Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gross Anatomy: Endos
Uploaded by
jellOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gross Anatomy: Endos
Uploaded by
jellCopyright:
Available Formats
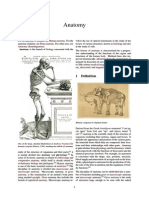
Anatomy is the identification and description of the structures of living things.
It is a branch of
biology and medicine.
The study of anatomy goes back over 2,000 years, to the Ancient Greeks. It can be divided into
three broad areas: Human anatomy, zootomy, or animal anatomy, and phytotomy, which is plant
anatomy.
Human anatomy is the study of the structures of the human body. An understanding of anatomy
is key to the practice of health and medicine.
The word “anatomy” comes from the Greek words “ana,” meaning “up,” and “tome,” meaning
“a cutting.” Studies of anatomy have traditionally depended on cutting up, or dissection, but
now, with imaging technology, it is increasingly possible to see how a body is made up without
dissection.
There are two ways of looking at anatomy: Gross, or macroscopic, anatomy and microscopic
anatomy.
Gross anatomy
In medicine, gross anatomy, macro anatomy, or topographical anatomy refers to the study of the
biological structures that are visible to the naked eye.
The study of gross anatomy may involve dissection or noninvasive methods. The aim is to
collect data about the larger structures of organs and organ systems.
In dissection, the scientist cuts open the human or animal cadaver is cut open and examines its
organs.
Endoscopy, inserting a tube with a camera at the end, might be used to study structures within
living animals. Endoscopy is performed either through the mouth or through the rectum, so the
gastrointestinal tract is often the primary organ of interest.
There are also less invasive methods. For example, to study the blood
You might also like
- What is Anatomy? The Study of Living StructuresDocument1 pageWhat is Anatomy? The Study of Living StructuresNeil DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Is The Identification and Description of The Structures of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesAnatomy Is The Identification and Description of The Structures of Living Thingsczenea velasquezNo ratings yet
- Study Anatomy Structure Human BodyDocument1 pageStudy Anatomy Structure Human BodyReina LuartezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, "Dissection") Is The Branch ofDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, "Dissection") Is The Branch ofankamraojNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Anatomē Anatémnō Aná TémnōDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Anatomē Anatémnō Aná TémnōsylNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and Physiology HandoutDocument9 pagesBasic Anatomy and Physiology HandoutKhenfred Emerald AlaroNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyMason PeinNo ratings yet
- Med 6Document3 pagesMed 6Lef RJNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - A brie-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesAnatomy - A brie-WPS OfficeGlay Cabañero TacanayNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyRom Yu NasolNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With TheDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With TheMarvin Espenocilla EspeñoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch ofDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch ofTrasnea IonutNo ratings yet
- Subjects and Topics in Basic Medical Science: A Imhotep Virtual Medical School PrimerDocument168 pagesSubjects and Topics in Basic Medical Science: A Imhotep Virtual Medical School PrimerMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (3)
- Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesHuman AnatomyaprilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMakhanVermaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyJez VaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDeane Marc TorioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To AnatomyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyGhh TyuNo ratings yet
- GenBio AnatomyDocument2 pagesGenBio AnatomyReniel V. Broncate (REHNIL)No ratings yet
- ANATOMY20230Document39 pagesANATOMY20230Ruben ToralloNo ratings yet
- Greek Organisms Tissues: A Dissected Body, Lying Prone On A Table, byDocument1 pageGreek Organisms Tissues: A Dissected Body, Lying Prone On A Table, byrajan civilNo ratings yet
- NewDocument1 pageNewAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To PhysiologyDocument6 pagesA Brief Introduction To PhysiologyGlay Cabañero TacanayNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document1 pageTopic 1PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Health Science Tool Kit Text BookDocument278 pagesHealth Science Tool Kit Text BookAidan Glasby100% (1)
- Anatomy Research PaperDocument4 pagesAnatomy Research PaperReina LuartezNo ratings yet
- Reflection About Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesReflection About Anatomy and PhysiologyMirasol CatadmanNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument16 pagesAnatomywakhalewakhaleNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesHuman AnatomyYhamNo ratings yet
- 444Document2 pages444Jonee SansomNo ratings yet
- Seven Organizational Approaches PaperDocument3 pagesSeven Organizational Approaches Paperavid_christinaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Is Primarily The Scientific Study of The Morphology of The Adult Human BodyDocument1 pageHuman Anatomy Is Primarily The Scientific Study of The Morphology of The Adult Human BodypowerleaderNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - IntroductionDocument31 pagesTopic 1 - Introductionmalakz376No ratings yet
- An Overview of Gross AnatomyDocument4 pagesAn Overview of Gross AnatomyMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Body SystemsDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Body SystemsEdron Bullo JrNo ratings yet
- Planes, Landmarks, Directions, Quadrants & Regions AnatomyDocument6 pagesPlanes, Landmarks, Directions, Quadrants & Regions AnatomyShane GempasaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyBibi Hayath AnamNo ratings yet
- Historia de La AnatomíaDocument13 pagesHistoria de La AnatomíaPaolo MafaldoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 1 (Introduction)Document13 pagesAnatomy Lec 1 (Introduction)abdulsaboor30No ratings yet
- Anatomy PhysiologyDocument213 pagesAnatomy PhysiologysyedshanNo ratings yet
- 3 - History and Scope of Anatomy in MedicineDocument28 pages3 - History and Scope of Anatomy in MedicinehNo ratings yet
- DR - Khin Myo Thu Faculty Perubatan UitmDocument19 pagesDR - Khin Myo Thu Faculty Perubatan UitmAshbirZammeriNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument30 pagesBiologyChristel Ramos100% (1)
- 2 basic approach to study anatomy Systemic anatomy 》Is the study of the body by systemDocument3 pages2 basic approach to study anatomy Systemic anatomy 》Is the study of the body by systemKatherineNo ratings yet
- All Branches of BiologyDocument31 pagesAll Branches of BiologyYhan Brotamonte Boneo100% (1)
- Aldwin A. Yaneza, MD Course Director. Gross AnatomyDocument40 pagesAldwin A. Yaneza, MD Course Director. Gross AnatomyfilchibuffNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument2 pagesEnglishGeorge ZdocaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Cza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Basics of Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument110 pagesBasics of Anatomy & PhysiologyDurga Prasad P80% (5)
- Anatomy 11th SeptDocument3 pagesAnatomy 11th SeptShreeraj BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: 1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesAnatomy: 1 DefinitionMeghan LangNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Human AnatomyDocument21 pagesIntroduction to Human AnatomyHasin's QueenNo ratings yet
- What Is Physiology? History Biological Systems Branches Physiology or Anatomy?Document2 pagesWhat Is Physiology? History Biological Systems Branches Physiology or Anatomy?exo oxeNo ratings yet
- 30-Second Anatomy: The 50 most important structures and systems in the human body each explained in under half a minuteFrom Everand30-Second Anatomy: The 50 most important structures and systems in the human body each explained in under half a minuteRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyPramisshila Nurnatasha Abd SamatNo ratings yet
- Topic: AnatomyDocument10 pagesTopic: AnatomyTess TessNo ratings yet
- Graduate Studies Butuan CityDocument1 pageGraduate Studies Butuan CityMaria Alyssa Antoniette NaranjoNo ratings yet
- T2021Document23 pagesT2021Jaden CalumbaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Systems: TraditionalDocument15 pagesManufacturing Systems: TraditionaljellNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Systems: TraditionalDocument15 pagesManufacturing Systems: TraditionaljellNo ratings yet
- Receipt of Bill Payment: Shopee Order IDDocument1 pageReceipt of Bill Payment: Shopee Order IDjellNo ratings yet
- Excise Taxes: Purposes of Excise TaxDocument9 pagesExcise Taxes: Purposes of Excise TaxjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 deductions guideDocument13 pagesChapter 13 deductions guidejellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Regular Income Tax: Inclusions in Gross IncomeDocument4 pagesChapter 9 - Regular Income Tax: Inclusions in Gross IncomejellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Compensation IncomeDocument5 pagesChapter 10 - Compensation IncomejellNo ratings yet
- Donors TaxDocument12 pagesDonors TaxjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Income Tax Schemes, Accounting Periods, Methods, & ReportingDocument3 pagesChapter 4 - Income Tax Schemes, Accounting Periods, Methods, & ReportingjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Fringe Benefit TaxDocument3 pagesChapter 11 - Fringe Benefit TaxjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Dealings in PropertiesDocument3 pagesChapter 12 - Dealings in PropertiesjellNo ratings yet
- Nation Philippines: Basic Demographic DescriptionDocument1 pageNation Philippines: Basic Demographic DescriptionjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Compensation IncomeDocument5 pagesChapter 10 - Compensation IncomejellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Introduction To Regular Income TaxDocument3 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To Regular Income TaxjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Capital Gains TaxationDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Capital Gains TaxationjellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Regular Income Tax: Exclusions From Gross IncomeDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Regular Income Tax: Exclusions From Gross IncomejellNo ratings yet
- Nation Philippines: Basic Demographic DescriptionDocument1 pageNation Philippines: Basic Demographic DescriptionjellNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation: Laws, Principles and Applications Solution Manual Rex Banggawan 2017 EditionDocument4 pagesIncome Taxation: Laws, Principles and Applications Solution Manual Rex Banggawan 2017 EditionjellNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentLucille MunozNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Introduction To Income TaxationDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Introduction To Income TaxationjellNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument1 pagePhysiologyjellNo ratings yet
- Financial ApplicationsDocument4 pagesFinancial ApplicationsjellNo ratings yet
- Types of Nouns and How to Form Plural NounsDocument3 pagesTypes of Nouns and How to Form Plural NounsjellNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument1 pageHuman BodyjellNo ratings yet
- Cframework Quiz1Document1 pageCframework Quiz1jellNo ratings yet
- Social Dances and Dance MixersDocument27 pagesSocial Dances and Dance Mixersjell100% (6)
- Module 1 Noun Subject Predicate: What Is A Verb?Document2 pagesModule 1 Noun Subject Predicate: What Is A Verb?jellNo ratings yet
- How to use personal pronouns correctlyDocument3 pagesHow to use personal pronouns correctlyjellNo ratings yet