Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osha3903 PDF
Uploaded by
getz_me0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesOriginal Title
OSHA3903.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesOsha3903 PDF
Uploaded by
getz_meCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
FactSheet
OSHA’s Final Rule to Update, Align, and Provide
Greater Flexibility in its General Industry Walking-
Working Surfaces and Fall Protection Standards
Background For example, the final rule replaces the outdated
Falls from heights and on the same level (a general industry scaffold standards with a
working surface) are among the leading causes requirement that employers comply with OSHA’s
of serious work-related injuries and deaths. construction scaffold standards.
OSHA estimates that, on average, approximately
The rule phases out a 1993 exception for
202,066 serious (lost-workday) injuries and 345
the outdoor advertising industry that allows
fatalities occur annually among workers directly
“qualified climbers” to forego fall protection.
affected by the final standard. OSHA’s final rule
At least three workers have fallen from fixed
on Walking-Working Surfaces and Personal Fall
ladders under this exception. One of them
Protection Systems better protects workers in
died. The final rule phases in the fixed ladder
general industry from these hazards by updating
fall protection requirements for employers in
and clarifying standards and adding training
outdoor advertising.
and inspection requirements. The rule affects a
wide range of workers, from window washers to Fall Protection Options
chimney sweeps. It does not change construction The rule requires employers to protect workers
or agricultural standards. from fall hazards along unprotected sides or
The rule incorporates advances in technology, edges that are at least 4 feet above a lower
industry best practices, and national consensus level. It also sets requirements for fall protection
standards to provide effective and cost-efficient in specific situations, such as hoist areas,
worker protection. Specifically, the rule updates runways, areas above dangerous equipment,
general industry standards addressing slip, trip, and wall openings, repair pits, stairways, scaffolds,
fall hazards (subpart D), and adds requirements for and slaughtering platforms. And it establishes
personal fall protection systems (subpart I). requirements for the performance, inspection,
use, and maintenance of personal fall protection
OSHA estimates this rule will prevent 29 fatalities systems.
and 5,842 lost-workday injuries every year.
OSHA defines fall protection as “any equipment,
The rule benefits employers by providing greater device, or system that prevents a worker from
flexibility in choosing a fall protection system. For falling from an elevation or mitigates the effect of
example, it eliminates the existing mandate to use such a fall.” Under the final rule, employers may
guardrails as a primary fall protection method and choose from the following fall protection options:
allows employers to choose from accepted fall
protection systems they believe will work best in a • Guardrail System – A barrier erected along an
particular situation — an approach that has been unprotected or exposed side, edge, or other
successful in the construction industry since 1994. area of a walking-working surface to prevent
In addition, employers will be able to use non- workers from falling to a lower level.
conventional fall protection in certain situations, • Safety Net System – A horizontal or semi-
such as designated areas on low-slope roofs. horizontal, cantilever-style barrier that uses
a netting system to stop falling workers
As much as possible, OSHA aligned fall before they make contact with a lower level
protection requirements for general industry with or obstruction.
those for construction, easing compliance for • Personal Fall Arrest System – A system that
employers who perform both types of activities.
arrests/stops a fall before the worker contacts as well as mobile ladder stands and platforms. (The
a lower level. Consists of a body harness, ladder requirements do not apply to ladders used
anchorage, and connector, and may include in emergency operations or ladders that are an
a lanyard, deceleration device, lifeline, or a integral part of or designed into a machine or piece
suitable combination. Like OSHA’s construction of equipment).
standards, the final rule prohibits the use of body
In general, ladders must be capable of supporting
belts as part of a personal fall arrest system.
their maximum intended load, while mobile
• Positioning System – A system of equipment
ladder stands and platforms must be capable of
and connectors that, when used with a body
supporting four times their maximum intended
harness or body belt, allows a worker to be
load. Each ladder must be inspected before initial
supported on an elevated vertical surface,
use in a work shift to identify defects that could
such as a wall or window sill, and work with
cause injury.
both hands free.
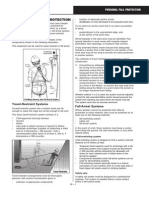
• Travel Restraint System – A combination of Fixed Ladders – Fixed ladders are permanently
an anchorage, anchorage connector, lanyard attached to a structure, building, or equipment.
(or other means of connection), and body These include individual-rung ladders, but not
support to eliminate the possibility of a worker ship stairs, step bolts, or manhole steps. The new
going over the unprotected edge or side of a rule phases in a requirement for employers to
walking-working surface. have ladder safety or personal fall arrest systems
• Ladder Safety System – A system attached to for fixed ladders that extend more than 24 feet,
a fixed ladder designed to eliminate or reduce and phases out the use of cages or wells for fall
the possibility of a worker falling off the ladder. protection under the following timeline: Starting in
A ladder safety system usually consists of two years, all new fixed ladders and replacement
a carrier, safety sleeve, lanyard, connectors, ladder/ladder sections must have a ladder safety
and body harness. Cages and wells are not or personal fall protection system. For existing
considered ladder safety systems. ladders, within two years, employers must install
a cage, well, ladder safety system, or personal fall
Rope Descent Systems arrest system on fixed ladders that do not have
The rule codifies a 1991 OSHA memorandum any fall protection. Within 20 years, all ladders
that permits employers to use Rope Descent extending more than 24 feet must have a ladder
Systems (RDS), which consist of a roof safety or personal fall arrest system.
anchorage, support rope, descent device,
carabiners or shackles, and a chair or seatboard. Portable Ladders – Portable ladders usually consist
These systems are widely used throughout of side rails joined at intervals by steps, rungs,
the country to perform elevated work, such as or cleats. They can be self-supporting or lean
window washing. against a supporting structure. The final rule will
be easier for employers and workers to understand
The rule adds a 300-foot height limit for the use of and follow because it uses flexible performance-
RDS. It also requires building owners to affirm in based language instead of detailed specification
writing that permanent building anchorages used and design requirements. Under the revisions,
for RDS have been tested, certified, and maintained employers must ensure that: rungs and steps are
as capable of supporting 5,000 pounds for each slip resistant; portable ladders used on slippery
worker attached. This mirrors the requirement in surfaces are secured and stabilized; portable ladders
OSHA’s Powered Platforms standard. are not moved, shifted, or extended while a worker
is on them; top steps and caps of stepladders are
Ladder Safety Requirements
not used as steps; ladders are not fastened together
Falls from ladders account for 20 percent of all to provide added length unless designed for such
fatal and lost work-day injuries in general industry. use; and ladders are not placed on boxes, barrels, or
The new rule includes requirements to protect other unstable bases to obtain added height.
workers from falling off fixed and portable ladders
Training Requirements
The rule adds a requirement that employers ensure • Installing personal fall arrest or ladder safety
workers who use personal fall protection and work systems on new fixed ladders over 24 feet and on
in other specified high hazard situations are trained, replacement ladders/ladder sections, including fixed
and retrained as necessary, about fall and equipment ladders on outdoor advertising structures (2 years),
hazards, including fall protection systems. A qualified • Ensuring existing fixed ladders over 24 feet,
person must train these workers to correctly: identify including those on outdoor advertising structures,
and minimize fall hazards; use personal fall protection are equipped with a cage, well, personal fall arrest
systems and rope descent systems; and maintain, system, or ladder safety system (2 years), and
inspect, and store equipment or systems used for • Replacing cages and wells (used as fall protection)
fall protection. with ladder safety or personal fall arrest systems on
all fixed ladders over 24 feet (20 years).
When there is a change in workplace operations or
equipment, or the employer believes that a worker Additional information
would benefit from additional training based on a Additional information on OSHA’s rule on walking-
lack of knowledge or skill, then the worker must be working surfaces and personal fall protection systems
retrained. The training must be provided in a language can be found at www.osha.gov/walking-working-
and vocabulary that workers understand. surfaces. OSHA can provide extensive help through
a variety of programs, including technical assistance
Timeline
about effective safety and health programs, workplace
Most of the rule will become effective 60 days after it is
consultations, and training and education.
published in the Federal Register, but some provisions
have delayed effective dates, including: For more information on other safety-related issues
impacting workers, to report an emergency, fatality,
• Ensuring exposed workers are trained on fall hazards
inpatient hospitalization, or to file a confidential
(6 months),
complaint, contact your nearest OSHA office, visit
• Ensuring workers who use equipment covered by
www.osha.gov, or call OSHA at 1-800-321-OSHA (6742),
the final rule are trained (6 months),
TTY 1-877-889-5627.
• Inspecting and certifying permanent anchorages for
rope descent systems (1 year),
This is one in a series of informational fact sheets highlighting OSHA programs, policies or
standards. It does not impose any new compliance requirements. For a comprehensive list of
compliance requirements of OSHA standards or regulations, refer to Title 29 of the Code of Federal
Regulations. This information will be made available to sensory-impaired individuals upon request.
The voice phone is (202) 693-1999; teletypewriter (TTY) number: (877) 889-5627.
DSG FS-3903 11/2016
You might also like
- Fall Protection PolicyDocument17 pagesFall Protection PolicymuhammadkashikNo ratings yet
- Sir Gelena ReportDocument16 pagesSir Gelena ReportReinier VisayanaNo ratings yet
- 19 Personal Fall Protection: Travel-Restraint Systems Fall-Arrest SystemsDocument6 pages19 Personal Fall Protection: Travel-Restraint Systems Fall-Arrest SystemsStill SatNo ratings yet
- Sheet: Reducing Falls During Residential Construction: Working in AtticsDocument3 pagesSheet: Reducing Falls During Residential Construction: Working in AtticsbsiofncNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guidelines For Working at Height in New ZealandDocument25 pagesBest Practice Guidelines For Working at Height in New ZealandPerwez21No ratings yet
- Fall ProtectionDocument24 pagesFall Protectionmdfahad0047No ratings yet
- Fall Protection Plan 2016 V 1Document19 pagesFall Protection Plan 2016 V 1Zeeshan AbbasiNo ratings yet
- 28 - Scaffolding ProceduresDocument17 pages28 - Scaffolding ProceduresLalit Tomar100% (1)
- 29 CFR PART 1926 Subpart M Fall ProtectionDocument43 pages29 CFR PART 1926 Subpart M Fall ProtectionAls اي AlsNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection PDFDocument6 pagesFall Protection PDFheitormartNo ratings yet
- Working at Heights - Harmonized - PolicyDocument15 pagesWorking at Heights - Harmonized - Policymohamed ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection Program: University of Wisconsin-Platteville Reviewed 4/2016Document10 pagesFall Protection Program: University of Wisconsin-Platteville Reviewed 4/2016i.kamalNo ratings yet
- Fall ProtectionDocument4 pagesFall ProtectionnainaNo ratings yet
- Reducing Falls Installing Roof Trusses FactsheetDocument4 pagesReducing Falls Installing Roof Trusses FactsheetvovobossNo ratings yet
- Guidelines PPEDocument25 pagesGuidelines PPE88sanNo ratings yet
- ARTBA Fall Fact Sheet TechAdvice Bridge Construction-508Document148 pagesARTBA Fall Fact Sheet TechAdvice Bridge Construction-508JhayNo ratings yet
- Working On HeightsDocument13 pagesWorking On HeightsRutuja ShikhareNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX 3 Use of Safety Harnesses and Running Line SystemsDocument2 pagesAPPENDIX 3 Use of Safety Harnesses and Running Line SystemsJulianna BakerNo ratings yet
- FallDocument1 pageFallAldrien CabinteNo ratings yet
- Working at Heights ManualDocument20 pagesWorking at Heights Manual1qazxcvbnmko098100% (1)
- Life Lines RequirementsDocument2 pagesLife Lines RequirementsAnsarMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection Orientation Refresher - FN000304Document68 pagesFall Protection Orientation Refresher - FN000304Predrag AndjelkovicNo ratings yet
- Safety Management - Module2Document27 pagesSafety Management - Module2Atienza ArjayNo ratings yet
- Life LineDocument10 pagesLife LineMukdad Al KaabiNo ratings yet
- Fy14 SH 26317 Sh4 StudentHandouts EnglishDocument20 pagesFy14 SH 26317 Sh4 StudentHandouts EnglishKatherineNo ratings yet
- PA Working at Heights PrimerDocument52 pagesPA Working at Heights PrimerkumhotriNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection PlanDocument15 pagesFall Protection PlanMuhammad Usman67% (3)
- Fall Protection Guideline: Construction Safety Education ProgramDocument17 pagesFall Protection Guideline: Construction Safety Education ProgramhazopmanNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection TrainingDocument48 pagesFall Protection Trainingazia100% (1)
- Fall ProtectionDocument34 pagesFall Protectionneo_chemistNo ratings yet
- (En) ManSafe For IndustryDocument8 pages(En) ManSafe For IndustryTey Chin WeiNo ratings yet
- Roof Safety C/o OSHADocument4 pagesRoof Safety C/o OSHAAlejo Raquel Jr.No ratings yet
- Mobile Aerial Platform Training Book - 2014Document193 pagesMobile Aerial Platform Training Book - 2014Alberth Mauricio Casteblanco GomezNo ratings yet
- Roof AtticDocument7 pagesRoof AtticrnarantsatsraltNo ratings yet
- SG16-14 Management of Fall Protection EquipmentDocument8 pagesSG16-14 Management of Fall Protection EquipmentMohammed HafizNo ratings yet
- Fall ProtectionDocument14 pagesFall ProtectionRajNo ratings yet
- Osha3722 PDFDocument2 pagesOsha3722 PDFTharaka Perera100% (1)
- Factsheet: Roof Tarping (Blue Roof) SafetyDocument2 pagesFactsheet: Roof Tarping (Blue Roof) SafetyIndermohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Student Reference MaterialsDocument31 pagesStudent Reference Materialsတိုး ေဝ ေအာင္No ratings yet
- SWP06 MSW WorkatHeight ChevronDocument34 pagesSWP06 MSW WorkatHeight Chevronpriyanta100% (1)
- Slip, Trips Personal - Fall - Arrest - SystemsDocument7 pagesSlip, Trips Personal - Fall - Arrest - SystemsRëy PañaresNo ratings yet
- Safe Operating Procedure: (Revised 4/19) Personal Fall Arrest SystemsDocument7 pagesSafe Operating Procedure: (Revised 4/19) Personal Fall Arrest SystemsUlviyye ElesgerovaNo ratings yet
- Fall ProtectionDocument8 pagesFall ProtectionTiago FernandesNo ratings yet
- Fall Protection DefinitionsDocument5 pagesFall Protection DefinitionsalphadingNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.2-Scaffold Safety RulesDocument3 pagesLESSON 2.2-Scaffold Safety RulesFelamae BaynosaNo ratings yet
- Fall ProtectionDocument17 pagesFall ProtectionCh Azeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Guide Suspended Swing Stage ScaffoldsDocument14 pagesGuide Suspended Swing Stage Scaffoldsahmed rafeeq100% (1)
- Fall Protection ANSIDocument5 pagesFall Protection ANSIsejudavisNo ratings yet
- Index: Cv. Dira Utama SejahteraDocument12 pagesIndex: Cv. Dira Utama SejahteraFreshop SurabayaNo ratings yet
- Guia Quedas 2Document93 pagesGuia Quedas 2hazopmanNo ratings yet
- The University of Chicago: Environmental Health & SafetyDocument7 pagesThe University of Chicago: Environmental Health & Safetykisan singhNo ratings yet
- G FG Code of PracticeDocument16 pagesG FG Code of PracticeAnonymous GfPSYi4nNo ratings yet
- SG29 - Internal Edge Protection On Scaffold PlatformsDocument2 pagesSG29 - Internal Edge Protection On Scaffold PlatformsAnupam GhoshNo ratings yet
- Osh 29 CFR 1910 Subpart DDocument39 pagesOsh 29 CFR 1910 Subpart DAnonymous I8nZsDqlmhNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Fall Arrest SystemsDocument6 pagesHorizontal Fall Arrest SystemsAchraf HosniNo ratings yet
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationFrom EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Residential Asphalt Roofing Manual Design and Application Methods 2014 EditionFrom EverandResidential Asphalt Roofing Manual Design and Application Methods 2014 EditionNo ratings yet
- AP-NozzleTutorial R01 PDFDocument31 pagesAP-NozzleTutorial R01 PDFbalumagesh1979No ratings yet
- Astm b622 10Document6 pagesAstm b622 10getz_meNo ratings yet
- Insulation Pins Install 512IGDocument4 pagesInsulation Pins Install 512IGgetz_meNo ratings yet
- Welded Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Pipe: Standard Specification ForDocument5 pagesWelded Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Pipe: Standard Specification ForZouhair BoukriNo ratings yet
- Survey of Insulation Used in Nuclear Power Plants and The Potential For Debris GenerationDocument117 pagesSurvey of Insulation Used in Nuclear Power Plants and The Potential For Debris Generationgetz_meNo ratings yet
- KC CottrellDocument47 pagesKC CottrellAnindya Paul Chowdhury100% (1)
- Clean - Copy - LiftingLugStress - 4 - Points - Rev - 1 - 5Document11 pagesClean - Copy - LiftingLugStress - 4 - Points - Rev - 1 - 5Hansen A JamesNo ratings yet
- Adobe PDF: Create Bookmark ReportDocument6 pagesAdobe PDF: Create Bookmark ReportachyNo ratings yet
- QHelp Pipe Weight CalculatorDocument2 pagesQHelp Pipe Weight Calculatoryaqub1979No ratings yet
- Lug Design R4Document4 pagesLug Design R4Esapermana RiyanNo ratings yet
- Pipe Reducer StandardDocument3 pagesPipe Reducer StandardSyifa Alfi HabibiNo ratings yet
- Honey Well Limit SwitchDocument1 pageHoney Well Limit Switchgetz_meNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Ebook PDFDocument22 pagesCovid 19 Ebook PDFRabi Sankar SahaNo ratings yet
- PipeHanger Feb18Document300 pagesPipeHanger Feb18Babu SundararamanNo ratings yet
- Diversified Fall Protection Guide OSHA Updates Slips Trips FallsDocument159 pagesDiversified Fall Protection Guide OSHA Updates Slips Trips FallsHomer SilvaNo ratings yet
- Auto-Highlight The Active Row When A Cell Is Selected - Excel Dashboards VBA and MoreDocument6 pagesAuto-Highlight The Active Row When A Cell Is Selected - Excel Dashboards VBA and Moregetz_meNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide To Metric Nuts and BoltsDocument10 pagesA Short Guide To Metric Nuts and BoltsSandra FerrellNo ratings yet
- Valve Flow and SizingDocument5 pagesValve Flow and Sizinggetz_meNo ratings yet
- Engineering Standards Manual ISD 341-2 Chapter 13, Welding & Joining Section WFP 2-09 - Welding Fabrication ProcedureDocument2 pagesEngineering Standards Manual ISD 341-2 Chapter 13, Welding & Joining Section WFP 2-09 - Welding Fabrication Proceduregetz_meNo ratings yet
- Article - Metric System & SpecificationsDocument5 pagesArticle - Metric System & Specificationsjchristoe2613No ratings yet
- 2 Page Monthly PlannerDocument31 pages2 Page Monthly Plannergetz_meNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide To Metric Nuts and BoltsDocument10 pagesA Short Guide To Metric Nuts and BoltsSandra FerrellNo ratings yet
- Valve Basics and Valve SizingDocument32 pagesValve Basics and Valve SizingDouglas Booyens100% (2)
- Branch Reinforcement: D D T T Tr c P E S Y β L d d t t A A A t ADocument2 pagesBranch Reinforcement: D D T T Tr c P E S Y β L d d t t A A A t Agetz_meNo ratings yet
- Material Equivalent TableDocument8 pagesMaterial Equivalent Tableprashantpan1776% (21)
- Form 6Document4 pagesForm 6tceterexNo ratings yet
- WFP 2-15-Att-1-R1 PDFDocument2 pagesWFP 2-15-Att-1-R1 PDFgetz_meNo ratings yet
- ASME Flange & PN RatingDocument7 pagesASME Flange & PN Ratinggetz_meNo ratings yet
- 3g Plans PrepayDocument2 pages3g Plans Prepaygetz_meNo ratings yet
- Medical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.: Notes From The Association ofDocument4 pagesMedical School Pediatric Department Chairs, Inc.: Notes From The Association ofChristian NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Doghouse BluesDocument6 pagesDoghouse Bluesnno067959No ratings yet
- Macrobiotic DietDocument2 pagesMacrobiotic DietMarcio AurélioNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManagementDocument6 pagesLaboratory ManagementJamille CarayuganNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 14 A0 Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument3 pagesHttps Doc 14 A0 Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Write A Toefl Essay About If You Preffer Virtual Classes or PresencialDocument5 pagesWrite A Toefl Essay About If You Preffer Virtual Classes or PresencialCarlos RoldanNo ratings yet
- 2016 PJC J1 H1 EOY ExamDocument5 pages2016 PJC J1 H1 EOY ExamTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-PSQ PSQ 1Document6 pagesChapter-PSQ PSQ 1balaji srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation 160410175058 PDFDocument37 pagesNewmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation 160410175058 PDFDevrathNo ratings yet
- Investigation The Effective of The Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determining Control (HIRADC) in Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 pagesInvestigation The Effective of The Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determining Control (HIRADC) in Manufacturing ProcessJames Laurence RavizNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Educ PDFDocument12 pagesInclusive Educ PDFHannahNo ratings yet
- Wound Care ChecklistDocument5 pagesWound Care ChecklistAngela Nicole MarcosNo ratings yet
- PATHFit2 Presentation - KTS (1) - 1 PDFDocument23 pagesPATHFit2 Presentation - KTS (1) - 1 PDFArenNo ratings yet
- Mrs - Jagadeeswari.J M.SC NursingDocument13 pagesMrs - Jagadeeswari.J M.SC NursingBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Finals Histo Lab - EDLAY2ADocument2 pagesActivity 2 Finals Histo Lab - EDLAY2ATom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing IntensiveDocument75 pagesOncology Nursing IntensiveVinsuiCzar BaylonNo ratings yet
- CSR Activities of Ultratech Cement LTD.: Submitted By: Aneesh Kumar (21MBMA80) Sreyas Sathees Babu (21MBMA81)Document8 pagesCSR Activities of Ultratech Cement LTD.: Submitted By: Aneesh Kumar (21MBMA80) Sreyas Sathees Babu (21MBMA81)SreyasNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDocument9 pagesHemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Rooms Division Area 5Document3 pagesRooms Division Area 5Hyne ValerioNo ratings yet
- Teaching P.E. and Health in The Elementary GradesDocument20 pagesTeaching P.E. and Health in The Elementary GradesTech VlogsNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Quality MetricsDocument10 pagesImprovement in Quality MetricsGodFather xNo ratings yet
- Davidovitch1995 PDFDocument6 pagesDavidovitch1995 PDFRahulLife'sNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-OMFS Interns 2020-Book Club (Corona Edition) PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 1-OMFS Interns 2020-Book Club (Corona Edition) PDFMGCNo ratings yet
- Paleco Safety PlanDocument17 pagesPaleco Safety PlanBobomo PoNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic Interventions (Management Therapy)Document5 pagesPsychotherapeutic Interventions (Management Therapy)Jenny Juniora AjocNo ratings yet
- Tele-Medicine: Presented by Shyam.s.s I Year M.SC NursingDocument12 pagesTele-Medicine: Presented by Shyam.s.s I Year M.SC NursingShyamNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- BookBit What Happened To You Oprah Winfrey Bruce PerryDocument2 pagesBookBit What Happened To You Oprah Winfrey Bruce Perrywacwic wydadNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Formula For Calculation of Global Hunger Index ScoresDocument1 pageStep 1: Formula For Calculation of Global Hunger Index ScoresSunday FiveNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument18 pagesResearch MethodologyAhmed Saleh100% (1)