Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C Programming Lab Subject Code: 20UCA1CC2P/20UIT1CC2P Class: BCA/BSC IT Programs Inside
Uploaded by
Hajiram BeeviOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C Programming Lab Subject Code: 20UCA1CC2P/20UIT1CC2P Class: BCA/BSC IT Programs Inside
Uploaded by
Hajiram BeeviCopyright:
Available Formats
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
C Programming Lab
Subject Code: 20UCA1CC2P/20UIT1CC2P
Class: BCA/BSC IT
Programs Inside
Develop a program in C
1. Using assignment statements.
2. Using different forms of If Statement.
3. To demonstrate Logical operators
4. Using While, Do-While & For Loop
5. Using Switch
6. To illustrate the use of Functions& Pointers
7. Using Macro definitions to test whether a character is
uppercase or lowercase
8. To make use of arrays.
9. To manipulate Strings.
10. To demonstrate structure.
11. Using console I/O Functions.
12. To copy the contents of one file into another
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 1
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
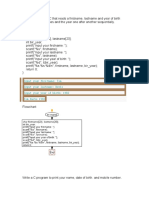
1. Using assignment statements.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=5, j=9, k=5;
int a=6,b=2;
int m=0,n=0;
printf("%d\t%d\n",i,j);
printf("%d\n",m);
m=i++-j--;
printf("%d\n",m);
printf("%d\t%d\n",i,j);
k+=++j+k;;
printf("%d\n",k);
a+=b;
printf("Value of a is after addition %d\n",a);
a-=b;
printf("Value of a is after subtraction %d\n",a);
a*=b;
printf("Value of a is after multiplication %d\n",a);
a/=b;
printf("Value of a is after integer division %d\n",a);
a%=b;
printf("Value of a is after modulo division %d\n",a);
return 1;
}
2.a. Using different forms of If statement (Simple IF)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num1,num2;
printf("Enter first integer\n");
scanf("%d",&num1);
printf("Enter second integer\n");
scanf("%d",&num2);
if(num1==num2)
printf("%d is equal to %d\n",num1,num2);
return 0;
}
2.b. Using different forms of If statement (IF…ELSE)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Please enter an integer:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n%2!=0)
printf("%d is odd\n",n);
else
printf("%d is even\n",n);
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 2
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
return 0;
}
2.c. Using different forms of If statement (Nested IF)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Please enter an integer:");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n<=15)
{
if(n>=10)
printf("%d is between 10 and 15\n",n);
}
else
printf("%d is not between 10 and 15\n",n);
return 0;
}
3. a.To demonstrate Logical operators (AND)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int m1,m2,m3,m4,m5,per;
printf("Enter marks in 5 subjects:\n");
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&m1,&m2,&m3,&m4,&m5);
per=(m1+m2+m3+m4+m5)/5;
if(per>=60)
printf("First Division\n");
if((per>=50)&&(per<60))
printf("Second Division\n");
if((per>=40)&&(per<50))
printf("Third division");
if(per<40)
printf("Fail\n");
}
3. b.To demonstrate Logical operators (OR)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ch;
printf("Enter any character");
ch=getchar();
if((ch>='A'&&ch<='Z')||(ch>='a'&&ch<='z'))
printf("%c is an alphabet\n",ch);
else
if(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')
printf("%c is digit\n",ch);
else
printf("%c is a special character\n",ch);
return 0;
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 3
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
}
3. c.To demonstrate Logical operators (NOT)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int number;
printf("Please enter an integer value:\n");
scanf("%d",&number);
if(!(number>40))
{
printf("Input check greater than 40 - True");
}
else
{
printf("Input check greater than 40 - False");
}
return 0;
}
4. a. Using While, Do-While & For Loop (While Loop)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num,original,factorial;
printf("Type a positive integer:\n");
scanf("%d",&num);
original=num;
factorial=1;
while(num>1)
{
factorial*=num;
num--;
}
printf("Factorial of %d=%d\n",original,factorial);
return 0;
}
4. b. Using While, Do-While & For Loop (Do..While Loop)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num,rev;
printf("Enter the number to be reversed:\n");
scanf("%d",&num);
printf("Reverse number is:\n");
do
{
rev=num%10;
printf("%d",rev);
num=num/10;
}
while(num!=0);
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 4
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
return 0;
}
4.c. Using While, Do-While & For Loop (Simple FOR Loop)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,low,high,sum=0;
printf("Please type the lower bound:\n");
scanf("%d",&low);
printf("Please type the higher bound:\n");
scanf("%d",&high);
for(i=low;i<=high;i++)
sum+=i;
printf("\n The sum of integers from %d to %d is:%d\n",low,high,sum);
return 0;
}
4.d. Using While, Do-While & For Loop (Nested For Loop)
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<4;i++)
for(j=1;j<3;j++)
printf("%5d%5d\n",i,j);
return 0;
}
5. Using Switch
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float value1,value2;
char operator;
printf("Type an expression:");
scanf("%f%c%f",&value1,&operator,&value2);
switch(operator)
{
case '+':
printf("%.2f\n",value1+value2);
break;
case '-':
printf("%.2f\n",value1-value2);
break;
case '*':
printf("%.2f\n",value1*value2);
break;
case '/':
if(value2==0)
printf("Divisible by zero\n");
else
printf("%.2f\n",value1/value2);
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 5
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
break;
default:
printf("Unknown operator\n");
}
}
6. a. To illustrate the use of Functions& Pointers (Functions)
#include<stdio.h>
int calc_area();
int length,width,area;
int main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter the length of rectangle\n");
scanf("%d",&length);
printf("Enter the width of rectangle\n");
scanf("%d",&width);
n=calc_area();
printf("Area is %d\n",area);
}
int calc_area()
{
area=length*width;
return area;
}
6. b. To illustrate the use of Functions& Pointers (Pointers)
#include<stdio.h>
void no_swap(int x,int y);
void swap(int *p1,int *p2);
int main()
{
int a=1,b=999;
printf("a=%d,b=%d\n",a,b);
no_swap(a,b);
printf("a=%d,b=%d\n",a,b);
swap(&a,&b);
printf("a=%d,b=%d\n",a,b);
}
void no_swap(int x,int y)
{
int temp;
temp=x;
x=y;
y=temp;
}
void swap(int *px,int *py)
{
int temp;
temp=*px;
*px=*py;
*py=temp;
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 6
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
}
7. Using Macro definitions to test whether a character is uppercase or lowercase
#include<stdio.h>
#define IS_UPPER(x) (x>='A'&&x<='Z')
#define IS_LOWER(x) (x>='a'&&x<='z')
int main()
{
char ch;
printf("Enter any character:\n");
ch=getchar();
if(IS_UPPER(ch))
printf("'%c' is uppercase\n",ch);
else if(IS_LOWER(ch))
printf("'%c' is lowercase\n",ch);
else
printf("Entered character is not alphabet");
return 0;
}
8. To make use of arrays.
#include <stdio.h>
void getMatrixElements(int matrix[][10], int row, int column)
{
printf("\nEnter elements: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; ++j)
{
printf("Enter a%d%d: ", i + 1, j + 1);
scanf("%d", &matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
void multiplyMatrices(int first[][10],int second[][10],int result[][10],int r1, int c1, int r2, int
c2)
{
for (int i = 0; i < r1; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < c2; ++j)
{
result[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < r1; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < c2; ++j)
{
for (int k = 0; k < c1; ++k)
{
result[i][j] += first[i][k] * second[k][j];
}
}
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 7
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
}
}
void display(int result[][10], int row, int column)
{
printf("\nOutput Matrix:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < column; ++j)
{
printf("%d ", result[i][j]);
if (j == column - 1)
printf("\n");
}
}
}
int main()
{
int first[10][10], second[10][10], result[10][10], r1, c1, r2, c2;
printf("Enter rows and column for the first matrix: ");
scanf("%d %d", &r1, &c1);
printf("Enter rows and column for the second matrix: ");
scanf("%d %d", &r2, &c2);
while (c1 != r2) {
printf("Error! Enter rows and columns again.\n");
printf("Enter rows and columns for the first matrix: ");
scanf("%d%d", &r1, &c1);
printf("Enter rows and columns for the second matrix: ");
scanf("%d%d", &r2, &c2);
}
getMatrixElements(first, r1, c1);
getMatrixElements(second, r2, c2);
multiplyMatrices(first, second, result, r1, c1, r2, c2);
display(result, r1, c2);
return 0;
}
9. To manipulate Strings.
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char words1[]="jamal";
char words2[]="JMC";
char words3[]="Jamal Mohamed College";
char words4[100]="Information";
char words5[100]="Technology";
int length=0,num=0;
//string length
length=strlen(words1);
printf("\n length of the string is %d\n",length);
//string copy
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 8
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
printf("\n Before:");
printf("\n %s\n",words2);
strcpy(words2,words3);
printf("\n After:");
printf("\n %s\n",words2);
//string concatenation
printf("\n Before:");
printf("\n %s\n",words4);
strcat(words4,words5);
printf("\n After:");
printf("\n %s\n",words4);
//string comparison
num=strcmp(words5,words4);
printf("\n%d\n",num);
return 0;
}
10. To demonstrate structure.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct mark_sheet{
char name[20];
long int rollno;
int marks[10];
int total;
float average;
char rem[10];
char cl[20];
}students[100];
int main(){
int a,b,n,flag=1;
char ch;
printf("How many students : \n");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(a=1;a<=n;++a){
printf("\n\nEnter the details of %d students : ", n-a+1);
printf("\n\nEnter student %d Name : ", a);
scanf("%s", students[a].name);
printf("\n\nEnter student %d Roll Number : ", a);
scanf("%ld", &students[a].rollno);
students[a].total=0;
for(b=1;b<=5;++b){
printf("\n\nEnter the mark of subject-%d : ", b);
scanf("%d", &students[a].marks[b]);
students[a].total += students[a].marks[b];
if(students[a].marks[b]<40)
flag=0;
}
students[a].average = (float)(students[a].total)/5.0;
if((students[a].average>=75)&&(flag==1))
strcpy(students[a].cl,"Distinction");
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 9
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
else
if((students[a].average>=60)&&(flag==1))
strcpy(students[a].cl,"First Class");
else
if((students[a].average>=50)&&(flag==1))
strcpy(students[a].cl,"Second Class");
else
if((students[a].average>=40)&&(flag==1))
strcpy(students[a].cl,"Third Class");
if(flag==1)
strcpy(students[a].rem,"Pass");
else
strcpy(students[a].rem,"Fail");
flag=1;
}
for(a=1;a<=n;++a){
printf("\n\n\t\t\t\tMark Sheet\n");
printf("\nName of Student : %s", students[a].name);
printf("\t\t\t\t Roll No : %ld", students[a].rollno);
printf("\n------------------------------------------------------------------------");
for(b=1;b<=5;b++){
printf("\n\n\t Subject %d \t\t :\t %d", b, students[a].marks[b]);
}
printf("\n\n------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("\n\n Totl Marks : %d", students[a].total);
printf("\t\t\t\t Average Marks : %5.2f", students[a].average);
printf("\n\n Class : %s", students[a].cl);
printf("\t\t\t\t\t Status : %s", students[a].rem);
}
return(0);
}
11. a. Using console I/O Functions.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
int main()
{
char ch,lower,upper;
puts("\n Enter any one character:");
ch=getchar();
if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z')
{
putchar(toupper(ch));
}
else
{
putchar(tolower(ch));
}
return 0;
}
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 10
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
11. b. Using console I/O Functions.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char c;
int word=1,digit=0,letter=0;
while((c=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(c==''||c=='\t')
word++;
if(c>='0'&&c<='9')
digit++;
if(c>='A'&&c<='Z'||c>='a'&&c<='z')
letter++;
}
printf("\n Total words\tTotal digits\tTotal letters");
printf("\n%d\t\t%d\t\t%d",word,digit,letter);
return 0;
}
12. To copy the contents of one file into another
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fptr1, *fptr2;
char filename[100], c;
printf("Enter the filename to open for reading \n");
scanf("%s", filename);
// Open one file for reading
fptr1 = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fptr1 == NULL)
{
printf("Cannot open file %s \n", filename);
exit(0);
}
printf("Enter the filename to open for writing \n");
scanf("%s", filename);
// Open another file for writing
fptr2 = fopen(filename, "w");
if (fptr2 == NULL)
{
printf("Cannot open file %s \n", filename);
exit(0);
}
// Read contents from file
c = fgetc(fptr1);
while (c != EOF)
{
fputc(c, fptr2);
c = fgetc(fptr1);
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 11
C PROGRAMMING LAB (2020 SYLLABUS)
}
printf("\nContents copied to %s", filename);
fclose(fptr1);
fclose(fptr2);
return 0;
}
Prepared by Lt.J.Hajiram Beevi, JMC, Trichy Page 12
You might also like
- IB Specification Vol 1-Release-1.4-2020!04!07Document1,981 pagesIB Specification Vol 1-Release-1.4-2020!04!07margaryandavid111No ratings yet
- Practical File Of “Programming for problem solvingDocument70 pagesPractical File Of “Programming for problem solvingrohit bishtNo ratings yet
- C Program ExamplesDocument10 pagesC Program ExamplesKamalakar SreevatasalaNo ratings yet
- PPS Unit 2 Question Bank: One Dimensional Array in CDocument46 pagesPPS Unit 2 Question Bank: One Dimensional Array in CParadox 1883No ratings yet
- CS8261 C Programming Lab Manual With All 18 ProgramsDocument42 pagesCS8261 C Programming Lab Manual With All 18 ProgramsKousheek VinnakotiNo ratings yet
- Questions From The CPS125 Final Exam - Winter 2008Document4 pagesQuestions From The CPS125 Final Exam - Winter 2008Harpreet Singh SahotaNo ratings yet
- Co FileDocument27 pagesCo FileHemonesh MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- DSA Lab Manual FinalDocument44 pagesDSA Lab Manual FinalIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- C10: Predict The Output and The ErrorsDocument10 pagesC10: Predict The Output and The Errorsbookworm_shashi100% (1)
- PdsDocument5 pagesPdsAnas MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design ProgramsDocument59 pagesCompiler Design ProgramsrajNo ratings yet
- C Test Questions and Answers PDFDocument15 pagesC Test Questions and Answers PDFVikas Bakoliya100% (1)
- C PracticalDocument65 pagesC PracticalPiyush Sharma100% (1)
- Lab Work Book for C Programming (BCA LevelDocument26 pagesLab Work Book for C Programming (BCA LevelVishwa PathakNo ratings yet
- DOTE TNDTE C Programming LABDocument14 pagesDOTE TNDTE C Programming LABsmagendiranNo ratings yet
- Practical File For CDocument68 pagesPractical File For CNarayan VermaNo ratings yet
- To Write A C Program To Find The Roots of A Quadratic EquationDocument12 pagesTo Write A C Program To Find The Roots of A Quadratic Equationroshni vargheseNo ratings yet
- C Questions: Predict The Output or Error(s) For The FollowingDocument33 pagesC Questions: Predict The Output or Error(s) For The FollowingAnju PriyaNo ratings yet
- C Record CORRECTEDDocument40 pagesC Record CORRECTEDMR KishoreNo ratings yet
- C, C++QuestionsDocument21 pagesC, C++QuestionsHarshad ChawlaNo ratings yet
- C Ques1Document45 pagesC Ques1Prashant ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- 1D Array and String: #Include Int Void Char CharDocument8 pages1D Array and String: #Include Int Void Char Charmayande rohiniNo ratings yet
- 05 Preprocessor Directives and Dynamic Memory AllocationWithAnswers Updated 1Document10 pages05 Preprocessor Directives and Dynamic Memory AllocationWithAnswers Updated 1Tejas RaneNo ratings yet
- C++ Practicals Shree Ram College BhandupDocument20 pagesC++ Practicals Shree Ram College BhandupUnknownNo ratings yet
- C++ Aptitude QuestionDocument44 pagesC++ Aptitude QuestionVicky SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- C QuestionsDocument19 pagesC Questionsramya53919No ratings yet
- Calculate trailings of grammar productionsDocument40 pagesCalculate trailings of grammar productionssurajrtkNo ratings yet
- DAG Program For Compiler LabDocument4 pagesDAG Program For Compiler Labsendhil2850% (2)
- C Programming Interview Questions and AnswersDocument68 pagesC Programming Interview Questions and AnswerskudaisyaNo ratings yet
- C Lab ProgrammingDocument47 pagesC Lab ProgrammingSandhya KandikatlaNo ratings yet
- Compiler Lab Report, DIUDocument13 pagesCompiler Lab Report, DIUAshik RabbaniNo ratings yet
- C programming code snippets with logical and arithmetic operationsDocument6 pagesC programming code snippets with logical and arithmetic operationsSanket Naik100% (1)
- 9.cohen Sutherland Line Clipping Algorithm in CDocument6 pages9.cohen Sutherland Line Clipping Algorithm in CPhotos .Students Council 2022No ratings yet
- Mindtree 2018 ProgramsDocument28 pagesMindtree 2018 Programsmd ajuNo ratings yet
- C ArrayDocument17 pagesC ArraymuucoolNo ratings yet
- Generate Three Address Codes For A Simple Program Using Lex and Yacc .Document6 pagesGenerate Three Address Codes For A Simple Program Using Lex and Yacc .privateashik2001No ratings yet
- C Lab - PDFDocument25 pagesC Lab - PDFSubin PS100% (2)
- C & C++Document11 pagesC & C++AbhiNo ratings yet
- Cs3271 Programming in CDocument52 pagesCs3271 Programming in CPriya MohanaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Assessment Test - IIDocument4 pagesContinuous Assessment Test - IIPranav RajNo ratings yet
- CPDS Lab ManualDocument107 pagesCPDS Lab ManualRajasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Let Us C SolutionDocument27 pagesLet Us C SolutionAmit Birwal50% (4)
- CG FileDocument59 pagesCG FileVisheshAnandNo ratings yet
- Control Flow Statements: PrintfDocument9 pagesControl Flow Statements: Printfmayande rohiniNo ratings yet
- C++ Practical FileDocument61 pagesC++ Practical FileHimanshu Sachdeva33% (3)
- Find Out The Perfect Number Using C ProgramDocument13 pagesFind Out The Perfect Number Using C ProgramM UsmithaNo ratings yet
- Oops Lab ManualDocument61 pagesOops Lab ManualVivekanandhan VijayanNo ratings yet
- 15CS302J OS LabManualDocument74 pages15CS302J OS LabManualManu RajNo ratings yet
- C++ Notes1Document33 pagesC++ Notes1vkpradeep33385No ratings yet
- 200 Objective-Type Questions RameshDocument32 pages200 Objective-Type Questions RameshAnkurTyagiNo ratings yet
- C&CPP LAB PROGRAMS BY CHANDU SIRDocument14 pagesC&CPP LAB PROGRAMS BY CHANDU SIRChandu RamanNo ratings yet
- DA2 SolutionDocument13 pagesDA2 SolutionPARTH SUNIL CHAVAN 20BCI0055No ratings yet
- Practical 1Document13 pagesPractical 1SpideyhNo ratings yet
- DA1 SolutionDocument32 pagesDA1 SolutionPARTH SUNIL CHAVAN 20BCI0055No ratings yet
- AnanySrivastava 21BLC1403Document18 pagesAnanySrivastava 21BLC1403ananyNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument21 pagesLab Manualvishal kumar oadNo ratings yet
- Programs On Functions 1) //program To Demonstrate Functions With Arguments and Return ValuesDocument14 pagesPrograms On Functions 1) //program To Demonstrate Functions With Arguments and Return ValuessanjeethaNo ratings yet
- C Language Lab ManualDocument35 pagesC Language Lab ManualSiddhartha KancharlaNo ratings yet
- C ProgrammingDocument24 pagesC ProgrammingshielaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 SolutionsDocument9 pagesWeek 11 SolutionsAnonymous pwyFg22vNo ratings yet
- #Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DDocument22 pages#Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DChinnaraoNo ratings yet
- Advantages of AngularjsDocument5 pagesAdvantages of AngularjsHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Advantages of AngularjsDocument5 pagesAdvantages of AngularjsHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Javascript FunctionDocument14 pagesUnit Ii Javascript FunctionHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Angular JS: General FeaturesDocument10 pagesAngular JS: General FeaturesHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- User Defined Functions GuideDocument42 pagesUser Defined Functions GuideHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Javanotes BCA 2017Document34 pagesJavanotes BCA 2017Hajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Javanotes BCA 2017Document34 pagesJavanotes BCA 2017Hajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Unit I - SLDocument41 pagesUnit I - SLHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Javascript FunctionDocument14 pagesUnit Ii Javascript FunctionHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Capacity PlanningDocument6 pagesCapacity PlanningHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Scripting Languages LabDocument14 pagesScripting Languages LabHajiram Beevi100% (1)
- Active Server PagesDocument12 pagesActive Server PagesHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- AndroidDocument28 pagesAndroidHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Installing HadoopDocument9 pagesInstalling HadoopHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Web Index: How Do Resources End Up in A Web Index?Document5 pagesWeb Index: How Do Resources End Up in A Web Index?Hajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Webtech PG LabmanDocument30 pagesWebtech PG LabmanHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Web Index: How Do Resources End Up in A Web Index?Document5 pagesWeb Index: How Do Resources End Up in A Web Index?Hajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing BasicsDocument21 pagesCloud Computing BasicsHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- QN 1Document12 pagesQN 1mugu_tenNo ratings yet
- WekaDocument6 pagesWekaHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Network Management Definition of Network ManagementDocument4 pagesNetwork Management Definition of Network ManagementHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Semester: II Hours/week: 2 Code: 08UCS2403:P Credits: 2Document31 pagesSemester: II Hours/week: 2 Code: 08UCS2403:P Credits: 2Hajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Computer Basic QuestionsDocument6 pagesComputer Basic QuestionsHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- A. //program For Biggest Number Using Else-If AldderDocument4 pagesA. //program For Biggest Number Using Else-If AldderHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Latex Tutorial: Jeff Clark Revised February 26, 2002Document35 pagesLatex Tutorial: Jeff Clark Revised February 26, 2002Hajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- OossDocument30 pagesOossHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- General KnowledgeDocument14 pagesGeneral KnowledgeHajiram BeeviNo ratings yet
- Basic PHPDocument34 pagesBasic PHPHajiram Beevi100% (1)
- Solution Manual Microprocessors and Interfacing DV HallDocument64 pagesSolution Manual Microprocessors and Interfacing DV HallFaro Val0% (2)
- Tugas Visual StudioDocument7 pagesTugas Visual StudioAmin LadenNo ratings yet
- Client Server Architecture QuestionsDocument27 pagesClient Server Architecture QuestionsSaravanan NallusamyNo ratings yet
- Error While Activating The Datasource in BW With HanaDocument4 pagesError While Activating The Datasource in BW With HanaKonatham Vinod ReddyNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals Study MaterialDocument36 pagesComputer Fundamentals Study Materialzingly31No ratings yet
- 134.4918.17 - DmOS 6.6 - DatasheetDocument23 pages134.4918.17 - DmOS 6.6 - DatasheetRaphaelNo ratings yet
- Ar86ctrl v1.41 ManualDocument22 pagesAr86ctrl v1.41 ManualAchmad Arizki KosasihNo ratings yet
- JWT Handbook PDFDocument106 pagesJWT Handbook PDFZoltán BalázsNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Foundation CourceDocument3 pagesHitachi Foundation CourcePravin KamtheNo ratings yet
- The counter recycles after reaching the count 1001 (9) by toggling FF3, causing it to return to 0000 (0Document80 pagesThe counter recycles after reaching the count 1001 (9) by toggling FF3, causing it to return to 0000 (0Waqas SalmanNo ratings yet
- Adianti FrameworkDocument29 pagesAdianti Frameworkinfo5001No ratings yet
- Pros Compact Headend OH Eng 05 2013Document16 pagesPros Compact Headend OH Eng 05 2013RobertNo ratings yet
- AvalpaBroadcastServerUserManual-v2 1Document87 pagesAvalpaBroadcastServerUserManual-v2 1Livio BelacNo ratings yet
- Config Guide v3 9 7Document224 pagesConfig Guide v3 9 7ixcanetNo ratings yet
- MallocDocument97 pagesMallocDip ShitNo ratings yet
- Huj GV7 U LDocument10 pagesHuj GV7 U LevermaniaNo ratings yet
- Vtu 3RD Sem Cse Data Structures With C Notes 10CS35Document64 pagesVtu 3RD Sem Cse Data Structures With C Notes 10CS35EKTHATIGER63359075% (24)
- Modern Database Management 6 Edition: Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary B. Prescott, Fred R. McfaddenDocument29 pagesModern Database Management 6 Edition: Jeffrey A. Hoffer, Mary B. Prescott, Fred R. McfaddenJanine Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Mysql Installation StepsDocument21 pagesMysql Installation StepsAyush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Apache Storm Tutorial PointDocument20 pagesApache Storm Tutorial PointashokmvanjareNo ratings yet
- Ignition User ManualDocument540 pagesIgnition User ManualRyan HildNo ratings yet
- TAFJ tLockManagerDocument24 pagesTAFJ tLockManagersajibarafatsiddiquiNo ratings yet
- NetappTS ExerciseGuideDocument36 pagesNetappTS ExerciseGuidelisten MeNo ratings yet
- Track 2 - Navigating Around The Clarity PPM Data ModelDocument32 pagesTrack 2 - Navigating Around The Clarity PPM Data ModelVicente RJNo ratings yet
- Brochure Ineo 250 Eng A4Document6 pagesBrochure Ineo 250 Eng A4GabiNo ratings yet
- AyushmanBhattacharya MCAN-102 CA2 121802Document4 pagesAyushmanBhattacharya MCAN-102 CA2 121802Ayushman BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Se342: Distributed Computing: Lecture # 03-b Fundamental ModelsDocument26 pagesSe342: Distributed Computing: Lecture # 03-b Fundamental ModelsMahmood SyedNo ratings yet
- PowerExchange CDC GuideForLinux (UNIX) AndWindows en PDFDocument298 pagesPowerExchange CDC GuideForLinux (UNIX) AndWindows en PDFShiva CHNo ratings yet
- Database Chapter 1 AssignmentDocument2 pagesDatabase Chapter 1 AssignmentSothearith SvayNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition README For Installing Windows Me OntoDocument7 pagesMicrosoft Windows Millennium Edition README For Installing Windows Me Ontoraymondbailey2002No ratings yet