate Market 3Q 2012Document14 pagesPhilippine Real Estate Market 3Q 2012joni_p9mNo ratings yet
- Test - 6 (Mock Test - 6) 03-Sep-17Document71 pagesTest - 6 (Mock Test - 6) 03-Sep-17VEDNo ratings yet
- 02 Assignment Abroad Times NewspaperDocument5 pages02 Assignment Abroad Times NewspaperDHANANJAY PAWARNo ratings yet
- Second Semester 2020 Second Year University of Assuit Faculty of Commerce English Program " Corporation" "Test Bank"Document10 pagesSecond Semester 2020 Second Year University of Assuit Faculty of Commerce English Program " Corporation" "Test Bank"Magdy KamelNo ratings yet
- DavyDocument8 pagesDavyAhmedRiaz64No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - CorporationDocument8 pagesChapter 6 - CorporationNyah MallariNo ratings yet
- Al Anwar Ceramic Tiles Company SAOGDocument11 pagesAl Anwar Ceramic Tiles Company SAOGAnila AslamNo ratings yet
- StartupFunnelModel Basic v3Document8 pagesStartupFunnelModel Basic v3Anil Kumar PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Role of Icici As A Financial Institution and Its Function in The Insurance SectorDocument40 pagesRole of Icici As A Financial Institution and Its Function in The Insurance SectorKanika KanodiaNo ratings yet
- ZenithOptimedia AdEx Forecasts 2017Document207 pagesZenithOptimedia AdEx Forecasts 2017Nasim JamesNo ratings yet
- MS - Draft IA Report - Q2Document66 pagesMS - Draft IA Report - Q2Christen CastilloNo ratings yet
- Investor Demand For Sell-Side Research: Lawrence@haas - Berkeley.eduDocument57 pagesInvestor Demand For Sell-Side Research: Lawrence@haas - Berkeley.eduBhuwanNo ratings yet
- PRELIMSDocument4 pagesPRELIMSJadon MejiaNo ratings yet
- Puc 6004 BuyDocument16 pagesPuc 6004 BuyJuanNo ratings yet
- 1 DeBeers ExerciseDocument5 pages1 DeBeers Exercisemosafer0% (1)
- Kanrich PDFDocument20 pagesKanrich PDFRandora LkNo ratings yet