Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Level 2. Tech Analyzes PDF
Level 2. Tech Analyzes PDF
Uploaded by
AbdirahmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Level 2. Tech Analyzes PDF
Level 2. Tech Analyzes PDF
Uploaded by
AbdirahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
1. Intro Trading View / MT4 /
2. Harmonic Scanner / Vibrata / Delorean
3. SUPPORT & RESISTANCE – Horizontal Line
4. MT4 PIVOT + IM PIVOT + SHOPPING CART - PIVOT indicator
5. TrendLines:
- UpTrend -> H/L/HH/HL/HH/HL – Swing High – Swing low
- DownTrend -> H/L/LH/LL/LH/LL – Swing low - Swing High
- Ranging Market - BOX
- Impulse / Pull Back or Correction or Retracement
6. Price Reversal Zone
7. Confirmation Checklist = High Probability Trades
8. Risk Management - Risk Reward Ratio + Position Size
Calculator
9. Harmonic Scanner1 – Simply Strategy
10. Indicators (Leading and Lagging) + RSI Indicator
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
11. Harmonic Scanner2 - SK5 Strategy – Set Up
12. Harmonic Scanner - SK5 Strategy – Entry Rule
13. Harmonic Scanner3 – SAR Strategy (Stop And Reverse)
14. Intro Vibrata Ex Web Analyzer + ECC11
15. ECC11 Strategy – Dr Kathy
16. ECC11 Strategy – MJ + Randy + Hidden
17. The Power of twin Trading + TP1, TP2 & TP3
18. Summary
Lesson 01. Intro
- MT4
- Trading View
- Harmonic Scanner
- Vibrata
- Delorean
What are the Technical Analyses:
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
1. Technical analysis is an analysis methodology for forecasting the direction of prices
through the study of past market data.
2. Technical analysis is a trading discipline employed to evaluate investments and identify
trading opportunities in price trends and patterns seen on charts. Technical analysts believe
past trading activity and price changes of a security can be valuable indicators of the
security's future price movements.
3. Technical analysis is a means of examining and predicting price movements in the
financial markets, by using historical price charts and market statistics. It is based on the
idea that if a trader can identify previous market patterns, they can form a fairly accurate
prediction of future price trajectories.
Candlesticks
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Note:
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
- Top
- Left
- Right
- Buttom
Lesson 03. SUPPORT & RESISTANCE
Support and Resistance
Support and Resistance is one of the most used techniques in technical analysis based on a
concept that's easy to understand but difficult to master. It identifies price levels where
historically the price reacted either by reversing or at least by slowing down and prior price
behavior at these levels can leave clues for future price behavior. There are many different
ways to identify these levels and to apply them in trading. Support and Resistance levels
can be identifiable turning points, areas of congestion or psychological levels (round
numbers that traders attach significance to). The higher the timeframe, the more relevant
the levels become.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Support and Resistance trading strategy:
• Mark your areas of Support & Resistance (SR)
• Wait for a directional move into SR.
• Wait for price rejection at SR.
• Enter on the next candle
• Use Risk Management
• Create TK and SL
Note:
Support – Area on your chart with potential buying pressure
Resistance – Area on your chart with potential selling pressure
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 04: IM Pivot, MT4 Pivot and Shopping Cart
Lesson 05: Trend-Lines
- UpTrend -> H/L/HH/HL/HH/HL – Swing High – Swing low
- DownTrend -> H/L/LH/LL/LH/LL – Swing low - Swing High
- Ranging Market – BOX
- Impulse or Run / Pull Back or Correction or Retracement
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 06: Price Reversal Zone
Lesson 07. Confirmation Checklist = High Probability Trades
- Support/Resistance
- Price Reversal Zone
- TrendLine
- Pull Back
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 07: Risk Reward Ratio + Position Size Calc
Risk Reward Ration
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Position Size Calculator
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 10: Indicators (Leading and Lagging)
+ RSI Indicator
Leading and lagging indicators: what you need to know:
Technical traders use indicators to identify market patterns and
trends. Most of these indicators fall into two categories: leading
and lagging. Discover some popular leading and lagging
indicators and how to use them.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
What is a leading technical indicator?
A leading indicator is a tool designed to anticipate the future direction
of a market, in order to enable traders to predict market movements
ahead of time.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
In theory, if a leading indicator gives the correct signal, a trader can
get in before the market movement and ride the entire trend. However,
leading indicators are by no means 100% accurate, which is why they
are often combined with other forms of technical analysis.
What is a lagging technical indicator?
A lagging indicator is a tool that provides delayed feedback, which
means it gives a signal once the price movement has already passed
or is in progress. These are used by traders to confirm the price trend
before they enter a trade.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
These indicators are commonly used by trend traders – they don’t
show any upcoming price moves but confirm that a trend is underway.
This tends to give traders more confidence that they are correct in
their assumptions, rather than providing a specific trigger for entering
the market.
Leading vs lagging technical indicators:
what’s the difference?
The most obvious difference is that leading indicators predict market
movements, while lagging indicators confirm trends that are already
taking place. Both leading and lagging indicators have their own
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
advantages and drawbacks, so it’s crucial to familiarise yourself with
how each works and decide which fits in with your strategy.
Leading indicators react to prices quickly, which can be great for
short-term traders, but makes them prone to giving out false signals –
these happen when a signal indicates it’s time to enter the market, but
the trend promptly reverses. Conversely, lagging indicators are far
slower to react, which means that traders would have more accuracy
but could be late in entering the market.
Relying solely on either could have negative effects on a strategy,
which is why many traders will aim to find a balance of the two.
Four popular leading indicators
Popular leading indicators include:
1. The relative strength index (RSI)
2. The stochastic oscillator
3. Williams %R
4. On-balance volume (OBV)
A lot of popular leading indicators fall into the category of oscillators as
these can identify a possible trend reversal before it happens.
However, not all leading indicators will use the same calculations, so
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
there is the possibility that different indicators will show different
signals.
Relative strength index (RSI)
The relative strength index (RSI) is a momentum indicator, which
traders can use to identify whether a market is overbought or
oversold. When the RSI gives a signal, it is believed that the market
will reverse – this provides a leading sign that a trader should enter or
exit a position.
The RSI is an oscillator, so it is shown on a scale from zero to 100. If
the RSI is above 70, the market would often be thought of as
overbought and appear as red on the chart (below). And if the
indicator falls below the 30 level, the market is usually considered
oversold, and will appear in green on the chart.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
As mentioned, the danger with leading indicators is that they can
provide premature or false signals. With the RSI, it is possible that the
market will sustain overbought or oversold conditions for long periods
of time, without reversing. This makes it important to have suitable risk
management measures in place, such as stops and limits.
Stochastic oscillator
Another popular example of a leading indicator is the stochastic
oscillator, which is used to compare recent closing prices to the
previous trading range.
The stochastic is based on the idea that market momentum changes
direction much faster than volume or price, so it can be used to predict
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
the direction of market movements. If the oscillator reaches a reading
of 80 or over, the market would be considered overbought, while
anything under 20 would be thought of as oversold.
The oscillator is shown as two lines on the chart, the %K (the black
line on the chart below) and the %D (the red dotted line below). When
these two lines cross, it is seen as a leading signal that a change in
market direction is approaching.
During volatile market conditions, the stochastic is prone to false
signals. To prevent this impacting your trades, you could use the
stochastic in conjunction with other indicators or use it as a filter for
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
your trades rather than a trigger. This would mean entering the market
once the trend is confirmed, as you would with a lagging indicator.
Williams %R
The Williams percent range, more commonly known as the Williams
%R, is very similar to the stochastic oscillator. The main difference
being that it works on a negative scale – so it ranges between zero
and -100, and uses -20 and -80 as the overbought and oversold
signals respectively.
So, on the below chart, the green line below -80 indicates that the
price is likely to rise. While the red line above -20 indicates the price is
likely to fall.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
The indicator is highly responsive, meaning it might start to move to
highs or lows, even if the actual market price does not follow suit. As
the Williams %R is leading, these signals can be premature and less
reliable than other entry signals, which is why some traders prefer to
use -10 and -90 as more extreme price signals.
On-balance volume (OBV)
On-balance volume (OBV) is another leading momentum-based
indicator. It looks at volume to enable traders to make predictions
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
about the market price – OBV is largely used in shares trading, as
volume is well documented by stock exchanges.
Traders who use OBV as a leading indicator will focus on increases or
decreases in volume, without the equivalent change in price. This is
believed to be an indication that the price will increase or decrease
imminently.
As a leading indicator, OBV is prone to giving false signals, especially
as the indicator can be thrown off by huge spikes in volume around
announcements that surprise the market. Although volume changes,
this is not always indicative of a trend and can cause traders to open
positions prematurely.
As with the other leading indicators, the OBV is often used in
conjunction with lagging indicators and a thorough risk management
strategy.
Three popular lagging indicators
Popular lagging indicators include:
1. Moving averages
2. The MACD indicator
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
3. Bollinger bands
Lagging indicators are primarily used to filter out the noise from short-
term market movements and confirm long-term trends. They are
usually drawn onto the price chart itself, unlike leading indicators
which usually appear in separate windows.
Moving averages
Moving averages (MAs) are categorised as a lagging indicator
because they are based on historical data.
Buy and sell signals are generated when the price line crosses the MA
or when two MA lines cross each other. However, because the moving
average is calculated using previous price points, the current market
price will be ahead of the MA.
In the below 50-day MA example, the moving average has crossed
the price from above, indicating an upward reversal is imminent.
However, we can see that the MA is slower to pick up the bullish trend
when it does occur.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Moving averages can be calculated over any timeframe, depending on
the trader’s goals – but the longer the time frame, the longer the lag.
So, a MA of 300 days would have a far longer delay than an MA of 50
days.
It is possible for lagging indicators to give off false signals, but it is less
likely as they are slower to react.
MACD indicator
Moving averages can be used on their own, or they can be the basis
of other technical indicators, such as the moving average
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
convergence divergence (MACD). As it is based on MAs, the MACD is
inherently a trend-following or lagging indicator. However, it has been
argued that different components of the MACD provide traders with
different opportunities.
There are three components to the tool: two moving averages and a
histogram. The two moving averages (the signal line and the MACD
line) are invariably lagging indicators, as they only provide signals
once the two lines have crossed each other, by which time the trend is
already in motion.
Source: IG charts
But the MACD histogram is sometimes considered a leading indicator,
as it is used to anticipate signal crossovers in between the two moving
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
averages. The bars on the histogram represents the difference
between the two MAs – as the bars move further away from the
central zero line, it means the MAs are moving further apart. Once this
expansion is over, a ‘hump’ appears on the histogram which is a sign
the MAs will tighten again, and a crossover will occur.
Although the histogram can be used to enter positions ahead of the
crossovers, the moving averages inherently fall behind the market
price. So, in general it is a lagging indicator. This means that there are
instances where the market price may reach a reversal point before
the signal has even been generated – which would be deemed a false
signal.
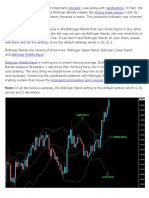
Bollinger bands
The Bollinger band tool is a lagging indicator, as it is based on a 20-
day simple moving average (SMA) and two outer lines. These outer
bands represent the positive and negative standard deviations away
from the SMA and are used as a measure of volatility. When levels of
volatility increase, the bands will widen, and as volatility decreases,
they will contract.
When the price reaches the outer bands of the Bollinger, it often acts
as a trigger for the market to rebound back towards the central 20-
period moving average.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Source: IG charts
There are strategies that suggest the bands have leading indicator
properties, but alone they do not give out leading trading signals.
Bollinger bands can give no indication of exactly when the change in
volatility might take place, or which direction the price will move in.
They are merely a sign that a breakout could soon take place, giving
bullish and bearish signals.
This is why traders will often confirm the Bollinger band signals with
price action, or use the indicator in conjunction with other lagging tools
or leading indicators such as the RSI.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Leading and lagging technical indicators
summed up
• A leading indicator is a tool designed to anticipate the future direction
of a market
• A lagging indicator is a tool that gives signal once the price movement
has already started
• Leading indicators react to prices quickly but this makes them prone to
giving out false signals
• Lagging indicators can be more accurate but this is because they are
far slower to react
• A lot of popular leading indicators fall into the category of oscillators,
including the RSI, stochastic oscillator, Williams %R and OBV
• Lagging indicators are drawn onto the price chart itself and include
moving averages, the MACD and Bollinger bands
• Relying solely on either could have negative effects on a strategy,
which is why many traders will aim to find a balance of the two
If you feel ready to start using lagging and leading indicators on live
markets, you can open an account with IG today. Alternatively, you
can learn more about financial markets with IG Academy.
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 13. Harmonic Scanner3 – SAR Strategy
SAR = STOP AND REVERSE
The parabolic SAR is a technical indicator used to determine the price direction of an asset, as
well as draw attention to when the price direction is changing. Sometimes known as the "stop
and reversal system," the parabolic SAR was developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr in 1978.
Parabolic SAR is by far the only good indicator. ... The only accurate and
suitable indicator out there for daytrading or scalping is PARABOLIC SAR. Although
considered by many to be the most inaccurate, I find it to be far more accurate than any
other indicator out there!
Parabolic SAR Buy Signals. ... Short for Parabolic Stop-and-Reverse, this indicator provides
both entries and exits. The indicator is composed of a series of dots, either above or below the
price. When dots move from below to above the price bars, it is time to get out of longs or get
short
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
- Setup: Color Black – Circle – 1h timeframe
- Buy Rule: SAR DOWN = BUY,
- Sell Rule: SAR UP = Sell
- Trendline must be broken – IM Educator
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 14. Intro Vibrata Ex Web Analyzer + ECC11
--------------------Watch video-------------------------
Lesson 15. ECC11 Strategy – Dr Kathy
Lesson 16. ECC11 Strategy – MJ + Randy + Hidden
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Dr Kathy Rule:
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
ECC11 Randy Rule:
Eng. Mohamed Jama
Level 2 - Technical Analyzes
IM
Lesson 17: The Power of twin Trading + TP1, TP2 & TP3
Eng. Mohamed Jama
You might also like
- The Three Point Reversal Method of Point & Figure Stock Market Trading by A.W. CohenDocument129 pagesThe Three Point Reversal Method of Point & Figure Stock Market Trading by A.W. CohenSal Cibus92% (26)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesFrom Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Carter J - Using Voodoo Lines-1 PDFDocument34 pagesCarter J - Using Voodoo Lines-1 PDFShabir Rizwan0% (1)
- I3T3 MEGA WEBINAR - 3 & 4 Module - Advanced Price Action TradingDocument3 pagesI3T3 MEGA WEBINAR - 3 & 4 Module - Advanced Price Action TradingLive NIfty0% (1)
- CMT CourseDocument8 pagesCMT Coursekumarkeshav50% (2)
- Trading Pivot PointsDocument5 pagesTrading Pivot Pointsherbak100% (1)
- CMT Level 1 Reading List 2011Document5 pagesCMT Level 1 Reading List 2011jeremysteinerNo ratings yet
- RP Moving Average Compedium The First WeaponDocument50 pagesRP Moving Average Compedium The First WeaponUserNo ratings yet
- Dark Cloud CoverDocument10 pagesDark Cloud Coverastro secretesNo ratings yet
- Patterns Fibo Candles IchimokuDocument82 pagesPatterns Fibo Candles IchimokuGeorge Akrivos88% (24)
- Andro STMEDocument17 pagesAndro STMEadesemowoadedareNo ratings yet
- An Implementation of Genetic Algorithms As A Basis For A Trading System On The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument7 pagesAn Implementation of Genetic Algorithms As A Basis For A Trading System On The Foreign Exchange Marketsatish sNo ratings yet
- Classroom: How To Identify Support & Resistance On Technical ChartsDocument11 pagesClassroom: How To Identify Support & Resistance On Technical ChartsusmanNo ratings yet
- 450 - Waves Strategy Advisors - Technical Analysis 20150403Document2 pages450 - Waves Strategy Advisors - Technical Analysis 20150403Suman Kumar50% (2)
- MDP - Technical Analysis - Web Brochure - Sep - 2015Document8 pagesMDP - Technical Analysis - Web Brochure - Sep - 2015Rupesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis EbookDocument83 pagesTechnical Analysis EbookFabio Baroni100% (1)
- Combining Trend and Oscillator SignalsDocument11 pagesCombining Trend and Oscillator SignalsKoyasanNo ratings yet
- Technical Analysis of Commonditie. (Gold, Silver, Zinc & Crude Oil) at Motilal Oswal Securities LTDDocument58 pagesTechnical Analysis of Commonditie. (Gold, Silver, Zinc & Crude Oil) at Motilal Oswal Securities LTDKirankumar AriNo ratings yet
- Complete Forex Market StructureDocument11 pagesComplete Forex Market Structureglyrad12No ratings yet
- Trade Plan StrategiesDocument5 pagesTrade Plan StrategiespithagorasNo ratings yet
- Smart Index Trader Programme: AcademyDocument8 pagesSmart Index Trader Programme: AcademyMadhur ChopraNo ratings yet
- Master Technical AnalysisDocument7 pagesMaster Technical AnalysissatishdinakarNo ratings yet
- Technical AnalysisDocument19 pagesTechnical AnalysisTarunima TabassumNo ratings yet
- NSE - Smart Index Trader Programme - Brochure SITP - Sept 20Document10 pagesNSE - Smart Index Trader Programme - Brochure SITP - Sept 20Viswa KeerthiNo ratings yet
- Pit Pivot PointsDocument7 pagesPit Pivot Pointsbua7582No ratings yet
- TYBFM - Technical Analysis FinalDocument57 pagesTYBFM - Technical Analysis Finalvyomthakkar17No ratings yet
- Program ON Technical Analysis FOR Successful Trading/ InvestingDocument6 pagesProgram ON Technical Analysis FOR Successful Trading/ InvestingkalelenikhlNo ratings yet
- What Are Pivots and Who CaresDocument7 pagesWhat Are Pivots and Who Careshaskellb2301No ratings yet
- File: Like ReplyDocument1 pageFile: Like ReplyTepongTalamNo ratings yet
- TMS-II Preview NotesDocument4 pagesTMS-II Preview NotesParesh ShahNo ratings yet
- AlphaFX Price Action Practical Guide v2Document82 pagesAlphaFX Price Action Practical Guide v2absar ahmed67% (3)
- Professional TrainingDocument2 pagesProfessional TrainingBreak ForexNo ratings yet
- Basic Stock Trading and Technical Analysis ModuleDocument1 pageBasic Stock Trading and Technical Analysis ModuleDhirajNo ratings yet
- 2007 CMTLevel 1Document5 pages2007 CMTLevel 1Mood OkNo ratings yet
- 201 Technical Analysis CourseDocument10 pages201 Technical Analysis CourseadityaNo ratings yet
- Stock MarketDocument10 pagesStock MarketmareddyNo ratings yet
- Technical Trading - Case6Document19 pagesTechnical Trading - Case6Avinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Trendsin Stock MarketDocument7 pagesTrendsin Stock MarketRahil KhanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 - Technical Analysis in InvestmentDocument22 pagesUNIT 5 - Technical Analysis in InvestmentmoltenadNo ratings yet
- VWAP Trading: Trade With TrendDocument22 pagesVWAP Trading: Trade With TrendAvijit Majumdar100% (1)
- TraderTalk, Pivot Points and Daily Support and ResistanceDocument3 pagesTraderTalk, Pivot Points and Daily Support and ResistanceSIightlyNo ratings yet
- TradeZilla 2.0 - Discover Your Trading EdgeDocument2 pagesTradeZilla 2.0 - Discover Your Trading EdgeAyesha MariyaNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Support & Resistance Levels - Chart of MIC ElectronicsDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Support & Resistance Levels - Chart of MIC ElectronicsVisu SamyNo ratings yet
- Wise Day Trading Strategy v.2 FREEDocument15 pagesWise Day Trading Strategy v.2 FREEarpittripathi.bhilwaraNo ratings yet
- M&T IndicatorsDocument12 pagesM&T Indicatorskaaviraj2020No ratings yet
- Techinacl Anlysis Report of Task 1 &2Document24 pagesTechinacl Anlysis Report of Task 1 &2Godha ManitejaNo ratings yet
- Commodity Trading CourseDocument6 pagesCommodity Trading CourseApNo ratings yet
- Technical and Fundamental AnalysisDocument9 pagesTechnical and Fundamental Analysistiktokmili77No ratings yet
- 17.forecasting of Forex Market Using Technical AnalysisDocument65 pages17.forecasting of Forex Market Using Technical Analysisharrydeepak100% (1)
- TECHNICAL ANALYSIS FOR BEGINNERS: A Beginner's Guide to Mastering Technical Analysis (2024 Crash Course)From EverandTECHNICAL ANALYSIS FOR BEGINNERS: A Beginner's Guide to Mastering Technical Analysis (2024 Crash Course)No ratings yet
- MMTC Student's Manual 2021Document105 pagesMMTC Student's Manual 2021Priyanshu Gupta100% (1)
- MMTC Student's Manual 2021Document105 pagesMMTC Student's Manual 2021Scribd ReaderNo ratings yet
- So, - You - Want - To - Thread - by - TRSTNGLRD - Dec 19, 22 - From - RattibhaDocument16 pagesSo, - You - Want - To - Thread - by - TRSTNGLRD - Dec 19, 22 - From - Rattibhasami lyNo ratings yet
- Refined MacdDocument17 pagesRefined Macdapolodoro7No ratings yet
- TC OverviewDocument2 pagesTC Overviewrk makNo ratings yet
- Technical AnalysisDocument2 pagesTechnical AnalysisKaushal LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Chartered Market Technician (CMT) Program - Level III: Exam Time Length: 4 Hours, 15 Minutes Exam Format: Short AnswerDocument6 pagesChartered Market Technician (CMT) Program - Level III: Exam Time Length: 4 Hours, 15 Minutes Exam Format: Short AnswerShailesh KhodkeNo ratings yet
- An Intelligent Market Making Strategy in PDFDocument13 pagesAn Intelligent Market Making Strategy in PDFLuca PilottiNo ratings yet
- A Mehanical Trading System Tom Joseph PDFDocument83 pagesA Mehanical Trading System Tom Joseph PDFDejan Jankuloski100% (1)
- Interpreting Technical IndicatorsDocument39 pagesInterpreting Technical Indicatorsapi-19771937No ratings yet
- MBA Analytics For Finance 13Document10 pagesMBA Analytics For Finance 13JOJONo ratings yet
- Trading Tactics in the Financial Market: Mathematical Methods to Improve PerformanceFrom EverandTrading Tactics in the Financial Market: Mathematical Methods to Improve PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Day Trading Strategies: Momentum Indicators: Day Trading Made Easy, #5From EverandDay Trading Strategies: Momentum Indicators: Day Trading Made Easy, #5No ratings yet
- Document PlanDocument2 pagesDocument PlanAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document10 pagesCH 6AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document19 pagesCH 5AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document10 pagesCH 4AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document7 pagesCH 3AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document12 pagesCH 1AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three ISO 9000 - Quality Management Planning: - Project RequirementsDocument26 pagesChapter Three ISO 9000 - Quality Management Planning: - Project RequirementsAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 1 Unit 3Document11 pagesFinancial Accounting 1 Unit 3AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document6 pagesCH 2AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Quality Management Must Know" Concepts For EngineersDocument22 pagesChapter One Quality Management Must Know" Concepts For EngineersAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1Document16 pagesChapter 2-1AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- CH - 6 Sampling Design and ProcedureDocument7 pagesCH - 6 Sampling Design and ProcedureAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 1 Unit 2Document22 pagesFinancial Accounting 1 Unit 2AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1. Definition: Coulomb (1773) Is Credited As The First Person To Use Mechanics To Solve Soil ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter One 1. Definition: Coulomb (1773) Is Credited As The First Person To Use Mechanics To Solve Soil ProblemsAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Research Methods: An Introduction 1. Overview of ResearchDocument8 pagesChapter One Research Methods: An Introduction 1. Overview of ResearchAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- R A & F Analysis & Interpretation OF DataDocument4 pagesR A & F Analysis & Interpretation OF DataAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Ece 204 Early Childhood Curriculum DevelopmentDocument114 pagesEce 204 Early Childhood Curriculum DevelopmentAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Research Report WritingDocument11 pagesResearch Report WritingAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- R A & F Data Collection Methods S - : It Has Predetermined Questions, ButDocument8 pagesR A & F Data Collection Methods S - : It Has Predetermined Questions, ButAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- R A & F Sampling IN Research S /SDocument5 pagesR A & F Sampling IN Research S /SAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Name of The Student Name of The School Registration Number: Instructions To CandidatesDocument7 pagesName of The Student Name of The School Registration Number: Instructions To CandidatesAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- RM-Research Design CH 2Document10 pagesRM-Research Design CH 2AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Qualitative Data Collection Methods and Devices: StructureDocument14 pagesUnit 2 Qualitative Data Collection Methods and Devices: StructureAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- R A & F Negotiating Access AND Research EthicsDocument3 pagesR A & F Negotiating Access AND Research EthicsAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Q 5 and 6Document37 pagesQ 5 and 6AbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Job And: Let Us Consider An Example From Our Daily Life. A Problem ThatDocument23 pagesJob And: Let Us Consider An Example From Our Daily Life. A Problem ThatAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- 108 VectorsDocument8 pages108 VectorsAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Community Mobilizer's Guide - EnglishDocument20 pagesCommunity Mobilizer's Guide - EnglishAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Ichimoku Analysis Sheet: P1: Ota BM JWBT273-Patel April 15, 2010 10:28 Printer: Yet To ComeDocument4 pagesIchimoku Analysis Sheet: P1: Ota BM JWBT273-Patel April 15, 2010 10:28 Printer: Yet To ComeMarcin P. FokaNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Moving Averages That Come With Market Liberator ADocument3 pagesHow To Use The Moving Averages That Come With Market Liberator ABabar MairajNo ratings yet
- 06 - Class 06 - Trade SetupsDocument12 pages06 - Class 06 - Trade SetupsChandler BingNo ratings yet
- Avwap FinalDocument12 pagesAvwap FinalRaviVerma0% (1)
- Andrew Lockwood: Trading Cheat SheetDocument20 pagesAndrew Lockwood: Trading Cheat SheetSeptiandi hendra SaputraNo ratings yet
- Методичка DR.ru.enDocument10 pagesМетодичка DR.ru.enSooraj SureshNo ratings yet
- Price Action Reversal StrategiesDocument7 pagesPrice Action Reversal Strategiesmanoj tomer100% (1)
- The RSI Pro The Core PrinciplesDocument34 pagesThe RSI Pro The Core PrinciplesHậu Đình NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Candle Stick ChartDocument10 pagesCandle Stick ChartbhuwanrpNo ratings yet
- Retire Young Forex Technical and Tactical Ebook: Y: Forex Mantra'S #MantraslegendDocument49 pagesRetire Young Forex Technical and Tactical Ebook: Y: Forex Mantra'S #MantraslegendCửu Lộc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- PDF Cci Trading CompressDocument7 pagesPDF Cci Trading CompressefendygtNo ratings yet
- SL Vip SecretDocument12 pagesSL Vip SecretYo Oo100% (1)
- Getting The GMMA RightDocument4 pagesGetting The GMMA RightBudi MulyonoNo ratings yet
- The All-Time High Stock System: Profit With WinnersDocument4 pagesThe All-Time High Stock System: Profit With WinnersFacuNo ratings yet
- Price Action Simplified by EmzetDocument25 pagesPrice Action Simplified by EmzetEmzet PremiseNo ratings yet
- Indicator Candlesticks Strong Trade SetupsDocument10 pagesIndicator Candlesticks Strong Trade SetupsQuang Daodang100% (1)
- Trading With RSI (2) Marke..Document8 pagesTrading With RSI (2) Marke..pderby1No ratings yet
- Alphaex Capital Candlestick Pattern Cheat Sheet InfographDocument1 pageAlphaex Capital Candlestick Pattern Cheat Sheet InfographFnudarman Fnudarman100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Rate of ChangeDocument37 pagesChapter 5 - Rate of ChangeNAJWA SYAKIRAH MOHD SHAMSUDDINNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Elliot Wave Corrective Rules and CharacteristicsDocument23 pages10.1 Elliot Wave Corrective Rules and CharacteristicsJustin Lim100% (1)
- Lower Low - Lower HighDocument5 pagesLower Low - Lower Highkarthick sudharsanNo ratings yet
- The Cartography Corner, March 2021Document9 pagesThe Cartography Corner, March 2021Speculation OnlyNo ratings yet
- Free Price Action Trading PDF GuideDocument20 pagesFree Price Action Trading PDF GuideSimamkele Ntwanambi100% (1)
- 2.1 2 Candlestick Patterns Price ActionDocument10 pages2.1 2 Candlestick Patterns Price ActionGwenethvine EscalanteNo ratings yet
- HondaHero Honda TEchnical AnalysisDocument126 pagesHondaHero Honda TEchnical AnalysisrahulNo ratings yet