Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Outline Chapter 1 Outline
Uploaded by
Ahmad MqdadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Outline Chapter 1 Outline
Uploaded by
Ahmad MqdadCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|5689164
Chapter 1 Outline
Introduction to Business (The University of Maine)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by ahmad mqdad (ahmad1991-6-17@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|5689164
Connor DiAngelo
Professor Demarco
BUA 101- 0007
11 September 2018
Chapter 1 Outline
Business Profit and the External Environment
Business and Profit
o Businesses: organizations supply goods and services, sell for profit
o Profits: revenue – expenses. Difference between business and non-profits (universities,
hospitals, govt.)
o Consumer Choice and Demand
Capitalism/free market allows free choices for both supply and demand
o Opportunity and enterprise
Enterprising business people use opportunity to reach success
Ex: failed tech stores liquidate inventory, remaining one’s profit and
receive assets
Ex: gas prices drop hurting oil, food distributors and shipping lower
expenses and profits rise
Demand for goods or inefficiency of supplied goods causes opportunity
o Benefits of business
Supply goods and services, labor and jobs, innovation, contribution to society
and quality of life, profits enhance income of investors and stockholders, taxes
benefit govt., philanthropy
Environmental harm and decisions for personal gain negative effects
External environment of business
o External environment: everything outside of organization that can affect it
o Environment plays major role in success/failure
o Managers must complete must completely and accurately understand environment to
operate and compete
o Impactors include domestic business envt., global business envt., tech envt.,
political/legal envt., sociocultural envt., economic envt.
o Domestic environment
Domestic business envt. is where they operate and gain revenue
Seek to be close to customers, establish strong supplier relationships, and
distinguish from competitors
Urban outfitters expanded from urban colleges to upscale areas as well,
good supplier relations and supplies others, and clear identity
o Global business environment
o Global business environment is international forces affecting businesses
Forces include international trade agreements, international economy, politics
Ex: political unrest in Middle East led to high prices and it had to protect
emplyees
Ex: oil surplus dropped prices extremely
Businesses are affected by international market and opportuinities,
suppliers, cultures, competitors, currency/economy
o Tech Environment
Tech envt. includes all ways of creating value for members
Includes human knowledge, work methods, physical equipment, electronics,
telecommunications, processing systems
Urban Outfitters has info system to track sales/inventory for enhanced
ecommerce
Downloaded by ahmad mqdad (ahmad1991-6-17@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|5689164
Connor DiAngelo
Professor Demarco
BUA 101- 0007
11 September 2018
o Political environment
o Political/Legal environment based on relationship between government and business
(usually regulation is impact)
Legal system defines guidelines for organizations (Urban Outfitters subject to
product ID laws, hiring restrictions, zoning)
o Govt agencies regulate advertising, safety and health, conduct
o Pro/anti-business sentiment is valuable to consider, especially intl.
Obama’s presidency imposed business regulations
Sociocultural Environment
Sociocultural environment includes surrounding customs, morals, values, demographic of society
Also determines goods and services sold, and levels of business conduct accepted
o Ex: Urban Outfitters Ghettoopoly
Economic Systems (system for allocation of resources between individual citizens and organization)
Factors of production
o Factors of production are resources for goods and services
o Labor, capital, entrepreneurs, physical resources (and info resources)
o Also applicable to specific organization’s production of goods and services
o Labor (human capital) is physical and intellectual contributions from people to the
economy
Ex: Starbucks positions vary from baristas to business and finance jobs, employ
182K
o Capital
o Capital is financial resources needed to operate business; necessary to start new and
maintain business
Ex: Starbucks company purchase with savings/loan, publicly traded stock, long
short/term debt
o Entrepreneurs
o Entrepreneurs are people who accept risk and opportunity of starting a new business
Ex: Starbucks initially fails, new entrepreneurship goes into retail
o Economic systems encourage entrepreneurs to start new businesses, and maximized jobs
and profit
Physical resources
Physical resources are tangible items that businesses and organizations use to conduct business
o Natural resources, raw materials, offices, storage, manufacturing, parts and supplies,
computer and tech
Ex: Starbucks has many levels: beans, shipment, manufacturing, food products,
paper products, business items too
o Info resources
o Info resources is data and other info used in business
Market forecasts, specialized knowledge of people, and even data
Types of economic systems
Planned economy is where govt./central power controls economy through factors of production
and allocation of resources
o Communism is where govt. owns and operates all factors of production
Market economy
Downloaded by ahmad mqdad (ahmad1991-6-17@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|5689164
Connor DiAngelo
Professor Demarco
BUA 101- 0007
11 September 2018
o Market is a mechanism for exchange between buyers and sellers for specific
goods/services
o Capitalism sanctions/regulates private ownership of factors and incentivizes new
businesses/entrepreneurship
Mixed market is a system that includes both other market styles
o Privatization is the transition from govt enterprise to private business
o Socialism is planned economy where govt only controls some major sources of
production
The Economics of Market Structures
Demand and supply in a market economy
o Consumers and producers have many decisions
o Law of supply and demand
Demand is the willingness and ability to buy
Supply is the willingness and ability to sell
Law of demand: P up Q down, P down Q up
Law of supply: P up Q up, P down Q down
Supply and demand schedule shows interaction between S, P, D at each price
Demand curve shows QD at each P
Supply curve shows QS at each P
Equilibrium: profit maximizing QD=QS
Surplus is QS>QD
Shortage is QS<QD
Private enterprise and competition in a market economy
o Private enterprise is a system that allows individuals to pursue interests without govt
restriction
Private property rights
Free choice
Profits
Competition (multiple businesses compete for customers)
o Degrees of competition
Perfect competition is many small firms with identical product
Products identical
Buyers and sellers know market prices
Easy to enter/exit market
Prices set by S+D, accepted by producers and consumers
Monopolistic competition is buyers and sellers who try to make product seem
unique from competition
Name brands, design/style, advertising to stand out
Can enter/exit easily
Differentiation gives some price control
Oligopoly is small number of sellers control market with high power to move
prices
More control over strategies
Monopoly is when industry/market only has one producer
Complete price control
Constraint is QD down when P up
Downloaded by ahmad mqdad (ahmad1991-6-17@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|5689164
Connor DiAngelo
Professor Demarco
BUA 101- 0007
11 September 2018
Natural monopoly is when producer can most effectively supply all
needed goods and services (utilities)
o Economic Growth, Aggregate Output, and Standard of Living
Business cycle is short term pattern of economic expansions and contractions
Aggregate output is total QS by an economic system during a given period
Increase in aggregate output growth
When output grows more quickly than population
o Output per capita goes up
o System provides more goods and services that people want
o These conditions raise standard of living, total quantity and
quality of goods and services available
GDP is total value of all goods and services produced within a given period by a
national economy through domestic factors of production
GNP (national) total value of goods and services produced by national
economy
Real growth rate is growth rate of GDP adjusted for inflation
GDP per capita GDP/total population
Real GDP is when GDP is adjusted for changes in currency value and
prices
Nominal GDP is GDP measured in currency, all components valued at
current prices
Purchasing power parity is a principle that exchange rates are set so
products cost the same across countries
Productivity is a measure of economic growth that compares how much a system
produces with production resources
More products produced with less resources allows price to drop and
standard of living to go up
Balance of trade and national debt can inhibit growth
Balance of trade is economic value of all exports – imports
o Positive when X>I
o Negative when X<I
o Negative balance often called trade deficit, harms growth
because imports have interest
o National debt is amount of money nation owes creditors
US sells bonds, or IOUs, which lowers amount of
private borrowing
o Economic Stability
Stability is when money in economy and Q of goods and services produced at
same rate
Inflation is when economic system experiences widespread price increases
CPI is measure of prices of typical products purchased by consumers in urban
areas
Unemployment is level of jobless people among those actively seeking work
If wages got too high, companies stop hiring as many workers and rate of
unemployment goes up
Businesses raise prices to account for increased labor cost, but sales drop
and they have to cut back, and unemployment goes up
Downloaded by ahmad mqdad (ahmad1991-6-17@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|5689164
Connor DiAngelo
Professor Demarco
BUA 101- 0007
11 September 2018
Government intervention through lowering taxes, lowering interest rate,
spending increase, inflation may set in
o Purchasing power parity allows us to compare similar items between countries and
analyze economies
Recession, GDP declines
Depression, GDP long term decline
Fiscal Policy – policies of govt. and how it collects/spends revenue
o Stabilization policy
Monetary Policy – control by govt. of money supply
o Smooth fluctuations
Downloaded by ahmad mqdad (ahmad1991-6-17@hotmail.com)
You might also like
- Midterm Review Chapters 1-2-3-4-6 Contemporary BusinessDocument9 pagesMidterm Review Chapters 1-2-3-4-6 Contemporary BusinessJohn MotleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Government & BusinessDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Government & Businessintallav51No ratings yet
- Understanding Canadian Business Systems and Economic ConceptsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Canadian Business Systems and Economic ConceptsSendu RasaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management CHAPTER 3Document12 pagesMarketing Management CHAPTER 3Trisha Mae Lyrica CastroNo ratings yet
- RSM100 Chapter 1 & 2 Notes on Business FundamentalsDocument44 pagesRSM100 Chapter 1 & 2 Notes on Business FundamentalsSalman SahirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Changing Face of BusinessDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - The Changing Face of BusinessArsalNo ratings yet
- Biz Studies RevisDocument5 pagesBiz Studies Revissam12gouldNo ratings yet
- BUS 100 Notes - CHP 1-3, 5, 7, 8 & 13Document48 pagesBUS 100 Notes - CHP 1-3, 5, 7, 8 & 13norhan alaliNo ratings yet
- Iphilbus PPT Group 4Document25 pagesIphilbus PPT Group 4Cherry-ann HuerteNo ratings yet
- Need and Importance of HRDDocument9 pagesNeed and Importance of HRDShreekant ShahNo ratings yet
- ITB NotesDocument30 pagesITB NotesUmmi AniNo ratings yet
- Business Igcse SummaryDocument92 pagesBusiness Igcse SummarymilyconteNo ratings yet
- IIB Tutorial Questions - Final Exam Prep PDFDocument27 pagesIIB Tutorial Questions - Final Exam Prep PDFMohamed JubranNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument22 pagesInternational BusinessHương GiangNo ratings yet
- Global Business Globalisation - Introduction: Jim RileyDocument10 pagesGlobal Business Globalisation - Introduction: Jim RileyNyeko FrancisNo ratings yet
- Labor Capital Natural Resources Entrepreneur Entrepreneurial AbilityDocument3 pagesLabor Capital Natural Resources Entrepreneur Entrepreneurial Abilityvivianguo23No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction (IE)Document28 pagesChap 1 Introduction (IE)ZeNo ratings yet
- Concept and Significance of Business EnvironmentDocument103 pagesConcept and Significance of Business EnvironmentsanjaymanochaNo ratings yet
- Intro-to-Business Administration - SummaryDocument14 pagesIntro-to-Business Administration - Summarydaisygetty32No ratings yet
- International Business Unit 1Document25 pagesInternational Business Unit 1Mathumitha Muniappan100% (2)
- Year 11 Eco NotesDocument38 pagesYear 11 Eco NotesNathan CaoNo ratings yet
- The Legal Environment: The Legal Environment of Business Is The Most Complex andDocument2 pagesThe Legal Environment: The Legal Environment of Business Is The Most Complex andtuyen hô thi thanhNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ConworldDocument59 pagesGroup 2 ConworldMaryflor EspinaNo ratings yet
- IBE AssignmentDocument7 pagesIBE AssignmentAishwarya KhopkarNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 MicroecoDocument23 pagesMod 1 MicroecoHeina LyllanNo ratings yet
- Group: Economics & BusinessDocument55 pagesGroup: Economics & BusinessAndrea WaganNo ratings yet
- Business Environment - NotesDocument43 pagesBusiness Environment - NotesShreyNo ratings yet
- Definition of Business: Unit IDocument6 pagesDefinition of Business: Unit ImanojNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Managment SystemDocument15 pagesComparitive Managment SystemAhsan Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Business Enivironment and LawDocument321 pagesBusiness Enivironment and Lawajit4allNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 01 Overview of BusinessDocument6 pagesChapter No. 01 Overview of BusinessMandar BhadangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Theories of International TradeDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Theories of International TradealimithaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of International BusinessDocument126 pagesFoundations of International BusinessVineet Walia80% (10)
- Kinds of Economic Decision / How Economic Analysis Is Useful in Managerial Decision MakingDocument5 pagesKinds of Economic Decision / How Economic Analysis Is Useful in Managerial Decision MakingHITESH BANGERANo ratings yet
- Discover opportunities through macro trends and industry analysisDocument18 pagesDiscover opportunities through macro trends and industry analysisRellie Castro100% (4)
- Comparative Advantage and Gains From TradeDocument27 pagesComparative Advantage and Gains From TradeMikylla Rodriguez VequisoNo ratings yet
- 3566 Micro EconomicsDocument60 pages3566 Micro EconomicsPirya HussainNo ratings yet
- IBE: Analyzing International Business EnvironmentsDocument23 pagesIBE: Analyzing International Business EnvironmentsNidhuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business Environment-pg-1-FinalDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Business Environment-pg-1-FinalAnantha NagNo ratings yet
- Global BusinessDocument78 pagesGlobal BusinessSIVA RAMA KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Adam Smith - Most Popular Personality in Microeconomics, Author of The Wealthy of Nations andDocument12 pagesAdam Smith - Most Popular Personality in Microeconomics, Author of The Wealthy of Nations andJacifiedNo ratings yet
- Group: Economics & BusinessDocument55 pagesGroup: Economics & BusinessAndrea WaganNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Industry Competition and Barriers to EntryDocument55 pagesAnalyzing Industry Competition and Barriers to EntryAizhan BaimukhamedovaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Key Revision BookletDocument97 pagesIGCSE Key Revision Bookletbẹjamin hoàngNo ratings yet
- BBI201 Business Review Economic BasicsDocument6 pagesBBI201 Business Review Economic BasicsxSubliminalNo ratings yet
- Overview of BusinessDocument5 pagesOverview of BusinessSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Global TradeDocument26 pagesGlobal TradeCrystal TitarNo ratings yet
- RSM100Y1 Ch1 NotesDocument6 pagesRSM100Y1 Ch1 NotesMichael GasparNo ratings yet
- Ibe PPT Unit 1Document19 pagesIbe PPT Unit 1amankhore86No ratings yet
- Int Bus. IntroDocument34 pagesInt Bus. IntroShweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Lesson on Scarce ResourcesDocument9 pagesManagerial Economics Lesson on Scarce ResourcesPrincess Dhazerene M. ReyesNo ratings yet
- IBE Shortest Short NotesDocument14 pagesIBE Shortest Short Notessuanshu15No ratings yet
- The Market and Its FailureDocument6 pagesThe Market and Its FailureStephanie SerapioNo ratings yet
- Environmental Factors Affecting Success of A New BusinessDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Factors Affecting Success of A New BusinessGurmeet singh86% (7)
- Competition Law Course GuideDocument24 pagesCompetition Law Course GuideSao Nguyễn ToànNo ratings yet
- Report Macro and MicroDocument55 pagesReport Macro and Microyellamrtnz03No ratings yet
- Economic NotesDocument38 pagesEconomic NotesAakriti BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Samenvatting LisauraDocument33 pagesBusiness Economics Samenvatting LisauraFiene NagtegaalNo ratings yet
- How COVID-19-is-changing-consumer-behaviornow-and-foreverDocument6 pagesHow COVID-19-is-changing-consumer-behaviornow-and-forevermesay83No ratings yet
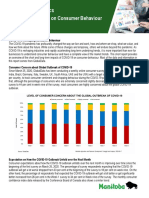
- Impact of COVID-19 On Consumer Behaviour: Manitoba AnalyticsDocument3 pagesImpact of COVID-19 On Consumer Behaviour: Manitoba AnalyticsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- 01 McKinsey & Company July 7 2020Document19 pages01 McKinsey & Company July 7 2020Gladwin Joseph100% (1)
- Creating Your First SSIS Project: 1. Start Business Intelligence Development StudioDocument10 pagesCreating Your First SSIS Project: 1. Start Business Intelligence Development StudioAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Online Shopping Factors That Affect Consumer Purchasing BehaviourDocument16 pagesOnline Shopping Factors That Affect Consumer Purchasing BehaviourAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 - Impact On Consumer Behavior Trends - AccentureDocument11 pagesCOVID-19 - Impact On Consumer Behavior Trends - AccentureAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Restrictions and Consumers Psychological Reactance Toward Offline Shopping Freedom RestorationDocument24 pagesCOVID 19 Restrictions and Consumers Psychological Reactance Toward Offline Shopping Freedom RestorationAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Adventures of Sherlock Holmes, by A. Conan DoyleDocument194 pagesAdventures of Sherlock Holmes, by A. Conan DoyleAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Change of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsDocument15 pagesChange of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Change of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsDocument15 pagesChange of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Change of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsDocument15 pagesChange of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Impact of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Online Consumer Purchasing BehaviorDocument19 pagesImpact of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Online Consumer Purchasing BehaviorBình BìnhNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Generation: Conceptual Framework of Consumer Behavioral ShiftsDocument11 pagesCOVID-19 Generation: Conceptual Framework of Consumer Behavioral ShiftsMac John PierreNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Has Changed Consumer Behavior. What Does It Mean For The Future - University of Arizona NewsDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Has Changed Consumer Behavior. What Does It Mean For The Future - University of Arizona NewsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- AhitofelAmir - Ahitofel - Amir - SQL at Main Amircohen87 - AhitofelAmir GitHubDocument25 pagesAhitofelAmir - Ahitofel - Amir - SQL at Main Amircohen87 - AhitofelAmir GitHubAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- HCI Individual Assignment Analysis of Priceline and True Lines Wear WebsitesDocument8 pagesHCI Individual Assignment Analysis of Priceline and True Lines Wear WebsitesAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Change of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsDocument15 pagesChange of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- The Rover Boys in BusinessDocument163 pagesThe Rover Boys in BusinessAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Impact of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Online Consumer Purchasing BehaviorDocument19 pagesImpact of The COVID-19 Pandemic On Online Consumer Purchasing BehaviorBình BìnhNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Case Study 1Document4 pagesUNIT III Case Study 1Ahmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- ERD FinalDocument1 pageERD FinalAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Change of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsDocument15 pagesChange of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- HCI Individual Assignment Analysis of Priceline and True Lines Wear WebsitesDocument8 pagesHCI Individual Assignment Analysis of Priceline and True Lines Wear WebsitesAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Business Essentials: Entrepreneurship, New Ventures, and Business OwnershipDocument45 pagesBusiness Essentials: Entrepreneurship, New Ventures, and Business OwnershipAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Summary Business Essentials Chapter 3 - Summary Business EssentialsDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Summary Business Essentials Chapter 3 - Summary Business EssentialsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire About The Pressure To Hire Family Members in The Family Business ResultesDocument13 pagesQuestionnaire About The Pressure To Hire Family Members in The Family Business ResultesAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Change of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsDocument15 pagesChange of Consumption Behaviours in The Pandemic of COVID-19: Examining Residents' Consumption Expenditure and Driving DeterminantsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Business Essentials: Marketing Processes and Consumer BehaviorDocument49 pagesBusiness Essentials: Marketing Processes and Consumer BehaviorAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Summary Business Essentials Chapter 2 - Summary Business EssentialsDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - Summary Business Essentials Chapter 2 - Summary Business EssentialsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- Business Essentials: Understanding Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilityDocument42 pagesBusiness Essentials: Understanding Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilityDee IsmailNo ratings yet
- Template Presentasi Technical Exchange Forum 2021 + BriefingDocument25 pagesTemplate Presentasi Technical Exchange Forum 2021 + Briefingdenstar silalahiNo ratings yet
- CMPT 16103Document289 pagesCMPT 16103Pratheesh KurupNo ratings yet
- Appendix - 27 Format of Project Authority CertificateDocument4 pagesAppendix - 27 Format of Project Authority Certificaterohitku10No ratings yet
- Problem Sets Micro1 2019Document7 pagesProblem Sets Micro1 2019Milad MohamadiNo ratings yet
- Reservation Information Itinerary ID: Total You Will Receive: IDR 1346400Document2 pagesReservation Information Itinerary ID: Total You Will Receive: IDR 1346400Achmad Furqon SyaifullahNo ratings yet
- File Xendit Transaction Report 1613976313476Document38 pagesFile Xendit Transaction Report 1613976313476jhonNo ratings yet
- G.Tian - Microeconomic TheoryDocument253 pagesG.Tian - Microeconomic Theorytony_stoyanov2108No ratings yet
- Business Environment WorkDocument13 pagesBusiness Environment WorkBensonOTJr.No ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Manufacturing Account - MCQDocument3 pagesChapter - 12 Manufacturing Account - MCQNRKNo ratings yet
- ConWorld - Quiz 4Document4 pagesConWorld - Quiz 4John Paul JalemNo ratings yet
- Signed Contract - Purchase OrderDocument3 pagesSigned Contract - Purchase OrderJong DrilonNo ratings yet
- Dksksabs DDocument70 pagesDksksabs DShalin ParikhNo ratings yet
- Welcome SpeechDocument2 pagesWelcome SpeechRahma SariNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTIVITY3Document2 pagesPRODUCTIVITY3Aira Cane EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- T-Sonic Facial Cle Ansing & Massaging DeviceDocument5 pagesT-Sonic Facial Cle Ansing & Massaging DeviceAnnesa Fadhila SariNo ratings yet
- Charles Correa's Incremental Housing SchemeDocument12 pagesCharles Correa's Incremental Housing SchemeMeghna jNo ratings yet
- Oman Roads and Bridges Project Snapshot: Batinah Coastal Road - Phase 2Document4 pagesOman Roads and Bridges Project Snapshot: Batinah Coastal Road - Phase 2ScribdInOmanNo ratings yet
- Online Couse Max B ForexDocument76 pagesOnline Couse Max B ForexUmair KhalidNo ratings yet
- Business Feasibility Report, TextilesDocument22 pagesBusiness Feasibility Report, TextilesPrashant Shinde100% (1)
- HK GRCC Platinum - Transfer-In App FormDocument1 pageHK GRCC Platinum - Transfer-In App FormpercysmithNo ratings yet
- ETHICS-LESSON 14.WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesETHICS-LESSON 14.WPS OfficeRichie EscoltaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ATW 108 USM Tutorial SlidesDocument18 pagesChapter 10 ATW 108 USM Tutorial Slidesraye brahmNo ratings yet
- Business, Government & Society: Brexit and Latest DevelopmentsDocument20 pagesBusiness, Government & Society: Brexit and Latest Developmentssameer prasadNo ratings yet
- 5 Maths NCERT Chapter 13 PDFDocument17 pages5 Maths NCERT Chapter 13 PDFIitjeepoint RiyadhNo ratings yet
- List of Properties Where Arrear Above Rs 50000Document219 pagesList of Properties Where Arrear Above Rs 50000Siddharth Kumar50% (2)
- Interwood MobelDocument32 pagesInterwood MobelHSNo ratings yet
- TPM Literature ReviewDocument49 pagesTPM Literature ReviewJosep PeterNo ratings yet
- EDULIGHT Volume - 2, Issue - 3, May 2013Document300 pagesEDULIGHT Volume - 2, Issue - 3, May 2013EDULIGHT JOURNAL - A Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- Core Complexities Bharat SyntheticsDocument4 pagesCore Complexities Bharat SyntheticsRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- LIC Plan SummaryDocument30 pagesLIC Plan SummaryDharmesh SettyNo ratings yet