Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isomerism PDF
Uploaded by
Erlin Elisabeth0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOriginal Title
8. Isomerism.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageIsomerism PDF
Uploaded by
Erlin ElisabethCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
413.
4 Exercise 2 – Isomerism
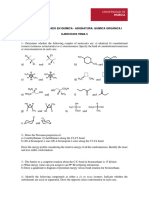
1. Draw all the possible structural isomers of C5H11Br (there are 8 in total). Label
the isomers A – H and name them.
a) Identify two molecules which are positional isomers.
b) Identify two molecules which are chain isomers.
c) Identify two molecules which are chiral and draw the two optical isomers
of each. Explain briefly how they could be distinguished.
2. Draw all the possible structural isomers of C5H10 which contain a double bond
(there are five in total). Label the isomers A – E and name them.
a) Identify two molecules which are positional isomers.
b) Identify two molecules which are chain isomers.
c) Identify one molecule which shows stereoisomerism, state the type of
stereoisomerism shown and draw and name the two stereoisomers.
d) Draw the structure of a molecule which is a functional isomer of all the
molecules A to E.
3.
a) Draw the two possible structures of a molecule with molecular formula
C4H8O2 and containing a carboxylic acid group. Name both of the
isomers.
b) Draw four possible structures of molecules with the same molecular
formula but containing a different functional group. Name the functional
group and the molecules containing it. What is the type of isomerism
shown between these molecules and the molecules drawn in 3 (a)?
4. a) Draw the structure of pentan-2-one
b) Draw a positional isomer of pentan-2-one
c) Draw a chain isomer of pentan-2-one
d) Draw a functional isomer of pentan-2-one (not an aldehyde)
5. State whether the following preparations will produce a racemate or a single
enantiomer:
a) butan-2-ol from but-2-ene
b) butan-2-ol from 2-bromobutane
c) 2-hydroxybutanenitrile from propanal
You might also like
- Test 4Document24 pagesTest 4TomNo ratings yet
- ChemX6X FinalDocument11 pagesChemX6X FinalPhương Nail TócNo ratings yet
- Chem Exam 4Document30 pagesChem Exam 4TomNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Optical Isomers)Document3 pagesTutorial 1 (Optical Isomers)Ahmed ZakyNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios - QO I T3Document5 pagesEjercicios - QO I T3dddddNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide JonesDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Study Guide Jonesdarkace00000No ratings yet
- CHEM1280 2011 Midterm Exam PDFDocument3 pagesCHEM1280 2011 Midterm Exam PDFLouisNo ratings yet
- OC Part B QuestionsDocument10 pagesOC Part B QuestionsSunanda 2004No ratings yet
- CML 100 Organic Chemistry (Tutorial 1) Answer These Following QuestionsDocument1 pageCML 100 Organic Chemistry (Tutorial 1) Answer These Following QuestionssatyamkumarmodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4 Goodie BagDocument29 pagesChemistry Unit 4 Goodie BagJacob Salkin100% (2)
- Chem 121 - Prob Set 1Document1 pageChem 121 - Prob Set 1Jayson FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Taller de ESTEREOQUIMICADocument6 pagesTaller de ESTEREOQUIMICAFrancisco Alejandro Rosero SeguraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1sylvieNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 Naming Practice QuestionsDocument33 pages3.1.1 Naming Practice QuestionsAyaan RaufNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Chemistry Chapter 12 Study MaterialDocument49 pages11th Class Chemistry Chapter 12 Study MaterialAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Neet Chemistry Notes-1Document37 pagesNeet Chemistry Notes-1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Ass.2 MayDocument4 pagesAss.2 Mays9n9No ratings yet
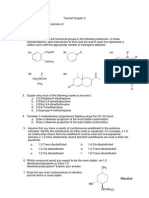
- Tutorial Chapter 3Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 3ShahrizatSmailKassimNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic ChemistrySamer EhabNo ratings yet
- CH 105Document3 pagesCH 105Rutul JainNo ratings yet
- Orgo 1 QuzzesDocument34 pagesOrgo 1 QuzzesDanny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Class X BAT 1 - CHEM 2ND 50% SLIP TEST-IIDocument2 pagesClass X BAT 1 - CHEM 2ND 50% SLIP TEST-IIphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 BLC F20Document2 pagesAssignment 1 BLC F20Rémi MartineauNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes QDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes Qlucylovesbooks6770No ratings yet
- Glance Through The Entire Questions and Solve The Easiest Problems FirstDocument4 pagesGlance Through The Entire Questions and Solve The Easiest Problems FirstRutul JainNo ratings yet
- Che 203 Cat 1Document1 pageChe 203 Cat 1KEVIN OMONDINo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Chapter 1: Introduction To Organic Chemistry: C C H CN H HDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 Chapter 1: Introduction To Organic Chemistry: C C H CN H HRAIN9393No ratings yet
- Kel 7 Chapter 5 StereochemistryDocument21 pagesKel 7 Chapter 5 StereochemistryFarid AkhechyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes - WorksheetDocument2 pagesAlkanes - WorksheetDoug GilmourNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5 PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Set 5 PDFLouisNo ratings yet
- Revision Booklet (5, S)Document33 pagesRevision Booklet (5, S)ashokNo ratings yet
- 2009 Intro Organic Chem Tutorial (Teachers)Document14 pages2009 Intro Organic Chem Tutorial (Teachers)Tommy Jing Jie NgNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument30 pagesIsomerismNorsyazaEdmiraNo ratings yet
- PYQs Chapter - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument6 pagesPYQs Chapter - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsSingh SahabNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry PDFDocument3 pagesStereochemistry PDFbencleese100% (1)
- 2015 Apr-Biochemistry & Physical ChemistryDocument2 pages2015 Apr-Biochemistry & Physical ChemistryD PrajnaNo ratings yet
- Fuel MoleculesDocument3 pagesFuel MoleculesPhillip CookNo ratings yet
- CHM 3201 Exp6Document8 pagesCHM 3201 Exp6ARMAN AKRAM BIN OMAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 2022 KEYDocument5 pagesExam 1 2022 KEYcody smithNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review Fall 2009 AnswersDocument14 pagesFinal Exam Review Fall 2009 AnswersCharisma SubaNo ratings yet
- Web Exam 3 Answers, Organic ChemistrtDocument6 pagesWeb Exam 3 Answers, Organic ChemistrtAshish Manatosh BarikNo ratings yet
- CHE1010 Chemical Bonding Tutorial Sheet 4Document3 pagesCHE1010 Chemical Bonding Tutorial Sheet 4Nicholas LukondeNo ratings yet
- ChemX6X MT 1Document8 pagesChemX6X MT 1Phương Nail TócNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 BLC F20Document3 pagesAssignment 2 BLC F20Rémi MartineauNo ratings yet
- Chem 112A Homework 1Document4 pagesChem 112A Homework 1Shyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument8 pagesStereochemistryAmalVijayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 6-7Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 6-7Azuana HalimNo ratings yet
- Assessments and Rubrics For Unit 2Document13 pagesAssessments and Rubrics For Unit 2api-302258576No ratings yet
- E4 StereoisomersDocument6 pagesE4 StereoisomersShaun Martel BantuganNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Glance Through The Entire Questions and Solve The Easiest Problems FirstDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Glance Through The Entire Questions and Solve The Easiest Problems FirstSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Organic Chemistry: Number 93 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument5 pagesIsomerism in Organic Chemistry: Number 93 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukslixsterNo ratings yet
- Organic Lab 1 (Theroectical)Document4 pagesOrganic Lab 1 (Theroectical)j234567No ratings yet
- Organic Lab 1 (Theroectical)Document4 pagesOrganic Lab 1 (Theroectical)j234567No ratings yet
- 11 GocDocument2 pages11 GocHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 15-24Document49 pagesChap 15-24Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CH1O3 Questions PDFDocument52 pagesCH1O3 Questions PDFPrince T MashandaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Exam 1 (Practice) Chem 237Document3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Exam 1 (Practice) Chem 237Ngoc Minh NgoNo ratings yet
- Q2 2022 OrgchemDocument2 pagesQ2 2022 OrgchemHazeljoyce AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Theory and Applications of the Empirical Valence Bond Approach: From Physical Chemistry to Chemical BiologyFrom EverandTheory and Applications of the Empirical Valence Bond Approach: From Physical Chemistry to Chemical BiologyFernanda DuarteNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationFrom EverandInfrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationNo ratings yet