Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology
Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology
Uploaded by
poleene de leon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
acyclovir.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology
Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology
Uploaded by
poleene de leonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
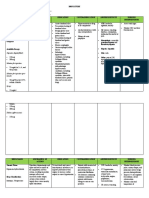
DRUG STUDY: NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY Instructor: _______________________________________ Date: ________________________
NAME: ____________________________________________________________ BLOCK and Year:___________________________Group: ______________________________
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING
ACTION INTERVENTIONS
Inhibits viral DNA Acute treatment of Hypersensitivity to drug or CNS: aggressive Patient monitoring
polymerase, thereby herpes zoster valacyclovir behavior, dizziness, -Monitor fluid intake and
Generic Name: inhibiting replication of viral (shingles) malaise, weakness, output.
Acyclovir DNA. Specific for herpes Initial episode of paresthesia, headache; -Assess for signs and
simplex types 1 (HSV-1) and genital Herpes with I.V. use— symptoms of encephalopathy.
2 (HSV-2), varicella- zoster Chronic suppressive encephalopathic -Evaluate patient frequently
virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and therapy for recurrent changes (lethargy, for adverse reactions,
cytomegalovirus (CMV). genital herpes tremors, obtunda- tion, especially bleeding tendency.
episodes confusion, -Monitor CBC with white cell
Drug Classification: Intermittent therapy hallucinations, agita- differential and kidney
Antiviral for recurrent genital tion, seizures, coma) function test results.
herpes episodes CV: peripheral edema
Management of initial EENT: vision Patient teaching
episodes of genital abnormalities -Instruct patient to keep
herpes and limited, GI: nausea, vomiting, taking drug exactly as
non-life threatening diarrhea prescribed, even after
mucocutaneous GU: proteinuria, symptoms improve.
Available Dosage: herpes simplex virus hematuria, crystal- -Advice patient to drink
Capsules: 200 mg infections ilmmuno- luria, vaginitis, enough fluids to ensure
Cream: 5%in 2-g tube compromised patients candidiasis, changes in adequate urinary output.
Injection: 50 mg/ml Treatment of menses, vulvitis, -Tell patient to monitor urine
Ointment: 5% in 15-g recurrent herpes oliguria, renal pain, output and report significant
tube labials (cold sores) renal failure, changes. > Instruct patient to
Powder for injection: glomerulonephritis immediately report unusual
Varicella
500 mg/vial, 1000 Hematologic: anemia, bleeding or bruising.
(chickenpox)
mg/vial lymphadenopa- thy, - Caution patient to avoid
Mucosal and
Suspension: 200 mg/5 thrombocytopenia, driving and other hazardous
cutaneous HSV-1 and
ml thrombotic activities until he knows how
HSV-2 in immuno-
drug affects concentration
Tablets: 400mg, 800 compromised patients thrombocytopenic
purpura/hemolytic and alertness.
mg Herpes simplex
uremic syndrome (in -Advice patient to minimize
encephalitis GI upset by eating small,
Varicella zoster immunocom- promised
patients), disseminated frequent servings of food and
infections in immuno- drinking plenty of fluids.
compromised patients intravascular
coagulation, hemolysis, -Tell patient to use soft
leukopenia, toothbrush and electric razor
leukoclastic vasculitis to avoid injury to gums and
Hepatic: jaundice, skin.
hepatitis -Advise patient to avoid
Musculoskeletal: sexual intercourse when
myalgia visible herpes lesions are
Skin: photosensitivity present.
rash, pruritus, -Inform patient that he may
angioedema, alopecia, need to undergo regular blood
urticaria, severe local testing during therapy.
inflammatory reactions -As appropriate, review all
(with I.V. other significant and life-
extravasation), toxic threatening adverse reactions
epidermal necrolysis, and interactions, especially
erythema multiforme those related to the drugs and
Other: gingival tests mentioned above.
hyperplasia, fever,
excessive thirst, pain at
injection site,
anaphylaxis, Stevens-
Johnson syndrome
You might also like
- The Child Survivor Healing Developmental Trauma AnDocument68 pagesThe Child Survivor Healing Developmental Trauma Anpetrila deboraNo ratings yet
- Clonidine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesClonidine Drug Studypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY AmoxicillinKhylamarie VillalunaNo ratings yet
- (26 29) Process Recording FormatDocument4 pages(26 29) Process Recording Formatpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Medical Examination Form SeafarersDocument5 pagesMedical Examination Form SeafarersHazem ElbananNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyGladys Joy Peña100% (1)
- Mksap 16 NephrologyDocument174 pagesMksap 16 Nephrologytingtingcrazy100% (5)
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDocument64 pagesDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaNo ratings yet
- Scrabble - Indoor Recreational ActivitiesDocument24 pagesScrabble - Indoor Recreational ActivitiesKimberly TanalasNo ratings yet
- The Use of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine in The Treatment of 5 Cases of Neoplastic Bone DiseaseDocument12 pagesThe Use of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine in The Treatment of 5 Cases of Neoplastic Bone DiseaseDonnaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RifampicinDocument1 pageDrug Study RifampicinEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDocument1 pageDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Medsurg QuizDocument11 pagesMedsurg Quizpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument34 pagesDrug Studypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Document2 pagesDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudybaniniycsebNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen Drug StudyDocument3 pagesIbuprofen Drug StudySeann Loresco100% (2)
- Drug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinDocument4 pagesDrug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinDeinielle Magdangal Romero100% (1)
- Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of HypokalemiaDocument16 pagesClinical Manifestations and Treatment of Hypokalemiagerontogeria100% (2)
- Acyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAcyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComJanaica JuanNo ratings yet
- CrossWards USMLE Step 2 Board Review PDFDocument210 pagesCrossWards USMLE Step 2 Board Review PDFICH KhuyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument2 pagesDrug Study Oxytocinrica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- January 2018 1516198794 146 PDFDocument1 pageJanuary 2018 1516198794 146 PDFGaby ZapataNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz50% (2)
- CHN Drug StudyDocument17 pagesCHN Drug StudyEdmel Pamplona DuquesaNo ratings yet
- Romeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeDocument8 pagesRomeo Victor M. Valderrama BSN-2A: CNS: Confusion, Depression, BeforeitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Gec ArtDocument25 pagesGec Artpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 - Concept of CommunityDocument5 pagesWEEK 1 - Concept of Communitypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamide Drug StudyDocument1 pageSulfonamide Drug StudyMenard VelascoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Silver SulfadiazineDocument1 pageDrug Study Silver SulfadiazineMaica Lectana100% (1)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- ONDANSETRONDocument1 pageONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSDocument4 pagesTrimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Name: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleDocument2 pagesName: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - VancomycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - VancomycinKhatlen BagaresNo ratings yet
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin PDFDocument3 pagesAmpicillin PDFandriNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LabetalolDocument2 pagesDrug Study LabetalolJanzelvine Lee MontenegroNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 04-21-09Document2 pagesDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocument3 pagesDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyzjoshuacNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeleen Margaret Atienza100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAngelique Ramos PascuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Amikacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAmikacin Drug StudyMark Angelo LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Thrombolic, Thrombocytopenic Purpurvhemoclytic Uremic Syndrome (SeizuresDocument1 pageThrombolic, Thrombocytopenic Purpurvhemoclytic Uremic Syndrome (Seizuresgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- GEC-RVA: Reading Visual Art and Principles of Design: Week 5 LessonDocument31 pagesGEC-RVA: Reading Visual Art and Principles of Design: Week 5 Lessonpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- NURSING INFORMATICS Review NotesDocument4 pagesNURSING INFORMATICS Review Notespoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Gec-Art - Art Appreciation: Week 4Document21 pagesGec-Art - Art Appreciation: Week 4poleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Week 2 GEC ARTDocument23 pagesWeek 2 GEC ARTpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Diagnosis Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Diagnosis Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Nursing NCP 3Document17 pagesNursing NCP 3poleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Gec-Art Art Appreciation: Course Code: Course Title: Course DescriptionsDocument14 pagesGec-Art Art Appreciation: Course Code: Course Title: Course Descriptionspoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Nursing NCP 2Document14 pagesNursing NCP 2poleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Anti Human Embryo What Is Embryo? "An Embryo Is The Early Stage of Human Development in WhichDocument3 pagesAnti Human Embryo What Is Embryo? "An Embryo Is The Early Stage of Human Development in Whichpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- DISCHARGE PLAN FormatDocument1 pageDISCHARGE PLAN Formatpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluationpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Initial Nursing AssessmentDocument2 pagesInitial Nursing Assessmentpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Terms NicuDocument1 pageTerms Nicupoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Imogene KingDocument1 pageImogene Kingpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion (During Procedure)Document1 pageBlood Transfusion (During Procedure)poleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Chrislelene-AfterBT ReportDocument1 pageChrislelene-AfterBT Reportpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Procedures After Blood TransfusionDocument1 pageProcedures After Blood Transfusionpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Quiz 1Document4 pagesNCM 106 Quiz 1poleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacologypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyDocument2 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacologypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Components of Labor (4 P's in Labor) : Pelvis of The MotherDocument2 pagesComponents of Labor (4 P's in Labor) : Pelvis of The Motherpoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Philosophy Material and Formal Object Lesson 2: Philosophy Meaning of PhilosophyDocument3 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Philosophy Material and Formal Object Lesson 2: Philosophy Meaning of Philosophypoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cord CareDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cord Carepoleene de leonNo ratings yet
- N Ati o Na L H Ea LT H PR o GR A M M Es, P Oli Ci Es An D Le Gi SL AtiDocument6 pagesN Ati o Na L H Ea LT H PR o GR A M M Es, P Oli Ci Es An D Le Gi SL AtiDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan UTBK Snsimak Fasting BahasDocument5 pagesSoal Latihan UTBK Snsimak Fasting BahasJoko PrihantoNo ratings yet
- Clinical BacteriologyDocument1 pageClinical BacteriologyJohannah Mae BilgeraNo ratings yet
- Telehealth RuralDocument16 pagesTelehealth RuralSanjay JacobNo ratings yet
- Why Groups Fail To Share Information EffectivelyDocument6 pagesWhy Groups Fail To Share Information EffectivelyNathan ArthurNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Course Code: SOC354Document26 pagesAssignment On: Course Code: SOC354Aaron LeonardNo ratings yet
- Pain Managment in Nursing (Fundamentals)Document21 pagesPain Managment in Nursing (Fundamentals)crosadotNo ratings yet
- LE5 ReportDocument10 pagesLE5 ReportJulliana ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument20 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeLevi PosadasNo ratings yet
- 3 - Development From Conception To BirthDocument50 pages3 - Development From Conception To BirthMa. Angelica PampagNo ratings yet
- Care of Comatose and Vulnerable PatientsDocument32 pagesCare of Comatose and Vulnerable PatientsPrince Jhessie L. AbellaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of Initial Crestal Bone Loss Around Dental Implants Using Flapless or Flap Method: An in Vivo StudyDocument9 pagesComparative Evaluation of Initial Crestal Bone Loss Around Dental Implants Using Flapless or Flap Method: An in Vivo StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Stress SymptomsDocument3 pagesStress SymptomsZuh KiNo ratings yet
- Winter Here New Title.Document184 pagesWinter Here New Title.Christopher VecchittoNo ratings yet
- A Study About The Relocation of Badjao Community in Totolan 4Document17 pagesA Study About The Relocation of Badjao Community in Totolan 4welpNo ratings yet
- Virocid™: Safety Data SheetDocument14 pagesVirocid™: Safety Data SheetMohammad RayhanNo ratings yet
- Modicare Digital Booklet English June 2021Document19 pagesModicare Digital Booklet English June 2021Sunita JadhavNo ratings yet
- Tips To Increase Speed of AssessmentDocument6 pagesTips To Increase Speed of AssessmentEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- The PartographDocument45 pagesThe PartographKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- My Financial Career-VI SemDocument8 pagesMy Financial Career-VI SemSamridhi VermaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Lesson 1Document7 pagesNervous System Lesson 1Yennifer NivarNo ratings yet
- MDSD FludarabinDocument10 pagesMDSD FludarabinImanda EsaNo ratings yet