Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arshi Zeb Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
arshi khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views4 pageswant
Original Title
Arshi zeb Nursing Care Plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentwant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views4 pagesArshi Zeb Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
arshi khanwant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Arshi zeb Nursing Care Plan
Class : Generic BCN 3rd Semester
NURSING
CUES/CLUES RATIONALE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE
DIAGNOSIS
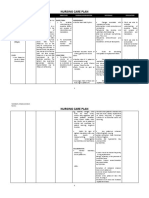
CUES: Hypokalemia Potassium is essential for SHORT-TERM: INDEPENDENT:
“Nagpacheck- many body functions. 1. To verbalize Monitor heart rate/rhythm. Changes associated with
up ako. understanding of hypokalemia include
Mababa daw Hypokalemia refers to a causative factors abnormalities in both conduction and
Potassium ko.” condition in which the and purpose of contractility.
“Dapat nga 15 concentration of interventions and Tachycardia may develop, and
minutes ‘di ba Potassium in the blood is medications. potentially life-threatening
ako mag- low. The most common atrial and ventricular dysrhythmias,
eexercise? Eh cause of excessive loss of e.g., PVCs, sinus
wala, ‘yung 15, Potassium is often bradycardia, atrioventricular (AV)
naging 7.” associated with heavy fluid 2. To demonstrate blocks, AV
(fatigue) losses that “flush” behaviors to dissociation, ventricular tachycardia.
Potassium out of the body monitor and
—a consequence of correct deficit.
vomiting and diarrhea. In
addition to this, the
patient may not be sick Maintain accurate record of Guide for calculating
but he/she does not take urinary, gastric, and wound fluid/potassium replacement needs.
enough Potassium in her losses.
diet that predisposed to
this particular condition. Monitor rate of IV potassium Ensures controlled delivery
The patient may administration using of medication to prevent bolus effect
experience generalized microdrop or pump infusion and reduce associated discomfort,
weakness, hypoventilation devices. Check for side e.g., burning sensation at IV site.
due to Potassium effects. Provide ice pack as When solution cannot be
defieciency. indicated. administered via central vein and
slowing rate is not
possible/effective, ice pack to infusion
site may help relieve discomfort.
Encourage intake of foods and Potassium may be
fluids high in potassium, replaced/level maintained through
e.g., bananas, oranges, dried the diet when patient is allowed oral
fruits, red meat, turkey, food and fluids. Dietary replacement
salmon, leafy vegetables, peas, of 40–60 mEq/L/day is typically
baked potatoes, tomatoes, sufficient if no abnormal losses are
winter squash, coffee, colas, occurring.
tea. Discuss use of potassium
chloride salt substitutes for
patient receiving long-term
diuretics.
Watch for signs of Low potassium enhances
digitalis intoxication when effect of digitalis, slowing
used (e.g., reports of cardiac conduction. Note: Combined
nausea/vomiting, blurred effects of digitalis,
vision, increasingatrial diuretics, and hypokalemia may
dysrhythmias, and heart produce lethal
block). dysrhythmias.
COLLABORATIVE:
Monitor laboratory Levels should be checked frequently
studies, e.g.: during replacement
Serum potassium; therapy, especially in the presence of
insufficient renal
function. Sudden excess/elevation
may cause cardiac
dysrhythmias.
ABGs; Correction of metabolic alkalosis
raises serum potassium
level and reduces replacement needs.
Correction of
acidosis drives potassium back into
cells, resulting in
decreased serum levels and increased
replacement needs.
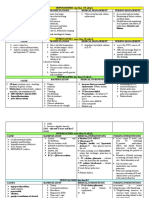
Nursing Care Plan Hyper Kalemia
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Intervention
Subjective cues: Activity Short Term Goal is met:
Verbal report of Intolerance Goal: After 2- 1. Assess 1. Injury may be related to
fatigue or 3h of nursing potential for falls or overexertion..
weakness interventions, physical injury
the patient with activity
Objective cues: will gradually
SOB resume usual 2. Observe and 2. Close monitoring serves
Bp : physical document as a guide for optimal
170/100 activities. response to progression of activity.
activity.
Long Term
Goal: 3. To promote rest. Patients
Pt will with limited activity
demonstrate tolerance need to prioritize
increased 3. Refrain from tasks.
tolerance to performing
activity by nonessential
discharge. procedures.
4. Acknowledgment that
living with activity
intolerance is both
physically and emotionally
difficult aids coping.
4. Encourage
verbalization of
feelings regarding
limitations.
You might also like
- Hypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingNo ratings yet
- The #1 Danger Of Prolonged Fasting You Have To Know About - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Eric Berg: The Most Important Risk To UnderstandFrom EverandThe #1 Danger Of Prolonged Fasting You Have To Know About - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Eric Berg: The Most Important Risk To UnderstandNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Nursing Care PlanIan Lelis100% (1)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesElectrolytesChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Hypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Metabolic AlkalosisDocument4 pagesMetabolic AlkalosisCay Sevilla100% (1)
- Hypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Case Report 3: Ectopic Pregnancy (Surgical) : Laboratory/Diagnostic FindingsDocument12 pagesCase Report 3: Ectopic Pregnancy (Surgical) : Laboratory/Diagnostic FindingsKM DelantarNo ratings yet
- NCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesNCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanVic Intia PaaNo ratings yet
- NCP AkdDocument3 pagesNCP AkdJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Short Bowel Syndrome, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Short Bowel Syndrome, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- MALABSORPTIONDocument3 pagesMALABSORPTIONZyra LagatNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMetabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperkalemia: Ateneo de Naga University College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanRenie Serrano100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyAUBREY GARATENo ratings yet
- Subjective and ObjectiveDocument1 pageSubjective and ObjectiveRiajoy AsisNo ratings yet
- Constipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationFrom EverandConstipation: How To Treat Constipation: How To Prevent Constipation: Along With Nutrition, Diet, And Exercise For ConstipationNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument7 pagesDeficient Fluid VolumeronronNo ratings yet
- Achalasia, (Swallowing Disorder) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAchalasia, (Swallowing Disorder) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- NCP (Hypokalemia)Document3 pagesNCP (Hypokalemia)Ann Mancuyas78% (9)
- Nursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Document26 pagesNursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Ric Nacional75% (4)
- NCP JagDocument10 pagesNCP JagArvinjohn GacutanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Translational Medicine: Practical Aspects in The Management of Hypokalemic Periodic ParalysisDocument8 pagesJournal of Translational Medicine: Practical Aspects in The Management of Hypokalemic Periodic ParalysisAndi Besse Ummu AmalyahNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes SummaryDocument3 pagesElectrolytes SummaryMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Case ScenarioDocument9 pagesCase ScenarioKM DelantarNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes TableDocument4 pagesElectrolytes TableMeg NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Renal DialysisDocument14 pagesRenal Dialysisjhodane100% (1)
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisDocument3 pagesAguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisSophia Kaye Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Metabolic Acid - Base ImbalancesDocument5 pagesMetabolic Acid - Base Imbalancesmardsz100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocument4 pagesManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeNo ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- F and E ReviewerDocument9 pagesF and E Revieweralifah.macabagoNo ratings yet
- AKI Developing Critical Thinking Through Understanding Pathophysiology-1-6Document5 pagesAKI Developing Critical Thinking Through Understanding Pathophysiology-1-6Anonymous StudentNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Laurente DrugstudyDocument3 pagesLaurente DrugstudyPao LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceDocument7 pagesCase: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceLovelyn GanirNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Document2 pagesMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENo ratings yet
- Kate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKate Drug StudyShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 43 Acid-Base BalanceDocument3 pagesLesson 43 Acid-Base BalanceDarren RossNo ratings yet
- NCPs (ABRIAN)Document23 pagesNCPs (ABRIAN)Rouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- Hypokalemia A H 20 637Document2 pagesHypokalemia A H 20 637Alexander KennedyNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document5 pagesWeek 8MARIKA BALONDONo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia NCPDocument2 pagesHyponatremia NCPMaica Lectana78% (9)
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study D5LRDocument2 pagesDrug Study D5LRCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- 122Document4 pages122arshi khanNo ratings yet
- NURSING DUTY ROSTER For CORONA VIRUS 2nd ShiftDocument2 pagesNURSING DUTY ROSTER For CORONA VIRUS 2nd Shiftarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Name Arshi ZebDocument6 pagesName Arshi Zebarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Office of The Hospital DirectorDocument4 pagesOffice of The Hospital Directorarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Rufaidah Nursing College: Kuwait Teaching Hospital, Abdara Road PeshawarDocument18 pagesRufaidah Nursing College: Kuwait Teaching Hospital, Abdara Road Peshawararshi khanNo ratings yet
- HEMORRHOIDSDocument4 pagesHEMORRHOIDSarshi khanNo ratings yet
- CV SafiaDocument4 pagesCV Safiaarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy QUIZZDocument5 pagesAnatomy QUIZZarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Anti Neoplastic Drugs 1Document8 pagesAnti Neoplastic Drugs 1arshi khanNo ratings yet
- Arshi Khan MCQSDocument8 pagesArshi Khan MCQSarshi khanNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument4 pagesAnswerarshi khanNo ratings yet
- PTS Test of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPTS Test of Anatomy and Physiologyarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Anti Neoplastic Drugs 1Document8 pagesAnti Neoplastic Drugs 1arshi khanNo ratings yet
- Job Duties and Tasks For: "Registered Nurse"Document7 pagesJob Duties and Tasks For: "Registered Nurse"arshi khanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy QUIZZDocument5 pagesAnatomy QUIZZarshi khanNo ratings yet
- NURSING DUTY ROSTER For CORONA VIRUS 2nd ShiftDocument2 pagesNURSING DUTY ROSTER For CORONA VIRUS 2nd Shiftarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Rufaidah Nursing College: Kuwait Teaching Hospital, Abdara Road PeshawarDocument18 pagesRufaidah Nursing College: Kuwait Teaching Hospital, Abdara Road Peshawararshi khanNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Nursing Council Islamabad: Annual Return FormDocument8 pagesPakistan Nursing Council Islamabad: Annual Return Formarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Rufaidah Nursing College: Kuwait Teaching Hospital, Abdara Road PeshawarDocument18 pagesRufaidah Nursing College: Kuwait Teaching Hospital, Abdara Road Peshawararshi khanNo ratings yet
- CorneaDocument8 pagesCorneaarshi khanNo ratings yet
- ApplicaionDocument2 pagesApplicaionarshi khanNo ratings yet
- NURSING DUTY ROSTER For CORONA VIRUSDocument2 pagesNURSING DUTY ROSTER For CORONA VIRUSarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Level of Critical ThinkingDocument1 pageLevel of Critical Thinkingarshi khanNo ratings yet
- List of Head Nurses of Zone 1 For The Follwing TrainingDocument1 pageList of Head Nurses of Zone 1 For The Follwing Trainingarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Supervisor Reporting Sheet of Zone OneDocument5 pagesNursing Supervisor Reporting Sheet of Zone Onearshi khanNo ratings yet
- Bloom%u2019s Taxonomy PPT Show - PPSXDocument12 pagesBloom%u2019s Taxonomy PPT Show - PPSXarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Duty List For Emergency From Hospital StaffDocument1 pageDuty List For Emergency From Hospital Staffarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Outside Staff Performing Duty in Emergency DepartmentDocument1 pageOutside Staff Performing Duty in Emergency Departmentarshi khanNo ratings yet
- L R H P .: Daily Work Assignment SheetDocument2 pagesL R H P .: Daily Work Assignment Sheetarshi khanNo ratings yet
- Perssuasive EssayDocument5 pagesPerssuasive Essayapi-512789628No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf - Merged (3) - 131-140Document10 pagesIlovepdf - Merged (3) - 131-140kanishka saxenaNo ratings yet
- Road To WWII RevisionDocument2 pagesRoad To WWII RevisionAngelWithAShotgun07No ratings yet
- 72-Finman Assurance Corporation vs. Court of Appeals, 361 SCRA 514 (2001)Document7 pages72-Finman Assurance Corporation vs. Court of Appeals, 361 SCRA 514 (2001)Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- Astm A489Document7 pagesAstm A489vtsusr fvNo ratings yet
- Diass (Module 6)Document41 pagesDiass (Module 6)Jocelyn Baculi AutenticoNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Studies IADocument18 pagesCaribbean Studies IAansa_france100% (1)
- CRPC Bail PresentationDocument8 pagesCRPC Bail PresentationDishant ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Emerging Treatment Options For Prostate CancerDocument8 pagesEmerging Treatment Options For Prostate CancerMax Carrasco SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pone 0187798Document20 pagesPone 0187798Aakriti DahalNo ratings yet
- Regular Verbs - FRENCHDocument8 pagesRegular Verbs - FRENCHdennis mavisNo ratings yet
- The Role of Significance Tests1: D. R. CoxDocument22 pagesThe Role of Significance Tests1: D. R. CoxMusiur Raza AbidiNo ratings yet
- SWOT ANALYSIS Dumaguin Ralph Justine B.Document3 pagesSWOT ANALYSIS Dumaguin Ralph Justine B.Edmarkmoises ValdezNo ratings yet
- Graham V Blissworld, LLCDocument16 pagesGraham V Blissworld, LLCcityfileNo ratings yet
- 哈佛大学开放课程 幸福课 (积极心理学) 视频英文字幕下载 (1-12集) (网易公开课提供) PDFDocument352 pages哈佛大学开放课程 幸福课 (积极心理学) 视频英文字幕下载 (1-12集) (网易公开课提供) PDFZiwei MiaoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management & Business Policy: 13 EditionDocument36 pagesStrategic Management & Business Policy: 13 EditionShaiful Hussain100% (2)
- Rules of DebateDocument2 pagesRules of DebateTom MendiolaNo ratings yet
- The Cave of Snakes: T D E RPG O: Exotic VistasDocument1 pageThe Cave of Snakes: T D E RPG O: Exotic VistasFabien WeissgerberNo ratings yet
- ONAP API Gateway ProposalDocument20 pagesONAP API Gateway ProposalPandji Mulia BudimanNo ratings yet
- The Story of My LifeDocument2 pagesThe Story of My LifeAnonymous lPd10LcAeNo ratings yet
- Oral Roberts - Attack Your LackDocument162 pagesOral Roberts - Attack Your LackCrAzYMaN10100% (10)
- Sample Professional - Engineer - Summary - StatementDocument5 pagesSample Professional - Engineer - Summary - StatementmrahmedNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Sutra English and ChineseDocument84 pagesCause and Effect Sutra English and ChineseVendyChenNo ratings yet
- BMS Brand ManagementDocument15 pagesBMS Brand ManagementRaviNo ratings yet
- 01 Qlik Sense Product PresentationDocument103 pages01 Qlik Sense Product PresentationDinesh KarthikNo ratings yet
- Session 4 LeadingSelf - FLA Expect The BestDocument16 pagesSession 4 LeadingSelf - FLA Expect The BesthendrikaNo ratings yet
- Indian Proverbs - WikiquoteDocument5 pagesIndian Proverbs - WikiquoteRahul7LMNo ratings yet
- Write Up Newsletter p1Document5 pagesWrite Up Newsletter p1api-378872280No ratings yet
- How To Pick Up Bitches.A5Document26 pagesHow To Pick Up Bitches.A5Tobias BlassNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Semana 1 - PDFDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 - Semana 1 - PDFLeonardo AlzateNo ratings yet