Professional Documents
Culture Documents
My Copy HW Proteins Enzymes
Uploaded by
api-521781723Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
My Copy HW Proteins Enzymes
Uploaded by
api-521781723Copyright:
Available Formats
HW Proteins/Enzymes
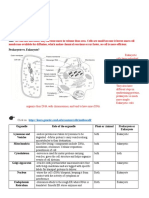
Find a model and label all these parts :
1. Enzyme, active site, enzyme- substrate complex, hydrogen bond, induced fit, correct orientation, substrate,
reactant, products, hydrolysis, water, maltose, glucose x2, feedback inhibition, off, on, allosteric site, reused,
denaturation, increase in temperature, protein shape.
Products:
Glucosex
Reactants: Maltose 2
Enzyme
Substrate substrate
Reaction=Hydrolysis
complex
; results in water
Active Site
Enzyme Induced Fit/ Correct Enzyme reused
Allosteric Site orientation
(Enzyme On) OH - - - H
Hydrogen Bond (Change in protein
shape)-Enzyme off
Increase in temp.
Denaturation;
change in protein
shape Feedback inhibition
2. Explain why the environment of an enzyme is so important for the functionality of an enzyme.
The environment of an enzyme is so important for the functionality of an enzyme because the factors in the
environment; such as drastic change in pH or temperature can break the bonds in the secondary or tertiary
structure of the enzyme. When these bonds break the enzyme will not be the same shape, meaning the substrate
will no longer be able to fit into the enzyme affecting the functionality.
Explain 2 ways how an enzyme can be inhibited.
Enzymes can be inhibited with a competitive inhibitor; which is a molecule that blocks the active site of an enzyme
meaning the substrate cannot attach to the enzyme. They can also be inhibited with a non-competitive inhibitor; this is a
molecule that attaches to the allosteric site of an enzyme which then changes the shape of the active site, prohibiting the
substrate from then attaching to it.
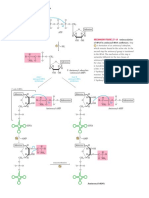
The following is an (admittedly terrible) representation of an enzyme protein folded into its proper 3-D
conformation. Go to the amino acid sheet from the textbook so you can see all the amino acids to answer some of
the questions below.
active site (involves amino acids 212,
213, 240, 242)
non-binding region (involves amino
allosteric site acids 304 - 307)
(involves amino acids
406, 407, 415, 417)
3. Let’s say that the proper amino acid sequence for the active site region (AAs 212, 213, 240 and 242) are the
following: Ser, Gln, Asn, Thr
A DNA mutation occurs that changes one of these amino acids – which change below will have a more detrimental
effect on the active site shape (and thus negatively affect its ability to bind to the proper substrate chemical)? Justify
your answer.
mutation 1: Ser, Tyr, Asn, Thr
mutation 2: Ser, Ala, Asn, Thr
Mutation 2 would have a more detrimental effect because in the original sequence, all the molecules are polar,
meaning they would be attracted to each other. However, Tyr is also a polar molecule, meaning it will likely
resemble close to the original sequence. However, Ala is a nonpolar molecule, meaning that there would most
likely be a change in folds since the molecule will not be attracted to the rest of the molecules. The remaining
molecules will likely surround the nonpolar molecule because they are attracted to each other and not the
nonpolar molecule, and surrounding the nonpolar molecule maximizes the surface area. This would probably
change the folding of the enzyme and have an effect on the active site shape.
You might also like
- NQO1: A Viable Biomarker For Colorectal CancerDocument1 pageNQO1: A Viable Biomarker For Colorectal CancerThe Only OneNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CompletedDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 Completedabby meadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics I (Statics) Spring 2015 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics I (Statics) Spring 2015 SyllabusTyler AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Empty Template-CompressedDocument6 pagesAssignment 4 Empty Template-Compressedabby meadNo ratings yet
- Quiz and BlueprintDocument6 pagesQuiz and Blueprintapi-545998611No ratings yet
- Biology 30 Syllabus 2020Document6 pagesBiology 30 Syllabus 2020api-236289588No ratings yet
- CompleteDocument9 pagesCompleteabby meadNo ratings yet
- Dott 1964 - Wacke, Graywacke and Matrixx - What Approach To Inmmature Sandstone Classification PDFDocument8 pagesDott 1964 - Wacke, Graywacke and Matrixx - What Approach To Inmmature Sandstone Classification PDFAlisson OrtegaNo ratings yet
- HW Proteins EnzymesDocument2 pagesHW Proteins Enzymesapi-524061079No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Enzymes: 4.1 Catalysis and Activation EnergyDocument16 pagesChapter 4: Enzymes: 4.1 Catalysis and Activation EnergyXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationDocument35 pagesEnzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: EnzymeDocument4 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: EnzymeMark Jayson ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biological Catalysts that Speed Up ReactionsDocument6 pagesEnzymes: Biological Catalysts that Speed Up ReactionsSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemistryLee LuceroNo ratings yet
- AP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersDocument12 pagesAP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersMehak BectorNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 3Document6 pagesEnzymes 3MituSamadderNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument46 pagesEnzymesHighlifeNo ratings yet
- GSDGSGDocument2 pagesGSDGSGLiling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- Amylase Activity Lab QUBES.v4-7386Document26 pagesAmylase Activity Lab QUBES.v4-7386Veneta GizdakovaNo ratings yet
- OUTLINE8Document8 pagesOUTLINE8Hjm ArNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BiocatalysisDocument8 pagesChapter 4 BiocatalysisNur HananiNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesAstro KeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman: Smt. Sharadchandrika Suresh Patil College of Pharmacy, Chopda, Maharashtra, IndiaDocument20 pagesDr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman: Smt. Sharadchandrika Suresh Patil College of Pharmacy, Chopda, Maharashtra, IndiaAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Enzyme InhibitionDocument124 pagesEnzyme Inhibitionayushi100% (1)
- Enzyme: Mode of Action of EnzymeDocument5 pagesEnzyme: Mode of Action of EnzymeAliza KhanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: TOPICS 3.6 AND 7.6Document27 pagesEnzymes: TOPICS 3.6 AND 7.6Khoi MaiNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument52 pagesBiochem NotesAnonymous 4Ib1ByFC100% (2)
- 2.1.4 Biology Ocr ADocument5 pages2.1.4 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNo ratings yet
- S.5 EnzymesDocument16 pagesS.5 Enzymesmusokelukia6No ratings yet
- EnzymologyDocument13 pagesEnzymologyRane MandapatNo ratings yet
- Biochem (Finals)Document5 pagesBiochem (Finals)cjyulo99710No ratings yet
- Cell Bio Chapter 6Document32 pagesCell Bio Chapter 6GuteNo ratings yet
- Biology presentation on enzymesDocument21 pagesBiology presentation on enzymesCarolina AnnNo ratings yet
- 222 Unit 3Document103 pages222 Unit 3Ning BalderasNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Properties of EnzymesDocument7 pagesCharacteristic Properties of EnzymesCaden LeeNo ratings yet
- $RZ2YE8ODocument2 pages$RZ2YE8OCrow LordNo ratings yet
- Lab 2. Enzyme Action-Effect of Enzyme Concentration, Temperature and PH On Catalase ActivityDocument24 pagesLab 2. Enzyme Action-Effect of Enzyme Concentration, Temperature and PH On Catalase ActivityRicardo SimõesNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.5 Enzymes: U.1. Enzymes Have An Active Site To Which Specific Substrates BindDocument7 pagesTopic 2.5 Enzymes: U.1. Enzymes Have An Active Site To Which Specific Substrates BindMajo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - BiochemistryDocument40 pagesEnzymes - Biochemistrysunil patelNo ratings yet
- Essential Idea: Enzymes Control The Metabolism of The Cell.: Sigma-Nicholson Metabolic Pathways ChartDocument21 pagesEssential Idea: Enzymes Control The Metabolism of The Cell.: Sigma-Nicholson Metabolic Pathways ChartMike BevanNo ratings yet
- 2.5 PPTDocument18 pages2.5 PPThzunigaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Enzymes 2022Document26 pages2.5 Enzymes 2022Katleho MokheleNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Enzymes PaineDocument21 pages2.5 Enzymes PaineIker GNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesArabela SimanganNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: By: Angela Marie Ferrer BSN 2BDocument13 pagesBiochemistry: By: Angela Marie Ferrer BSN 2BNoemi Martinez FerrerNo ratings yet
- P.Babu M.Pharm.,Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument72 pagesP.Babu M.Pharm.,Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryBabu Palani100% (1)
- CC-LEC-NOTES-1Document4 pagesCC-LEC-NOTES-1CDNo ratings yet
- C4 (Biocatalysis)Document12 pagesC4 (Biocatalysis)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- MCAT - BioDocument64 pagesMCAT - BioUmair KhanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Anushree ChaturvediDocument39 pagesEnzymes: Anushree ChaturvediDeepal ShahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 3 - EnzymesDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 3 - EnzymesMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesOliver QNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Specific Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical: Constituents of Enzyme MoleculeDocument6 pagesEnzyme: Specific Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical: Constituents of Enzyme MoleculeAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PPTDocument39 pagesEnzymes PPTsunil patelNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting ActivityDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting Activitytiyf mojaleedNo ratings yet
- Assignment #5 EnzymesDocument5 pagesAssignment #5 EnzymesFengari CresentNo ratings yet
- 2 5enzymesDocument28 pages2 5enzymesKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Final Study On EnzymeDocument9 pagesFinal Study On Enzymerosariopraveen007No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument22 pagesEnzymeslovelykissNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Heredity Unit Study Guide Part 1Document7 pagesReproduction and Heredity Unit Study Guide Part 1api-521781723100% (1)
- Metabolic Pathways Study Guide MyDocument12 pagesMetabolic Pathways Study Guide Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life Unit Book Guide: Chapter 1: Reviewing Introductory BiologyDocument6 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life Unit Book Guide: Chapter 1: Reviewing Introductory Biologyapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Fall Semester Review 2020Document5 pagesFall Semester Review 2020api-521781723No ratings yet
- Signaling Pathways Unit Study Guide MyDocument11 pagesSignaling Pathways Unit Study Guide Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Cells and Transport Study Guide MyDocument12 pagesCells and Transport Study Guide Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- My Copy Building Blocks of Life Study GuideDocument12 pagesMy Copy Building Blocks of Life Study Guideapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Model Two Show 1 Signaling PathwaysDocument2 pagesModel Two Show 1 Signaling Pathwaysapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Inihibitors Review MyDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Inihibitors Review Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument3 pagesFeedback Mechanismapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ModelingDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Modelingapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Organism Energetics ReviewDocument2 pagesOrganism Energetics Reviewapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Reviewing Mitosis Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesReviewing Mitosis Discussion Questionsapi-521773978No ratings yet
- Immune System Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesImmune System Review Questionsapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 HWDocument4 pagesChapter 8 HWapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Overview Chapter 11 QuestionsDocument1 pageOverview Chapter 11 Questionsapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Respiration DiagramDocument3 pagesRespiration Diagramapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Chapter 36 Water Potential HWDocument3 pagesChapter 36 Water Potential HWapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Diffusion Gizme ScreenshotsDocument3 pagesDiffusion Gizme Screenshotsapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation Inhibition ActivityDocument2 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation Inhibition Activityapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Water Potential Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesWater Potential Word Problemsapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Cell Modeling 1 MyDocument2 pagesCell Modeling 1 Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Why Are Cells So Small MyDocument2 pagesWhy Are Cells So Small Myapi-521781723No ratings yet
- My Copyautotrophs and Hetertrophs Making Macromolecules HWDocument3 pagesMy Copyautotrophs and Hetertrophs Making Macromolecules HWapi-521781723No ratings yet
- My Copy Cell Organelle Ws 1Document4 pagesMy Copy Cell Organelle Ws 1api-521781723No ratings yet
- Claire Enzyme LabDocument2 pagesClaire Enzyme Labapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cell Transport HWDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Cell Transport HWapi-521781723No ratings yet
- My Copyprotein Folding Virtual ActivityDocument7 pagesMy Copyprotein Folding Virtual Activityapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Nutrition Label Ap ProjectDocument5 pagesNutrition Label Ap Projectapi-521781723No ratings yet
- Simplechip Plus Enzymatic Chromatin Ip Kit (Magnetic Beads)Document8 pagesSimplechip Plus Enzymatic Chromatin Ip Kit (Magnetic Beads)chan ka yuNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lec4 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocument23 pagesGenbio Lec4 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsErika Jane BulanhaguiNo ratings yet
- Alteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensDocument7 pagesAlteration of Host Cell Behavior by PathogensAbhijit SatpatiNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of drug action and pharmacodynamicsDocument47 pagesMechanisms of drug action and pharmacodynamicseciNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument40 pagesElectron Transport ChainUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ZymogramDocument18 pagesZymogramSubhradeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument25 pagesCilia and FlagellaLia Savitri RomdaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication PDFDocument109 pagesCell Communication PDFediaz_956003100% (1)
- Rho-Family Gtpases: It'S Not Only Rac and Rho (And I Like It)Document12 pagesRho-Family Gtpases: It'S Not Only Rac and Rho (And I Like It)Akhilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- 3.#Amino#Acids# (Chapter#4) #: Proteins#And## Protein#Funclons#Document11 pages3.#Amino#Acids# (Chapter#4) #: Proteins#And## Protein#Funclons#Ferell GerryNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA codon table with protein size calculationDocument2 pagesDNA and RNA codon table with protein size calculationM.TAUFIQ HIDAYATNo ratings yet
- Invitrogen 2012Document251 pagesInvitrogen 2012Deepak Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Calculations of Enzyme Activity Units and RatesDocument12 pagesCalculations of Enzyme Activity Units and RatesksboopathiNo ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism PDFDocument15 pagesProtein Metabolism PDFFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Student Biographies and Elastin BiologyDocument4 pagesGroup 2 Student Biographies and Elastin BiologyRay CanivelNo ratings yet
- Enzyme MCQ Study Guide ReviewDocument5 pagesEnzyme MCQ Study Guide ReviewMrs Rehan100% (1)
- Biochemistry of Enzymes & Clinical Enzymology: By: Tesfahun MollaDocument156 pagesBiochemistry of Enzymes & Clinical Enzymology: By: Tesfahun MollaAddis MémñøňNo ratings yet
- Lec 04 TranscriptDocument11 pagesLec 04 TranscriptbujjbabuNo ratings yet
- The Bacterial Cytoskeleton 1Document2 pagesThe Bacterial Cytoskeleton 1EdnaCharryNo ratings yet
- Comparing the Sensitivity of Silver Nanoparticles Using Chicken and Duck Egg Albumin Reductors for Mercury AnalysisDocument12 pagesComparing the Sensitivity of Silver Nanoparticles Using Chicken and Duck Egg Albumin Reductors for Mercury AnalysisIswati Iis016No ratings yet
- 978 1 62100 769 2 - ch1Document45 pages978 1 62100 769 2 - ch1João RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Jones Et - Al.1994Document6 pagesJones Et - Al.1994Sukanya MajumderNo ratings yet
- Molinie 2018Document24 pagesMolinie 2018Veronica JanethNo ratings yet
- A Review Leptin Structure and Mechanism Actions"Document8 pagesA Review Leptin Structure and Mechanism Actions"elenNo ratings yet
- Group Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineDocument13 pagesGroup Two'S Seminar Work: Topic: Enzyme Regulation Allosteric Regulation and Models OutlineOluwasegun ModupeNo ratings yet
- BC0103 ch13Document93 pagesBC0103 ch13oreaNo ratings yet
- 2ITODocument11 pages2ITORIFKI ALIYUSIDIKNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Interphase NucleusDocument17 pagesTutorial 3 - Interphase NucleusKhryss PantuaNo ratings yet
- 2020B1A70383H BioPhy Ass1Document6 pages2020B1A70383H BioPhy Ass1polsaagyapolsNo ratings yet
- Inter ProDocument7 pagesInter Prowilliam919No ratings yet