Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reliance-Fresh Deb Part
Reliance-Fresh Deb Part
Uploaded by
debojyoti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Reliance-Fresh_Deb_Part
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesReliance-Fresh Deb Part
Reliance-Fresh Deb Part
Uploaded by
debojyotiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Store Operators:
A. Store Manager- Operations of a particular outlet on a daily basis
B. Visual merchandiser- Decides how to display the products to maximize sales
C. Category Heads- Collect information about the performance of different products and
take calls on promotion schemes etc.
D. Supervisor- Responsible for coordination amongst the cash manager and other
employees down the line.
E. Cash Manager- Deployed at the Point-of-Sales
F. Customer Associates- Set-up the goods, engage in in-store customer interaction, ensure
the right flow of information to the customers about the products
G. House-Keeper- Responsible for overall hygiene of the store
H. Guards- Maintaining the overall security of the outlet
Supply Chain Strategies
Procurement- Source the perishable goods directly from farmers from areas that are
close-by to the distribution centers. Hence middlemen commissions and high
transportation costs are eliminated. Products with longer shelf life are sourced through
centralized purchasing directly from the manufacturers.
Distribution Centers- Large distribution centers to enhance the efficiency of the Supply
Chain via large scale of economies. Strategically located from the collection points as
well as the retail stores.
Supplier Contracts- Pre-negotiated agreements with local farmers to procure the
perishable goods, involving payment terms, measure of quality & quantity and pre-agreed
prices. Flexible contracts with multiple suppliers for the non-perishable goods, including
agreements like return goods at lower prices after expiry, bulk purchase at lower prices,
etc.
Inventory- Cold storage facility for perishable goods in the distribution centers whereas
the non-perishable goods are stocked and reordered based on minimum order quantity
levels. Storage facilities in the retail stores are limited and hence are supplied with goods
based on their demand forecasts. Perishables are ordered by the retail stores on a daily
basis depending on the estimated demand whereas the non-perishables are managed via
the SAP system centrally depending on the historical sales data.
Supply Chain Problems Encountered:
1. Poor Inventory management- Persistent cost of lost sales during the weekends and
holidays whereas increasing holding inventory costs during the weekdays.
2. Storage and Quality control- With their rapid growth in number of the retail outlets
across India and limited in-store storage facilities, frequency of stale & expired items are
increasing.
Solution and Recommendations:
In-store Inventory Management- Centralize the demand information amongst all the
cluster heads of the distribution centers and the retail store managers to reduce the bull-
whip effect.
Cross-Docking- Perishable farm products can be graded at the collection centers itself
rather than at the distribution centers
Every-day low pricing- Increase the efficiency of the supply chain by eliminating
discounts mechanism, stabilizing the price levels. This would reduce the uncertainty.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- List of GIC CompaniesDocument49 pagesList of GIC Companiesdebojyoti89% (37)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Workbook Annas ArchiveDocument188 pagesThe Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Workbook Annas ArchiveRaquel100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Project Assessment at Railways FinalDocument5 pagesProject Assessment at Railways FinaldebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Contactless Mobile Payment Architecture Overview 2010062808363068Document28 pagesContactless Mobile Payment Architecture Overview 2010062808363068Dian Agung NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Business and Marketing Plan Reflective Report - Filip JankovicDocument2 pagesBusiness and Marketing Plan Reflective Report - Filip JankovicFilip Jankovic50% (2)
- Candito Deadlift Program: What Date Do You Want To Start The Program?Document16 pagesCandito Deadlift Program: What Date Do You Want To Start The Program?Nishant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Metals - Elara Securities - 20 January 2021Document43 pagesFerrous Metals - Elara Securities - 20 January 2021debojyotiNo ratings yet
- S7 BuiltinFunctions StartDocument9 pagesS7 BuiltinFunctions StartdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Excel 18Document11 pagesExcel 18debojyotiNo ratings yet
- Tusk Investments - Case Study (Round 1) - Metals and MiningDocument9 pagesTusk Investments - Case Study (Round 1) - Metals and MiningdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Activity Description Activity Symbol Preceeding Activity Completion Times (In Weeks)Document2 pagesActivity Description Activity Symbol Preceeding Activity Completion Times (In Weeks)debojyotiNo ratings yet
- Volcker Rule: What Is It?Document2 pagesVolcker Rule: What Is It?debojyotiNo ratings yet
- TOPSISDocument1 pageTOPSISdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Leveraged Leasing Hardware Leasing Company Data:: PV of Net Lease Receipts $88,606Document2 pagesLeveraged Leasing Hardware Leasing Company Data:: PV of Net Lease Receipts $88,606debojyotiNo ratings yet
- NBFCs and Their Regulation - ClassDocument8 pagesNBFCs and Their Regulation - ClassdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Financial Services (FS) Instructor: Golaka C Nath, PH.D.: Overview of The CourseDocument3 pagesFinancial Services (FS) Instructor: Golaka C Nath, PH.D.: Overview of The CoursedebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Examples Bank BalancesheetDocument3 pagesExamples Bank BalancesheetdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- IIM Sambalpur ExampleDocument2 pagesIIM Sambalpur ExampledebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On India's Current Account DeficitDocument6 pagesAssignment On India's Current Account DeficitdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- George Soros and His Speculative Activities: Assignment OnDocument3 pagesGeorge Soros and His Speculative Activities: Assignment OndebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Excel 19Document6 pagesExcel 19debojyotiNo ratings yet
- Assets, Liabilities, and The Balance SheetDocument19 pagesAssets, Liabilities, and The Balance Sheetdebojyoti100% (1)
- Chapter - 8 Foreign Exchange Forwards and Futures: Example 8.1Document40 pagesChapter - 8 Foreign Exchange Forwards and Futures: Example 8.1debojyotiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Options On Stock Indexes, Foreign Currencies, Futures Contracts, and Volatility IndexesDocument49 pagesChapter - 13 Options On Stock Indexes, Foreign Currencies, Futures Contracts, and Volatility IndexesdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Debits, Credits, and The Trial BalanceDocument17 pagesChapter-4 Debits, Credits, and The Trial BalancedebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Company - Swiggy Position - AnalyticsDocument1 pageCompany - Swiggy Position - AnalyticsdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Recommendation Rough SketchDocument4 pagesRecommendation Rough SketchdebojyotiNo ratings yet
- Vanguard U.S. Total Market Index ETF (CAD-hedged)Document4 pagesVanguard U.S. Total Market Index ETF (CAD-hedged)Shi SamNo ratings yet
- Dpco Price List April 2015Document82 pagesDpco Price List April 2015sppNo ratings yet
- Test Y5p2Document6 pagesTest Y5p2SYARILAH BINTI MOHD SIDEK MoeNo ratings yet
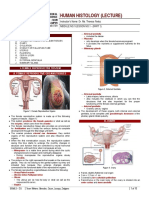
- Histo Lec - Female Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesHisto Lec - Female Reproductive SystemJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Spring 2021 Final Exam Answers Anna AnchutinaDocument4 pagesSpring 2021 Final Exam Answers Anna AnchutinaAnna AnchutinaNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment: Introduction To Sociology Soc101.10Document5 pagesFinal Assignment: Introduction To Sociology Soc101.10Navila FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument77 pagesFinancial ServicesGiridhara Raju80% (5)
- T-1486-19 Furlanetto Order TOR - 20200127160015 - FRL PDFDocument13 pagesT-1486-19 Furlanetto Order TOR - 20200127160015 - FRL PDFHoward KnopfNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - LatestDocument93 pagesCHAPTER 1 - LatestMOHAMAD ZAIM BIN IBRAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 9th Edition Mankiw Test Bank DownloadDocument40 pagesMacroeconomics 9th Edition Mankiw Test Bank DownloadEric Gaitor100% (29)
- Oakland County Health InspectionDocument1,051 pagesOakland County Health InspectionWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 HRMDocument3 pagesCase Study 2 HRMrienahsanari99No ratings yet
- Sep 2012Document8 pagesSep 2012DandavatsNo ratings yet
- FBS Final Result 22Document25 pagesFBS Final Result 22Sadman Saqib ZahinNo ratings yet
- Division School ID Name of School Name of Intervention: Enclosure 2: Profile of ActivityDocument3 pagesDivision School ID Name of School Name of Intervention: Enclosure 2: Profile of ActivityMomi BearFruitsNo ratings yet
- Annexure Ii Income Tax Calculation For The Financial Year 2020-2021 Name: Jeevana Jyothi. B Designation: Junior Lecturer in ZoologyDocument3 pagesAnnexure Ii Income Tax Calculation For The Financial Year 2020-2021 Name: Jeevana Jyothi. B Designation: Junior Lecturer in ZoologySampath SanguNo ratings yet
- DFA1101GZ5AD6J 907 Operational Manual 200606 - EnglishDocument0 pagesDFA1101GZ5AD6J 907 Operational Manual 200606 - EnglishSelmirije2No ratings yet
- Jurassic Park Script Scene 1Document3 pagesJurassic Park Script Scene 1Mapacha CerónNo ratings yet
- Durga Puja in Frankfurt, GermanyDocument16 pagesDurga Puja in Frankfurt, GermanySvanhild WallNo ratings yet
- Except: Chapter 11 - Allocation of Joint Costs and Accounting For By-Products Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesExcept: Chapter 11 - Allocation of Joint Costs and Accounting For By-Products Multiple ChoicearonnunagNo ratings yet
- CREST Industrial Control Systems Technical Security Assurance Position PaperDocument15 pagesCREST Industrial Control Systems Technical Security Assurance Position PaperwaleedNo ratings yet
- EdgeDocument6 pagesEdgeStanley NgiamNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics For Teams 4th Edition Levi Test BankDocument35 pagesGroup Dynamics For Teams 4th Edition Levi Test Bankjeffreymelendeztxnpwjbksc100% (24)
- SecuritizationDocument76 pagesSecuritizationsrinu RizarrdsNo ratings yet
- Script For "Is University Worth It?"Document2 pagesScript For "Is University Worth It?"Simran KabotraNo ratings yet
- AEG1004 Spycraft 1e - Shadowforce Archer - The ShopDocument129 pagesAEG1004 Spycraft 1e - Shadowforce Archer - The Shopbyeorama100% (2)
- RA 1225 - Air Safety Documentation Audit Trail: RationaleDocument2 pagesRA 1225 - Air Safety Documentation Audit Trail: RationaleZeraris DerNo ratings yet