0% found this document useful (0 votes)
945 views14 pagesACCT4110 Advanced Accounting PRACTICE Exam 2 KEY v2
This document provides a practice exam for an advanced accounting course. It includes 10 multiple choice questions worth 3 points each, totaling 75 points, as well as problems on non-controlling interests worth 10 points and partnership capital accounts worth 15 points, for a total of 100 points on the exam. The questions cover topics such as accounting for business combinations, consolidation procedures, equity method, and partnership admissions.
Uploaded by
accounts 3 lifeCopyright
© Public Domain
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
945 views14 pagesACCT4110 Advanced Accounting PRACTICE Exam 2 KEY v2
This document provides a practice exam for an advanced accounting course. It includes 10 multiple choice questions worth 3 points each, totaling 75 points, as well as problems on non-controlling interests worth 10 points and partnership capital accounts worth 15 points, for a total of 100 points on the exam. The questions cover topics such as accounting for business combinations, consolidation procedures, equity method, and partnership admissions.
Uploaded by
accounts 3 lifeCopyright
© Public Domain
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Acquisition and Equity Problems: Covers problems related to acquisition dates, control of investee companies, and calculation of equity.
- Practice Exam Introduction: Introduces the practice exam, outlining the format, point distribution, and exam content areas.
- Depreciation and Amortization Calculations: Focuses on problems regarding depreciation, amortization, and valuation adjustments in financial statements.
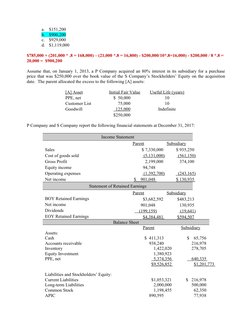
- Non-controlling Interests and Retained Earnings: Explores calculations of retained earnings, non-controlling interest, and acquisition impacts.
- Governmental Fund Accounting: Includes multiple-choice questions on types of governmental funds and fund accounting practices.
- Journal Entries and Fund Allocation: Examines journal entries and fund allocation for various municipal and capital projects.
- Problem Sets on Budgeting and Partnerships: Provides comprehensive problems dealing with budgeting, partnerships, and accounting entries for different scenarios.