Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 4 Form 4 Biology
Uploaded by
Tavonga ChinogureiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 4 Form 4 Biology
Uploaded by
Tavonga ChinogureiCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 4 Form 4 Biology
The following is an extract from your syllabus
Core
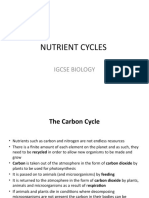
•• Describe the carbon cycle, limited to
photosynthesis, respiration, feeding,
decomposition, fossilisation and combustion
•• Discuss the effects of the combustion of fossil
fuels and the cutting down of forests on the
carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere
•• Describe the water cycle, limited to evaporation,
transpiration, condensation and precipitation
Supplement
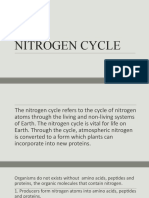
•• Describe the nitrogen cycle in terms of:
– decomposition of plant and animal protein to
ammonium ions
– nitrification
– nitrogen fixation by lightning and bacteria
– absorption of nitrate ions by plants
– production of amino acids and proteins
– feeding and digestion of proteins
– deamination
– denitrification
•• State the roles of microorganisms in the nitrogen
cycle, limited to decomposition, nitrification,
nitrogen fixation and denitrification (generic
names of individual bacteria, e.g. Rhizobium, are
not required)
The objective of this lesson is to make certain that we have covered and understood all these
outcomes.
We will do this by completing the worksheet on questions on the nitrogen cycle and discussing the
water cycle.
1. why can the nitrogen in the atmosphere not be utilised by plants.
N2 is diatomic gas hold together by three covalent bonds which require much energy to break. It is
therefore unreactive and inert.
2. what forms of nitrogen can plants utilise?
Ammonia and nitrates
3. what Is the changing of nitrogen gas into a more reactive form called? Nitrogen fixation
4. this process is brought about by nitrogen fixing bacteria in the soil and in thenodules of nitrogen
fixing plants. It can also occur in the atmosphere when lightning strikes occur. Nitrogen oxide forms
and the form nitrates.
5. plants need nitrogen to make amino acids/proteins.
6. Nitrates and ammonia are soluble and readily absorbed by roots of plants.
7. animals eat the plants and form proteins in their bodies
8. These proteins are returned to the soil in three ways
Faeces
Urine contains nitrogenous wastes produced in the process of deamination.
Decomposition of dead or decaying bodies.
9. when these products become part of the earth decomposing bacteria bring about decay and
produce ammonia.
10. ammonia is converted to nitrites and then nitrates. This is called nitrification. The bacteria are
called nitrifying bacteria.
10. the denitrifying bacteria bring about the return of nitrates to nitrogen and so reduce the fertility
of the soil.
Eutrophication occurs when fertilizers which contain high levels of nitrates are washed into rivers.
These cause the algae to grow rapidly this is called algal bloom. These then compete for light and
some of them die. The aerobic bacteria that cause their decomposition utilise the oxygen and so the
fish start to die. This leads to the pollution of rivers.
Water Cycle
The key words for the water cycle are evaporation, transpiration, condensation and
evaporation.
I would like you to draw this cycle into your notebooks from page 272.
We will now use the diagram below to understand eutropication fully.
Eutrophication
I would like you to use the above diagram to give
me the main points.
You might also like
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument34 pagesCarbon CycleHimanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Document7 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument12 pagesNitrogen Cycleasa bspcpkNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle W QuestionsDocument2 pagesNitrogen Cycle W QuestionsemmaNo ratings yet
- The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles ExplainedDocument19 pagesThe Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles ExplainedTanyaradzwa MugutaNo ratings yet
- College of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesCollege of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesPatrick Philip BalletaNo ratings yet
- 7 Nitrogen Cycle W Questions AnsDocument3 pages7 Nitrogen Cycle W Questions AnselamorylapurezaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle Explained - Definition, Stages and ImportanceDocument1 pageNitrogen Cycle Explained - Definition, Stages and Importanceappiahsarpong7906No ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles - "Energy Flows and Matter Cycles" ANSWER KEYDocument2 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles - "Energy Flows and Matter Cycles" ANSWER KEYJay Astillo NicanorNo ratings yet
- Answers To Water, Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet The Water CycleDocument2 pagesAnswers To Water, Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet The Water CycleMrfatasianNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle by Diksha MamDocument6 pagesNitrogen Cycle by Diksha MamAnuj & PrachiNo ratings yet
- Cycles of MatterDocument28 pagesCycles of MatterRamil NacarioNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Cycles 241 2018Document33 pagesNutrient Cycles 241 2018LeondreNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument15 pagesNitrogen CycleCris TineNo ratings yet
- Course: CPE665Document8 pagesCourse: CPE665aleeyazahardiNo ratings yet
- World Soil DayDocument15 pagesWorld Soil DayLindsey DapulagNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument5 pagesBiogeochemical Cyclesjaimejeannepoot.martinezNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle: Proudly Present By, MD Adib Fikri Kavisya Logadharshini Suganeya AlkhalwarizmiDocument36 pagesCarbon and Nitrogen Cycle: Proudly Present By, MD Adib Fikri Kavisya Logadharshini Suganeya AlkhalwarizmiSuganeya UdiasoorianNo ratings yet
- BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: CARBON, NITROGEN & OXYGENDocument13 pagesBIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: CARBON, NITROGEN & OXYGENPrince MpofuNo ratings yet
- Biogeography PDFDocument63 pagesBiogeography PDFKudzai MwandimutsiraNo ratings yet
- The Nitrogen CycleDocument2 pagesThe Nitrogen CycleLucia TNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nitrogen CycleDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Nitrogen CycleSweetrose GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Biology Note On Nutrient Cycles & PopulationsDocument8 pagesBiology Note On Nutrient Cycles & PopulationsFritzNo ratings yet
- Why Does Copper Not React With Nitrogen?: ChemistryDocument2 pagesWhy Does Copper Not React With Nitrogen?: ChemistryDoaa NassarNo ratings yet
- CyclesDocument34 pagesCyclesRose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Environment - Nitrogen CycleDocument5 pagesEnvironment - Nitrogen CycleMugal AslamNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 2Document2 pagesCape Biology Unit 2MasOom Si ChuRail100% (1)
- STS 11 My ReportDocument31 pagesSTS 11 My ReportCaroline ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument6 pagesNitrogen CycleAngelica Soriano100% (1)
- Cycles of Life: Photosynthesis, Biogeochemical Processes and Their ImportanceDocument11 pagesCycles of Life: Photosynthesis, Biogeochemical Processes and Their ImportanceElaine Jane ArmadaNo ratings yet
- Cycles of Matter: Lesson ObjectivesDocument8 pagesCycles of Matter: Lesson ObjectivesJason ChenNo ratings yet
- The Nitrogen Cycle: Processes, Players, and Human ImpactDocument8 pagesThe Nitrogen Cycle: Processes, Players, and Human ImpactKesto LoriakNo ratings yet
- Cycles of Matter: Lesson ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCycles of Matter: Lesson Objectivesapi-593653104No ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument2 pagesNitrogen CycleKalsoom AsadNo ratings yet
- Module 04 - Materials Cycle and ChangeDocument10 pagesModule 04 - Materials Cycle and ChangeMarian Grace CanaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument14 pagesNitrogen CycleRafaela Eunice D CorreaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen cycleDocument21 pagesNitrogen cycleAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Handouts On Atmosphere and Lithosphere OuDocument3 pagesHandouts On Atmosphere and Lithosphere OuMiraquel Añonuevo LabogNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument3 pagesNitrogen CycleAliyaNo ratings yet
- Cyle of N, O and MineralDocument13 pagesCyle of N, O and MineralFikrah Hafiz SuniNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument3 pagesNitrogen Cyclejminati54No ratings yet
- The Nitrogen Cycle: By: Aakash GoelDocument45 pagesThe Nitrogen Cycle: By: Aakash GoelaakgoelNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument4 pagesNitrogen CycleJadeNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.4 - Cycles of MatterDocument3 pagesActivity 3.4 - Cycles of MatterRAMIL BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical CyclesDocument31 pagesBio-Chemical CyclesNouman TariqNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle Explained in Microbiology ClassDocument19 pagesNitrogen Cycle Explained in Microbiology ClassUswa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hardness of Water and FertilizersDocument10 pagesHardness of Water and FertilizersDennis NdoloNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles Compatibility ModeDocument52 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles Compatibility ModeAkshay EtwareeaNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument4 pagesThe Water CycleCris TineNo ratings yet
- How Nutrients Are Recycled Through Ecosystems (Nutrient CyclesDocument4 pagesHow Nutrients Are Recycled Through Ecosystems (Nutrient CyclesAnna Marie LaganzonNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument15 pagesNitrogen CycleHamza UmmarNo ratings yet
- Jimma Institute of Technology Advanced Wastewater TreatmentDocument40 pagesJimma Institute of Technology Advanced Wastewater TreatmentyaredNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument29 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesKhadija ZaheerNo ratings yet
- L - Ch3.4 Cycles of Matter Guided ReadingDocument5 pagesL - Ch3.4 Cycles of Matter Guided ReadingHexagon LyricsNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle NotesDocument2 pagesNitrogen Cycle NotesAjit PatelNo ratings yet
- 18 - Biogeochemical Cycles L R200305101003031515Document13 pages18 - Biogeochemical Cycles L R200305101003031515JibinaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen CycleDocument5 pagesNitrogen CycleVamsi K Kuchibhotla100% (1)
- Topic 3 - Nutrient CyclesDocument5 pagesTopic 3 - Nutrient CyclesJomari TawatNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 4, Fertilisers and NitrogenDocument3 pagesChem Form 4, Fertilisers and NitrogenshshbshshsjsjNo ratings yet
- D4373 Contenido Carbonato en SueloDocument5 pagesD4373 Contenido Carbonato en SueloDaniela Bernal100% (1)
- Ib Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2Document5 pagesIb Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2omarnasriNo ratings yet
- ENDOTOXIN (E. Coli O113:H10) Control Standard Endotoxin (CSE)Document2 pagesENDOTOXIN (E. Coli O113:H10) Control Standard Endotoxin (CSE)deepanmb007No ratings yet
- Autochem 2950 HP - BrochureDocument8 pagesAutochem 2950 HP - Brochurerestor3dNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses and Strains PDFDocument104 pagesSimple Stresses and Strains PDFyaminiNo ratings yet
- Construction Chemicals: Total Solution ofDocument4 pagesConstruction Chemicals: Total Solution ofdwijNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials MCQs PDFDocument41 pagesEngineering Materials MCQs PDFRamesh KondriNo ratings yet
- OptoelectronicsDocument11 pagesOptoelectronicsJohn Paul DirayNo ratings yet
- Borophene As A Prototype For Synthetic 2D Materials DevelopmentDocument7 pagesBorophene As A Prototype For Synthetic 2D Materials DevelopmentparsmessengerNo ratings yet
- 13 - Baker Hughes - Kennedy enDocument36 pages13 - Baker Hughes - Kennedy enSpecule100% (1)
- L.3.2 Fate and BehaviorDocument29 pagesL.3.2 Fate and BehaviorGerald Luy CorderoNo ratings yet
- Example of Research ProposalDocument4 pagesExample of Research ProposalBlankSyaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 5623Document6 pagesAstm D 5623Daniel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - MetamaterialsDocument31 pagesLecture 13 - MetamaterialsAaa MmmNo ratings yet
- Applications of Protein Sericin From The SilkglandDocument5 pagesApplications of Protein Sericin From The SilkglandMadiha AshrafNo ratings yet
- RAC Introduction ClassDocument32 pagesRAC Introduction ClassRuturaj UmaranikarNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology: What Is Nano Technology?Document5 pagesNanotechnology: What Is Nano Technology?Francis PrasadNo ratings yet
- MF52 NTC Thermistor GuideDocument3 pagesMF52 NTC Thermistor GuideROHAN DARVENo ratings yet
- Handbook of Sic Properties For Fuel Performance ModelingDocument49 pagesHandbook of Sic Properties For Fuel Performance ModelingAbhiraj MeenaNo ratings yet
- Hanna Instruments S.R.L.: Safety Data Sheet According To Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006Document9 pagesHanna Instruments S.R.L.: Safety Data Sheet According To Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006Renaldo MoontriNo ratings yet
- Defects in Hot Rolled Products1Document33 pagesDefects in Hot Rolled Products1eng_ahmedkassemNo ratings yet
- Reynolds ExperimentDocument13 pagesReynolds ExperimentAngelia Maharani Putri LeanNo ratings yet
- Comfort Air PDFDocument79 pagesComfort Air PDFSunny OoiNo ratings yet
- 122Document10 pages122Bayangan HatiNo ratings yet
- Naturvital-Plus - ING - Technical Data Sheet PDFDocument1 pageNaturvital-Plus - ING - Technical Data Sheet PDFPetre ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Semi-Empirical MethodsDocument3 pagesSemi-Empirical MethodsludihemicarNo ratings yet
- Pulse Firing BasicsDocument3 pagesPulse Firing BasicsdrbaneNo ratings yet
- EPA METHOD 5 CALCULATIONSDocument42 pagesEPA METHOD 5 CALCULATIONSDipeshBardoliaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Lab GuideDocument10 pagesMicroscope Lab GuideBrian Luo67% (3)