Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Performance Evaluation Using Variances From Standard Costs
Uploaded by
Jhoylie BesinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Performance Evaluation Using Variances From Standard Costs
Uploaded by
Jhoylie BesinCopyright:
Available Formats
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION USING VARIANCES FROM STANDARD COSTS
Key points
1
2
5
6
8
9
10
11
NONFINANCIAL PERFORMANCE MEASURE
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION USING VARIANCES FROM STANDARD COSTS
Key points
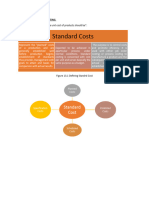
Standards represent performance goals that can be compare to actual results in evaluating performance.
Standards are established so that they are neither too high or too low, but are attainable
Budgets are prepared by multiplying the standard cost per unit by the planned production.
To measure performance, the standard cost per unit is multiplied by the actual number of units produced and
the actual results are compared with the standard cost at actual volumes (cost variance)
Direct materials cost variance can be separated into direct material price and quantity variance
The direct labor cost variance can be separated into direct labor rate and time variances
The factory overhead cost variance can be separated into a variable factory overhead controllable variance
and a fixed factory overhead volume variance
Standard costs and variances can be recorded in the accounts at the same time the manufacturing costs are
recorded in the accounts
Work in process is debited at standard.
under standard cost system, the COGS will be reported at standard cost
Manufacturing variances can be disclosed on the income statement to adjust the gross profit at standard to the actual gross
NONFINANCIAL PERFORMANCE MEASURE
expresses performance in a measure other than dollars
1. inventory turnover
2. percent on-time delivery
3. elapsed time between a customer order and product delivery
4. customer preference rankings compared to competitors
5. response time to a service call
6. time to develop new products
7. employee satisfaction
8. number of customer complaints
dard to the actual gross profit
You might also like
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mas 9403 Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument21 pagesMas 9403 Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisBanna SplitNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Raiborn Smdoc PDF FreeDocument49 pagesCh7 Raiborn Smdoc PDF FreeTiffany Monique ValienteNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 - Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument7 pagesMODULE 4 - Standard Costing and Variance AnalysissampdnimNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument82 pagesStandard CostingLucio Indiana WalazaNo ratings yet
- Mas 9203 - Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument20 pagesMas 9203 - Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisShefannie PaynanteNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis InsightsDocument6 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis InsightsClouie Anne TogleNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: A Functional-Based Control Approach: Questions For Writing and DiscussionDocument40 pagesStandard Costing: A Functional-Based Control Approach: Questions For Writing and DiscussionKeith Alison Arellano100% (1)
- Essay Los 2015 Section D. Cost Management 20 %Document18 pagesEssay Los 2015 Section D. Cost Management 20 %lassaadNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis GuideDocument17 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis GuideDave DinopolNo ratings yet
- Overhead Costing and Activity Based Costing (W)Document11 pagesOverhead Costing and Activity Based Costing (W)Muhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument6 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisCeacer Julio SsekatawaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis ExplainedDocument15 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis ExplainedRashi Desai100% (1)
- Gross Profit MarginDocument3 pagesGross Profit MarginShie RontaloNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING (Learning Insights)Document1 pageSTANDARD COSTING (Learning Insights)Riel BerdigayNo ratings yet
- LP5 Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument23 pagesLP5 Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisGwynette DalawisNo ratings yet
- Mas 9303 - Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument21 pagesMas 9303 - Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisJowel BernabeNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing and Varibale CostingDocument6 pagesAbsorption Costing and Varibale Costinghoney beeNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument7 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisNicko CrisoloNo ratings yet
- MODULE 8 Standard CostingDocument11 pagesMODULE 8 Standard CostingAlexandra AbasNo ratings yet
- MS103 SendingDocument3 pagesMS103 SendingEthel Joy Tolentino GamboaNo ratings yet
- 209384Document14 pages209384Jayson HoangNo ratings yet
- W1 Cost 1 LessonDocument11 pagesW1 Cost 1 LessonMoniette JimenezNo ratings yet
- MAS 3 - Standard Costing For UploadDocument9 pagesMAS 3 - Standard Costing For UploadJD SolañaNo ratings yet
- MAS Absorption Costing/Variable Costing Study ObjectivesDocument6 pagesMAS Absorption Costing/Variable Costing Study ObjectivesMarjorie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance Analysis ExplainedDocument40 pagesStandard Costing & Variance Analysis ExplainedNguyễn Thanh MaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Ailene QuintoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Standard Cost Accounting CompressDocument13 pagesChapter 8 Standard Cost Accounting CompressJohn Kenneth Jarce CaminoNo ratings yet
- Mas 2605Document6 pagesMas 2605John Philip CastroNo ratings yet
- Sec C - Cost Behavior and Cost ObjectsDocument11 pagesSec C - Cost Behavior and Cost ObjectsDao Mai PhuongNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Raiborn and Kinney Solman Chapter 07 CompressDocument35 pagesCost Accounting Raiborn and Kinney Solman Chapter 07 CompressMa. Paula JabunganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Standard CostingDocument8 pagesChapter 8 - Standard CostingJoey LazarteNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Standard CostingDocument43 pagesQuiz - Standard CostingDan RyanNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument56 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisJoyce Mamoko100% (2)
- Standard Costing Variance AnalysisDocument95 pagesStandard Costing Variance AnalysisErika Villanueva MagallanesNo ratings yet
- ACT121 - Topic 5Document5 pagesACT121 - Topic 5Juan FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument30 pagesStandard CostingDivine DaduyaNo ratings yet
- Account 203Document1 pageAccount 203RAVI KISHANNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument31 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisFrederick GbliNo ratings yet
- Vendmart - TheDocument6 pagesVendmart - TheSagarrajaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Systems ExplainedDocument11 pagesStandard Costing Systems Explainedace zeroNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5: Objectives of Standard CostingDocument16 pagesUnit - 5: Objectives of Standard CostingThigilpandi07 YTNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation Using Variances From Standard Costs: Class Discussion QuestionsDocument48 pagesPerformance Evaluation Using Variances From Standard Costs: Class Discussion QuestionsMoko ajaNo ratings yet
- MS 3404 Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument6 pagesMS 3404 Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mas 1304Document5 pagesMas 1304Vel JuneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Standard CostingDocument9 pagesChapter 13 Standard Costingprmsusecgen.nfjpia2324No ratings yet
- 04 Absorption Vs Variable CostingDocument4 pages04 Absorption Vs Variable CostingBanna SplitNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Introduction To Standard CostingDocument15 pagesUnit 5: Introduction To Standard CostingAsim Hasan UsmaniNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument5 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingAllan Jay CabreraNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis FullDocument83 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis FullGian Carlo Ramones0% (1)
- STCM 03AbsorptionandVariableCostingDocument5 pagesSTCM 03AbsorptionandVariableCostingdin matanguihanNo ratings yet
- Flexible budgeting for overhead cost controlDocument4 pagesFlexible budgeting for overhead cost controlHuong LanNo ratings yet
- Standard Costs Presentation v2Document7 pagesStandard Costs Presentation v2Joel BartolomeNo ratings yet
- C.A Standard CostingDocument26 pagesC.A Standard CostingMaya Shetty100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Standard Costing PDFDocument107 pagesChapter 5 Standard Costing PDFjigyasaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Standard CostingDocument49 pagesModule 8 - Standard Costingkaizen4apexNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Questions and Their AnswersDocument5 pagesCost Accounting Questions and Their Answerszulqarnainhaider450_No ratings yet
- WMSU Chapter 3 Costing MethodsDocument6 pagesWMSU Chapter 3 Costing Methodschelsea kayle licomes fuentesNo ratings yet
- A Synthesis On Global International IssuesDocument2 pagesA Synthesis On Global International IssuesJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Emergency Loan (Active Member) Application FormDocument2 pagesEmergency Loan (Active Member) Application FormenzoNo ratings yet
- Transformers Movie Guide & ReviewsDocument1 pageTransformers Movie Guide & ReviewsJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- A Synthesis On Basic Concepts of Strategic ManagemDocument2 pagesA Synthesis On Basic Concepts of Strategic ManagemJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Steps in Decision MakingDocument2 pagesSteps in Decision MakingJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Emergency Loan (Active Member) Application FormDocument2 pagesEmergency Loan (Active Member) Application FormenzoNo ratings yet
- Transformers Movie Guide & ReviewsDocument1 pageTransformers Movie Guide & ReviewsJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- CSC Form 6 (Leave Form-New)Document3 pagesCSC Form 6 (Leave Form-New)Jhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis 3. Jona Car RentalDocument1 pageCase Analysis 3. Jona Car RentalJhoylie Besin86% (7)
- Case Analysis 3. Jona Car RentalDocument1 pageCase Analysis 3. Jona Car RentalJhoylie Besin86% (7)
- Dynamics of Management Course Outline Xavier UniversityDocument5 pagesDynamics of Management Course Outline Xavier UniversityJhoylie Besin100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter 2018 Social Security System PPA ReportDocument2 pages2nd Quarter 2018 Social Security System PPA ReportJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATIONDocument83 pagesMOTIVATIONJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Org Structure and DesignDocument30 pagesOrg Structure and DesignJhoia BesinNo ratings yet
- COA Employee Handbook GuideDocument85 pagesCOA Employee Handbook GuideBilly Nortyu73% (11)
- Case Analysis 5. Hillbilly CaseDocument2 pagesCase Analysis 5. Hillbilly CaseJhoylie Besin60% (25)
- Required ExpertsDocument1 pageRequired ExpertsJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Coa Vacancies01242018Document59 pagesCoa Vacancies01242018Due WellNo ratings yet
- Ra 10587Document14 pagesRa 10587Cesar ValeraNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Travel CompletedDocument1 pageCertificate of Travel CompletedJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- CP Case No. 2011-029 14624Document1 pageCP Case No. 2011-029 14624Jhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Coa C2014-001Document10 pagesCoa C2014-001JOHAYNIENo ratings yet
- Audit Engagement Monitoring System: March 2017Document20 pagesAudit Engagement Monitoring System: March 2017Jhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- AdminComplianceJointAssessQuestionnaire March 09 PDFDocument16 pagesAdminComplianceJointAssessQuestionnaire March 09 PDFJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- The State Audit Code of the PhilippinesDocument37 pagesThe State Audit Code of the PhilippinesDswdCoaNo ratings yet
- Control Self AssessmentDocument4 pagesControl Self AssessmentLiew Chee KiongNo ratings yet
- Revised Standards On FoodDocument10 pagesRevised Standards On FoodJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet
- Coa C2012-003 PDFDocument28 pagesCoa C2012-003 PDFRolly AcunaNo ratings yet
- Competencies:: Must Have Communication Skills Knowledgeable in Underwriting/claimsDocument3 pagesCompetencies:: Must Have Communication Skills Knowledgeable in Underwriting/claimsJhoylie BesinNo ratings yet