0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesFunctional Assessment
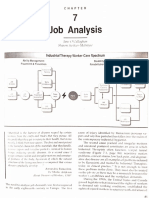
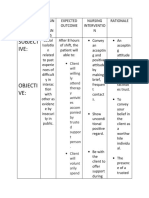
A functional assessment measures an individual's ability to perform tasks and activities of daily living. It consists of several components, including a physical assessment, health history, self-care assessment, and psychological assessment. A comprehensive nursing assessment of function should evaluate multiple domains, including physiological, behavioral, safety, family, and community. It involves gathering health information from the patient and other sources to develop a care plan with goals and interventions tailored to the individual.
Uploaded by
Cindy Mae de la TorreCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesFunctional Assessment
A functional assessment measures an individual's ability to perform tasks and activities of daily living. It consists of several components, including a physical assessment, health history, self-care assessment, and psychological assessment. A comprehensive nursing assessment of function should evaluate multiple domains, including physiological, behavioral, safety, family, and community. It involves gathering health information from the patient and other sources to develop a care plan with goals and interventions tailored to the individual.
Uploaded by
Cindy Mae de la TorreCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd