Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155
Uploaded by
Caroline ChaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155
Uploaded by
Caroline ChaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
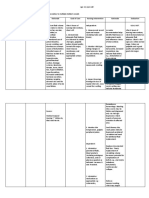
Problem Identified: Difficulty of breathing
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion secondary to surgery as evidenced by decreased respiratory depth.
Cause Analysis: Respiratory depression is the most serious adverse effect of opioid analgesics administered by IV, SubQ, or epidural routes. Specific notable changes are
decreasing respiratory rate or shallow respirations. (Brunner & Suddarth’s Medical Surgical Nursing, Page 190)
Cues Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Objective: STO: Independent actions: Independent actions: STO:
Tachypnea: 26 breathes After 10 minutes of nursing 1. Administer oxygen at lowest 1. For management of underlying Goal met, the patient
per minute intervention, the patient will be concentration indicated and pulmonary condition, respiratory was able to decrease
Decreased respiratory able to decrease breathes per prescribed respiratory medications. distress, or cyanosis. breathes per minute
depth minute from 26 to 12-20. 2. Monitor pulse oximeter, as indicated. 2. To verify maintenance and from 26 to 12-20.
Cyanotic 3. Suction airway, as needed. improvement in oxygen saturation.
LTO: 4. Elevate head of bed, as appropriate. 3. To clear secretions. LTO:
5. Provide/encourage use of adjuncts, 4. To promote physiological ease of
After 20 minutes of nursing such as incentive spirometer. maximal inspiration. Goal met, the patient
intervention, the patient will 5. To facilitate deeper respiratory established normal
establish normal breathing effort. breathing pattern as
pattern as evidenced by the evidenced by the
absence of cyanosis. absence of cyanosis.
References: Nurse’s Pocket Guide Pages 151-155
You might also like
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument3 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPyasayayasay yasayNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivNo ratings yet
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- HTP of AsthmaDocument1 pageHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- NCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingDocument3 pagesNCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingCedie BarcaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAPDocument6 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAPIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Difficulty Breathing Intervention and EvaluationDocument1 pageDifficulty Breathing Intervention and EvaluationJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDocument1 pageSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaJason A. AdoyoganNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsDocument1 pageAcute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsAi RouNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesSubjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermCamille SesaldoNo ratings yet
- Breathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionDocument3 pagesBreathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceBenly Grace Rebuyon MosquedaNo ratings yet
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 pagesNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyHennah ReblandoNo ratings yet
- Mothers' Experiences of Premature Infants in the NICUDocument4 pagesMothers' Experiences of Premature Infants in the NICUMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Acute Pain Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMeljonesDaanNo ratings yet
- NCP AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP AirwayjlucandoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDanielle Patricia Valencia OtedaNo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- NCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Document2 pagesNCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Arnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPCamille VirayNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPSarah Younes AtawnehNo ratings yet
- BerodualDocument1 pageBerodualAelysa PabloNo ratings yet
- Impaired Breathing PatternDocument1 pageImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKhat100% (1)
- NCP Mandibular)Document5 pagesNCP Mandibular)yellarfNo ratings yet
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFDocument3 pagesNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarNo ratings yet
- Oks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!Document10 pagesOks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!CiaraNo ratings yet
- Angel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAngel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisSalvaje CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Risk for Aspiration Nursing Care Plan During CholecystectomyDocument1 pageRisk for Aspiration Nursing Care Plan During CholecystectomyJess GoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageNursing Interventions for Ineffective Breathing PatternnikkilyceeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMikhaelEarlSantosTacordaNo ratings yet
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDocument2 pagesProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Problem Identified: Difficulty of BreathingDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Problem Identified: Difficulty of BreathingCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Patients with Uterine Fibroids and Acute Abdominal PainDocument10 pagesNursing Care for Patients with Uterine Fibroids and Acute Abdominal PainPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan #2:: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGeraldine SantosNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 2Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- SecretoDocument2 pagesSecretoKeepItSecretNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study-Metformin 1Document2 pagesDrug-Study-Metformin 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- SecretoDocument2 pagesSecretoKeepItSecretNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- SecretoDocument2 pagesSecretoKeepItSecretNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Lung CancerDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Lung Cancerderic80% (15)
- Hypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Assessment, Diagnosis and InterventionCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Sample Cliical Focus For Online RleDocument2 pagesSample Cliical Focus For Online RleFitz JaminitNo ratings yet
- SGNA StandardsofClinicalNursingPractice 2014 FinalDocument26 pagesSGNA StandardsofClinicalNursingPractice 2014 FinalSimona Adaniloae0% (1)
- Recreational Therapy Presentee: Sukhdeep Kaur Msc. (N) 1 YearDocument26 pagesRecreational Therapy Presentee: Sukhdeep Kaur Msc. (N) 1 YearSatbir GillNo ratings yet
- Clinical Formulation For Mental Health Nursing PracticeDocument8 pagesClinical Formulation For Mental Health Nursing PracticeLuis Antonio Buitron RamirezNo ratings yet
- AssumptionsDocument2 pagesAssumptionsizaj150No ratings yet
- Role of Community Health Nurse in Disaster ManagementDocument3 pagesRole of Community Health Nurse in Disaster ManagementyselleamNo ratings yet
- NCP JaundiceDocument9 pagesNCP JaundiceMeena Koushal100% (1)
- Med Errors CertificationDocument2 pagesMed Errors Certificationapi-372034151No ratings yet
- Lorraine O. Walker, EdD, MPHDocument10 pagesLorraine O. Walker, EdD, MPHSevalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus SpringDocument11 pagesSyllabus SpringMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Organization structure of rural healthcare systemDocument2 pagesOrganization structure of rural healthcare systemSweta MishraNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Learning Assessment #3 Date: February 2, 2017 Subject: Love Trumps Hate Location and Business NameDocument3 pagesEvidence of Learning Assessment #3 Date: February 2, 2017 Subject: Love Trumps Hate Location and Business Nameapi-339158068No ratings yet
- Thomasian Nurses: Heart over Hard WorkDocument3 pagesThomasian Nurses: Heart over Hard WorkCharlene SibugNo ratings yet
- HX FDN of Health Educ LECDocument3 pagesHX FDN of Health Educ LECKate AllysonNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Childhood Obesity 1Document9 pagesPrevention of Childhood Obesity 1MrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- HOLY FAMILY COLLEGE OF NURSING CLINICAL ROTATION PLANDocument2 pagesHOLY FAMILY COLLEGE OF NURSING CLINICAL ROTATION PLANManisha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Journal List of SSCI October 2022Document160 pagesJournal List of SSCI October 2022JuanaNo ratings yet
- CMS Place of Service Codes 2009Document6 pagesCMS Place of Service Codes 2009Rakshith KambleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Associate Curriculum FrameworkDocument63 pagesNursing Associate Curriculum FrameworkLidya MaryaniNo ratings yet
- MDC EHS Progress Report Presentation 21 Nov 09Document37 pagesMDC EHS Progress Report Presentation 21 Nov 09Eze FoncardasNo ratings yet
- Staffing and Human Resources IssuesDocument17 pagesStaffing and Human Resources IssuesJaneNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesPediatric Nursing Thesis Topicsmonicacartergrandrapids100% (2)
- Castle Ward Leaflet FINAL 26.05.2016Document4 pagesCastle Ward Leaflet FINAL 26.05.2016Sebastian BujorNo ratings yet
- Artikel 1 PDFDocument5 pagesArtikel 1 PDFChristine Yunike AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- UDSM Transfer VacanciesDocument13 pagesUDSM Transfer VacanciesAyman ComplicatorNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management Information System ProjectDocument4 pagesHospital Management Information System ProjectAlfredo Jimenez CharlesNo ratings yet
- Nurses' EBP Beliefs Improved with EducationDocument48 pagesNurses' EBP Beliefs Improved with EducationJacam BcglNo ratings yet
- Prnu 115 Portfollio Part B Shaylie Jobbagy-2Document5 pagesPrnu 115 Portfollio Part B Shaylie Jobbagy-2api-661556403No ratings yet
- Grid PlanDocument2 pagesGrid Planapi-315592452No ratings yet
- 3 Floor, DPT Building Matina Campus, Davao City Telefax: (082) Phone No.: (082) 300-5456/300-0647 Local 117Document2 pages3 Floor, DPT Building Matina Campus, Davao City Telefax: (082) Phone No.: (082) 300-5456/300-0647 Local 117Rheynel NietesNo ratings yet