Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TDDS Evaluation Methods
Uploaded by
IVLS AKCPOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TDDS Evaluation Methods
Uploaded by
IVLS AKCPCopyright:
Available Formats
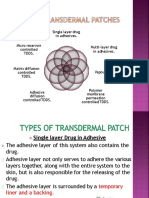
Evaluation of TDDS
Evaluation of adhesive:Pressure sensitive adhesives are evaluated for followingproperties.Peel adhesion properties:- Peel
adhesion is the force required to remove an adhesive coatingfrom a test substrate. It is important in transdermal device
because theadhesive should not damage the skin on removal. peel adhesionproperties are affected by the molecules
weight of the adhesive polymer,the type and amount of additives, and polymer composition.
• It is tested by measuring the force required to pull a single coated tape, applied to a substrate at a 1800C angle.• No
residue on the substrate indicates adhesive failure which is desirable for transdermal devices.• Remnants on all substrate
indicates ‘cohesive failure’ signifying a deficit of cohesive strength in the coating.
Shear Strength properties:• Shear strength is the measurement of cohesive strength of an adhesive polymer. Adequate
strength means device will not slip on application and will not leave any residue on removal. It is determined by
measuring the time it takes to pull an adhesive coated tape off a stainless steel plate, when a specified wt is hung from
the tape which pulls the tape in a direction parallel to the plate.
In vitro drug release evaluation:1.In vitro permeation kinetics studies can be performed on hairlessmouse skin or human
cadaver skin by using franz diffusion cell or tworeservoir diffusion cell.2.In two reservoir diffusion cells, sink conditions
can be maintained.3.The permeation of nitroglycerins across human cadaver and hairlessmouse skin from different
Transdermal Drug Delivery therapeuticsystem was compared for their kinetics.4.It was noted that the rates of skin
permeation generated from theexcised skins of hairless mouse agree fairly with the date obtained fromhuman cadaver
skin, suggesting that hairless mouse skin could be anacceptable animal modes for human skin permeation kinetics
studies.
Franz diffusion cell• Franz diffusion cell and the keshary-chien (K-C) cell . the most widely used of these are the franz
diffusion cell and the k-c cell . The K-C Diffusion has an effective receptor volume of 12ml and skin surface area
3.14cm2 .The receptor solution is stirred by a star-head magnate rotating at a constant speed of 600 rpm .
In-vivo evaluation:AnimAl model:In vivo animal models are preferred because considerable time andresource are
required to carry out studies in human. Some of the animalare used to in vivo studies are mouse, rat, guinea pig, rabbit,
hairlessmouse, hairless rat, hairless dog, cat, dog, miniature pig, pig, horse, goat,squirrel, monkey. Etc.
Human model:The final stage in the development of transdermal device involves thecollection of pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic data followingapplication of the device to human volunteers.Determination of absorption following
topical administration requiresthe investigator to know the amount of radioactivity retained in thebody, or excreted by
routs not monitored (assayed).This necessitates measurement of elimination following parenteral(ideally i.v.)
administration of the compoundThe percentage of dose absorbed transdermally is then calculated as% dose absorbed
=Total radioactivity excreted after topical administration /Total radioactivity excreted after I.v administration x100
You might also like
- Evaluation Test'S For Transdermal Patch: 1. Thickness of The PatchDocument14 pagesEvaluation Test'S For Transdermal Patch: 1. Thickness of The Patchmurali2manojNo ratings yet
- Tape Stripping by VyasDocument22 pagesTape Stripping by VyasvunnamnareshNo ratings yet
- Single Layer Drug in Adhesives. Multi-Layer Drug in Adhesives. Micro Reservoir Controlled TddsDocument47 pagesSingle Layer Drug in Adhesives. Multi-Layer Drug in Adhesives. Micro Reservoir Controlled Tddsshamma shahulhameedNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing & Quality Assurance: Crease RecoveryDocument5 pagesTextile Testing & Quality Assurance: Crease RecoveryTauqeer Raza100% (1)
- Microencapsulation: Presented By:-Prabhjot Singh Bajwa Mpharm - 2 SemDocument40 pagesMicroencapsulation: Presented By:-Prabhjot Singh Bajwa Mpharm - 2 Sembajwa001No ratings yet
- Preparation of Histological SpecimensDocument26 pagesPreparation of Histological SpecimensMuhammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Histological SpecimensDocument4 pagesPreparation of Histological SpecimensAqilah HazwaniNo ratings yet
- 8 CharacterizationDocument3 pages8 Characterizationsree anugraphicsNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Fabric Abrasion Resistance FOR LABDocument5 pagesMeasurement of Fabric Abrasion Resistance FOR LABSudip TalukdarNo ratings yet
- Research Article Characterization of Microchannels Created by Metal Microneedles: Formation and ClosureDocument9 pagesResearch Article Characterization of Microchannels Created by Metal Microneedles: Formation and ClosureAmina Tucak-SmajićNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing & Quality: Title: Martyndale Pilling Testing MethodDocument6 pagesTextile Testing & Quality: Title: Martyndale Pilling Testing MethodTauqeer RazaNo ratings yet
- Lasers Surg Med - 2023 - AhnDocument11 pagesLasers Surg Med - 2023 - AhnBoeroNo ratings yet
- 1526970702H08TM35 QiDocument11 pages1526970702H08TM35 QiJhilik DeyNo ratings yet
- Title: Textile Testing and Quality AssuranceDocument5 pagesTitle: Textile Testing and Quality AssuranceTauqeer RazaNo ratings yet
- AicheposterkoDocument1 pageAicheposterkoapi-277213829No ratings yet
- 4-Fluid Control &tissue DilationDocument57 pages4-Fluid Control &tissue Dilationyahia salahNo ratings yet
- Observation of Viable Alloskin Vs Xenoskin Grafted Onto Subcutaneous Tissue Wounds After Tangential Excision in Massive BurnsDocument10 pagesObservation of Viable Alloskin Vs Xenoskin Grafted Onto Subcutaneous Tissue Wounds After Tangential Excision in Massive BurnsAngelica SerbulNo ratings yet
- Full Thickness Skin GraftDocument13 pagesFull Thickness Skin GraftironNo ratings yet
- What Does It Measure? Advantages: Technical DataDocument2 pagesWhat Does It Measure? Advantages: Technical DataloisNo ratings yet
- Test Skin PDFDocument368 pagesTest Skin PDFherfuentesNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Testing Fundamentals - DefinisiDocument8 pagesDiffusion Testing Fundamentals - DefinisiDesy M WenasNo ratings yet
- Skin Grafts: BY DR - Surapol ChagkornbureeDocument30 pagesSkin Grafts: BY DR - Surapol Chagkornbureedaniel situngkirNo ratings yet
- Surgical Dressing QCDocument9 pagesSurgical Dressing QCdrgdswNo ratings yet
- D 4752 - 98 - Rdq3ntitotgDocument8 pagesD 4752 - 98 - Rdq3ntitotgmorchedtounsiNo ratings yet
- Sutures and Ligatures-1Document4 pagesSutures and Ligatures-1Pranjali ParkheNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Static Flow Through-Clowes1994Document4 pagesDiffusion Static Flow Through-Clowes1994NURULARFIYANTIYUSUFNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Skin Permeation TechicalDocument14 pagesIn Vitro Skin Permeation TechicaldanielsinagaNo ratings yet
- Histology - Wet Lab 1Document36 pagesHistology - Wet Lab 1Victoria RennaNo ratings yet
- Gingival Retraction JC 5Document65 pagesGingival Retraction JC 5rajaniNo ratings yet
- Astm d4752 Rub TestDocument8 pagesAstm d4752 Rub Testhelioxavier2100% (1)
- Particle Size AnalysisDocument31 pagesParticle Size Analysisحبيبه بيبيNo ratings yet
- Gingival Retraction TechniquesDocument86 pagesGingival Retraction TechniquesNaomi Singh100% (1)
- tOPICAL sKIN aDHESIFDocument14 pagestOPICAL sKIN aDHESIFMusa GunawanNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing and Quality Assurance: Submitted byDocument7 pagesTextile Testing and Quality Assurance: Submitted byTauqeer RazaNo ratings yet
- Abrasion, Pilling, PH, Tear, Tensile, Crease Recovery: M.Muslim Umair BS (H) App - Chemistry 8 Semester (Evening)Document5 pagesAbrasion, Pilling, PH, Tear, Tensile, Crease Recovery: M.Muslim Umair BS (H) App - Chemistry 8 Semester (Evening)Muslim Umair ButtNo ratings yet
- Journal Club PresentationDocument39 pagesJournal Club PresentationArchana PanwarNo ratings yet
- Pilling Resistance TestsDocument7 pagesPilling Resistance TestsTauqeer RazaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in Dental X-Ray RoomDocument13 pagesInfection Control in Dental X-Ray RoomAlaa MoradNo ratings yet
- Textile Testing and Quality Control: 1 Assignment SubmissionDocument26 pagesTextile Testing and Quality Control: 1 Assignment Submissiontripti keshanNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4752 MEK Test (Zinc Test)Document8 pagesASTM D4752 MEK Test (Zinc Test)vlong300389% (9)
- Skin Graf Dan FlapDocument28 pagesSkin Graf Dan FlapAlparisyi MuhamadNo ratings yet
- 1526970602H08TM34 QiDocument11 pages1526970602H08TM34 QiJhilik DeyNo ratings yet
- E 276 - 98 - Rti3ni05oaDocument4 pagesE 276 - 98 - Rti3ni05oaMd Ahtesham DanishNo ratings yet
- White Paper Safety and Performance Eval of Remfd Harmonic ScalpelsDocument7 pagesWhite Paper Safety and Performance Eval of Remfd Harmonic ScalpelscarcavaNo ratings yet
- Presentation EvaPerendreu-Mata (Refinement Suggestions)Document6 pagesPresentation EvaPerendreu-Mata (Refinement Suggestions)watiNo ratings yet
- ADDS RecordDocument31 pagesADDS RecordSruthija Since 1998No ratings yet
- Skin GraftDocument6 pagesSkin Graftnavyblue333No ratings yet
- Sutures: Dr. Oyebode OyeyiolaDocument50 pagesSutures: Dr. Oyebode Oyeyiolaoyebode oyeyiolaNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument8 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Phardose - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument25 pagesPhardose - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemEdrick RamoranNo ratings yet
- Herbal PatchDocument6 pagesHerbal PatchRiana Maya OktavianiNo ratings yet
- D1474Document5 pagesD1474hdanyealNo ratings yet
- 2011 Article 9715Document8 pages2011 Article 9715Junior LopesNo ratings yet
- Leishmaniasis Guide Collection 2021Document3 pagesLeishmaniasis Guide Collection 2021Amii CcNo ratings yet
- Lab Course IDocument5 pagesLab Course IHudson PoloniniNo ratings yet
- Plastic & Hand Surgery in Clinical Practice: Classifications and DefinitionsFrom EverandPlastic & Hand Surgery in Clinical Practice: Classifications and DefinitionsNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Adsorption at Liquid Interfaces: Theory, Experiment, ApplicationFrom EverandDynamics of Adsorption at Liquid Interfaces: Theory, Experiment, ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Mirachip: Miracle Computer Chip Combats Airborne Viruses and Fosters a Cyber Virus to Debilitate ChinaFrom EverandMirachip: Miracle Computer Chip Combats Airborne Viruses and Fosters a Cyber Virus to Debilitate ChinaNo ratings yet
- CPP: Types of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsDocument2 pagesCPP: Types of Ligands in Coordination CompoundsAshmit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Balancing Chemical EquationsMichael Benson0% (1)
- Class-7-Assessment TestDocument4 pagesClass-7-Assessment Testchinu321No ratings yet
- The Efficiency of Melanoidin Based-Waste Degradation With Different Biological MethodsDocument9 pagesThe Efficiency of Melanoidin Based-Waste Degradation With Different Biological MethodsTiaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGEAR SHC XMP 460Document12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGEAR SHC XMP 460Om Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety in The Clinical Microscopy SectionDocument6 pagesLaboratory Safety in The Clinical Microscopy SectionFarida WongNo ratings yet
- Klüberlectric KR 44-102: Special Grease For The Lubrication of Electrical Switches, Contacts and SensorsDocument2 pagesKlüberlectric KR 44-102: Special Grease For The Lubrication of Electrical Switches, Contacts and SensorsSenousyIbrahimNo ratings yet
- ISA standards, materials, and control room conceptsDocument8 pagesISA standards, materials, and control room conceptsGiovanniNo ratings yet
- Bottled Water Should Be BannedDocument8 pagesBottled Water Should Be BannedSafayet AzizNo ratings yet
- Solid State - DPP 01 - DPP-01 - Solid State - (Chemistry) - Accelerate 2.0 - Sikander Sir - SandeepDocument2 pagesSolid State - DPP 01 - DPP-01 - Solid State - (Chemistry) - Accelerate 2.0 - Sikander Sir - Sandeepsneha duttaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Leadership and The YouthDocument7 pagesLesson 4: Leadership and The Youthciedelle arandaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy Chapter 6 Plants Used As Surgical Dressings NotesDocument11 pagesPharmacognosy Chapter 6 Plants Used As Surgical Dressings NotesAbhishek palNo ratings yet
- Rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis) : Brief BackgrounDocument13 pagesRosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis) : Brief BackgrounOsama Mohammed BeshrNo ratings yet
- Download ebook Goldfranks Toxicologic Emergencies 11E True Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Goldfranks Toxicologic Emergencies 11E True Pdf full chapter pdfjames.farnan170100% (20)
- Multisorb Silica Gel Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesMultisorb Silica Gel Safety Data SheetAmir RahbariNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction Coursework Sodium Thiosulphate and Hydrochloric AcidDocument6 pagesRate of Reaction Coursework Sodium Thiosulphate and Hydrochloric Acidbcqy65mx100% (1)
- Production Optimization and Quality Assessment of Biodiesel From Waste Vegetable OilDocument8 pagesProduction Optimization and Quality Assessment of Biodiesel From Waste Vegetable OilNilmar NasaanNo ratings yet
- Ferric Chloride ProductionDocument3 pagesFerric Chloride ProductionamalinaNo ratings yet
- Protolytic Equilibriaof Picric AcidDocument7 pagesProtolytic Equilibriaof Picric AcidMuhammad Fiqih AlayubiNo ratings yet
- Selecting The Right Soldering IronDocument4 pagesSelecting The Right Soldering IronHow EverNo ratings yet
- Study On Important Biochemical Quality Parameters in Black TeaDocument15 pagesStudy On Important Biochemical Quality Parameters in Black TeaBagmishNo ratings yet
- Journal of Catalysis (2022) - Size-Dependent Activity of Supported Ru Catalysts For Ammonia Synthesis at Mild ConditionsDocument11 pagesJournal of Catalysis (2022) - Size-Dependent Activity of Supported Ru Catalysts For Ammonia Synthesis at Mild ConditionsKatiane Mesquita100% (1)
- Lesson 8 AlkenesDocument10 pagesLesson 8 AlkenesSideka ResalsinghNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of SteelsDocument9 pagesHeat Treatment of SteelsAnkit MauryaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High AlertDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat High AlertStore ApotekerNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Organic ReactionsDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts of Organic ReactionsPraveen Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Properties of MineralsDocument31 pagesProperties of MineralsJenzen fe PalmaNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials Lab #2 HandoutDocument4 pagesBiomaterials Lab #2 HandoutMai Phương LêNo ratings yet
- Prelim Quiz 2 - Attempt Review ECE6342Document10 pagesPrelim Quiz 2 - Attempt Review ECE6342Allen JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Aflas EngDocument11 pagesAflas EngVictor Flores ResendizNo ratings yet