Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources Under PFRS 6
Uploaded by
missyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources Under PFRS 6
Uploaded by
missyCopyright:
Available Formats
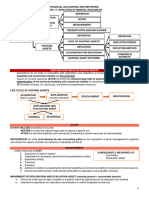
Exploration and evaluation of mineral resources under PFRS 6.
The objective of this standard is to specify the financial reporting for the exploration and evaluation of
mineral resources.
Mineral resources include minerals, oil, natural gas and similar non-regenerative resources.
The term exploration and evaluation of mineral resources is defined as the search for mineral resources
after the entity has obtained legal rights to explore in a specific area as well as the determination of the
technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting the mineral resources.
The expenditures incurred by an entity in connection with the exploration and evaluation of mineral
resources before the technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting a mineral resource are
known as exploration and evaluation expenditures.
Expenditures related to development of mineral resources, for example, preparation for commercial
production, such as building roads and tunnels, cannot be recognized as exploration and evaluation
expenditures.
Examples of exploration and evaluation expenditures.
a. Acquisition of rights to explore;
b. Topographical, geological, geochemical and geophysical studies;
c. Exploratory drilling;
d. Trenching;
e. Sampling; and
f. Activities in relation to evaluating technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting a mineral
resource.
The qualifying expenditures notably exclude those that are incurred in connection with the development
of a mineral resource once technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting a mineral resource
have been established. Additionally, any administration and other general overhead costs are explicitly
excluded from the definition of qualifying expenditures.
The treatment of exploration and evaluation expenditures?
The exploration and evaluation expenditures may qualify as exploration and evaluation asset.
Under PFRS 6, an entity must develop an accounting policy for the recognition of such asset. An entity is
permitted to continue to apply a previous accounting policy provided that the resulting information is
relevant reliable.
An exploration and evaluation asset shall be measured initial at cost.
After initial recognition, an entity shall apply either the model or the revaluation model.
Exploration and evaluation asset is classified either tangible asset or an intangible asset.
Wasting assets.
Wasting assets are material objects of economic value and utility to man produced by nature. Actually,
wasting assets are natural resources.
Natural resources usually include coal, oil, ore, precious metals like gold and silver, and timber.
Wasting assets are so called because these are physically consumed and once consumed, the wasting
assets cannot be replaced anymore.
If ever, the wasting assets can be replaced only by the process of nature. Natural resources cannot be
produced by man.
Thus, wasting assets are characterized by two main features:
a) The wasting assets are physically consumed.
b) The wasting assets are irreplaceable.
What is the cost of wasting asset?
Costs of Wasting Assets
Acquisition cost, Exploration and evaluation cost
,Development cost, Restoration cost
Explain the acquisition cost of a wasting asset.
Acquisition cost is the price paid to obtain the property containing the natural resource.
Unquestionably, this is the initial cost of the wasting asset.
Generally, the acquisition cost is charged to any descriptive natural resource account.
You might also like
- The BIM Manager A Practical Guide For BIM Project ManagementDocument306 pagesThe BIM Manager A Practical Guide For BIM Project ManagementBelen RG100% (4)
- Sample Regular Employment ContractDocument13 pagesSample Regular Employment ContractLora Soriano100% (1)
- Hedging Against Rising Coal Prices Using Coal FuturesDocument38 pagesHedging Against Rising Coal Prices Using Coal FuturesSunil ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- The Estimated Restoration Cost Must Be DiscountedDocument2 pagesThe Estimated Restoration Cost Must Be DiscountedNey GascNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument2 pagesChapter 34 Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesEllen MaskariñoNo ratings yet
- C34 - PFRS 6 Mineral ResourcesDocument1 pageC34 - PFRS 6 Mineral ResourcesAllaine ElfaNo ratings yet
- 41 DepletionDocument5 pages41 DepletionjsemlpzNo ratings yet
- CONFRACS - Module 8 - Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument8 pagesCONFRACS - Module 8 - Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesMatth FlorezNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Acc For Exploration and Evaluating of Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesPFRS 6 Acc For Exploration and Evaluating of Natural ResourcesElaiza Jane CruzNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6Document13 pagesPFRS 6Princess Jullyn ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Audit of Wasting Assets Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAudit of Wasting Assets Learning ObjectivesTrisha Mae RodillasNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 - 1Document1 pagePFRS 6 - 1Ella MaeNo ratings yet
- Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources (PFRS 6)Document3 pagesExploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources (PFRS 6)Ragnar LothbrokNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources With IllustrationsDocument31 pagesPFRS 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources With IllustrationsHannah TaduranNo ratings yet
- Depletion of Mineral Resources (Millan)Document3 pagesDepletion of Mineral Resources (Millan)didit.canonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesMODULE 9 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesKim JisooNo ratings yet
- MODULE 31 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesMODULE 31 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesAngelica Sanchez de VeraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 31 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesMODULE 31 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesAngelica Sanchez de VeraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesMODULE 9 Exploration For An Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesEarl ENo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance - Mining Industries WORDDocument16 pagesAuditing and Assurance - Mining Industries WORDJazmine Hupp UyNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources: Fact SheetDocument8 pagesIfrs 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources: Fact SheetTun Win KyawNo ratings yet
- Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument7 pagesExploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesJerome_JadeNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Mineral Exploration Properties Using The Cost ApproachDocument11 pagesValuation of Mineral Exploration Properties Using The Cost ApproachHamit AydınNo ratings yet
- Mining ReportDocument2 pagesMining ReportSoremn PotatoheadNo ratings yet
- Evaluacion de YacimientosDocument5 pagesEvaluacion de YacimientospaolodgrNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument5 pagesPFRS 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesMartha Nicole MaristelaNo ratings yet
- ACC107 P2-Quiz1Document7 pagesACC107 P2-Quiz1itsayuhthingNo ratings yet
- 20 - Wasting AssetsDocument5 pages20 - Wasting AssetsYudna YuNo ratings yet
- Mineral Exploration and Development Risk and RewardDocument16 pagesMineral Exploration and Development Risk and RewardПростой ЧеловекNo ratings yet
- Aud Application 2 - Handout 7 Wasting Asset (UST)Document5 pagesAud Application 2 - Handout 7 Wasting Asset (UST)RNo ratings yet
- (Intermediate Accounting 1B) : Lecture AidDocument12 pages(Intermediate Accounting 1B) : Lecture AidAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- ManeksDocument11 pagesManeksMiko Rc SevenNo ratings yet
- CIM Definition Standards For Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves PDFDocument10 pagesCIM Definition Standards For Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves PDFcmendozatNo ratings yet
- FAR 11 Depletion of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesFAR 11 Depletion of Mineral ResourcesShaira Mae DausNo ratings yet
- 2 Ass-02Document8 pages2 Ass-02mouniNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Mineral Resources in Selected FinanciDocument12 pagesValuation of Mineral Resources in Selected FinanciBill LiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Upstream TransactionsDocument38 pagesLecture 2 Upstream TransactionsclementNo ratings yet
- Notes-INTERM 2-Module 4-Depletion of Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesNotes-INTERM 2-Module 4-Depletion of Natural ResourcesLeonoramarie BernosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Upstream Transactions UpdatedDocument64 pagesLecture 2 Upstream Transactions UpdatedclementNo ratings yet
- DepletionDocument3 pagesDepletioncheesequesoNo ratings yet
- Samval - Code2008 South AfricaDocument15 pagesSamval - Code2008 South AfricaAndy RiveraNo ratings yet
- Disposal of Investment PropertyDocument4 pagesDisposal of Investment Propertyglaide lojeroNo ratings yet
- Wasting AssetsDocument2 pagesWasting AssetsAdan NadaNo ratings yet
- As Numerosas Etapas Podem Incluir Fragmentação, Granulação, Moagem, Classificação e ConcentraçãoDocument8 pagesAs Numerosas Etapas Podem Incluir Fragmentação, Granulação, Moagem, Classificação e ConcentraçãoZainadine Alfredo AguiarNo ratings yet
- FAR.2910 - Wasting Assets.Document4 pagesFAR.2910 - Wasting Assets.Edmark LuspeNo ratings yet
- Exploration and Evaluation ExpendituresDocument1 pageExploration and Evaluation ExpendituresIrish NicdaoNo ratings yet
- Depletion: Jazel Mae C. Delmonte, Cpa ACC 211Document40 pagesDepletion: Jazel Mae C. Delmonte, Cpa ACC 211Juliemar Frances PadilloNo ratings yet
- Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources: Ifrs 6Document26 pagesExploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources: Ifrs 6Danna Claire100% (1)
- Oil and Gas Companies - Understanding The Industry and The RisksDocument3 pagesOil and Gas Companies - Understanding The Industry and The RisksJoris YapNo ratings yet
- 2 S 31 Mineral Economic 31 EP 2017Document42 pages2 S 31 Mineral Economic 31 EP 2017TapiaNo ratings yet
- Query: When An Exploration and Evaluation Asset Shall No Longer Be Classified As Such?Document1 pageQuery: When An Exploration and Evaluation Asset Shall No Longer Be Classified As Such?elsana philipNo ratings yet
- Example 3BA21 033130050 TMA1Document10 pagesExample 3BA21 033130050 TMA1Hamshavathini YohoratnamNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 - Here Are Problems and Solutions. There Are Some Theories As Well That May HelpDocument5 pagesPFRS 6 - Here Are Problems and Solutions. There Are Some Theories As Well That May HelpJezela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mine ValuationDocument30 pagesMine ValuationAnkush kumarNo ratings yet
- PHILIPPINE VALUATION STANDARDS NotesDocument15 pagesPHILIPPINE VALUATION STANDARDS NotesPrince EG DltgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Accounting For Plant Assets and Intangile Assets Revised 2011Document20 pagesChapter 3 Accounting For Plant Assets and Intangile Assets Revised 2011Biru EsheteNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Accounting Acc614 - Intermediate Financial Accounting 2 Topic: Accounting For Extractive IndustriesDocument14 pagesBachelor of Accounting Acc614 - Intermediate Financial Accounting 2 Topic: Accounting For Extractive IndustriesGEORGINA KINIKANo ratings yet
- Divisão de Engenharia Engenharia de Minas: 2-ANO TURMA: Unica Curso: NoturnoDocument5 pagesDivisão de Engenharia Engenharia de Minas: 2-ANO TURMA: Unica Curso: NoturnoZainadine Alfredo AguiarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five and Six: Mineral Resources Evaluation and Ore Reserve CalculationDocument57 pagesChapter Five and Six: Mineral Resources Evaluation and Ore Reserve CalculationTemesgen workiyeNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 6 PDFDocument8 pagesIfrs 6 PDFSanket AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Economic Geology and Mining Economics: Example QuestionsDocument12 pagesEconomic Geology and Mining Economics: Example QuestionsGabriel Gurrea MatusNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mining: Valuation, Organization and AdministrationFrom EverandPrinciples of Mining: Valuation, Organization and AdministrationNo ratings yet
- Fine Reservoir Description: Techniques, Current Status, Challenges, and SolutionsFrom EverandFine Reservoir Description: Techniques, Current Status, Challenges, and SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Merge 11Document37 pagesMerge 11Sajj PrrtyNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong Civil Procedure - Order 22 Payment Into and Out of CourtDocument36 pagesHong Kong Civil Procedure - Order 22 Payment Into and Out of CourtWilliam TongNo ratings yet
- WindForce PLC AR 2021Document232 pagesWindForce PLC AR 2021Wishva WidanagamageNo ratings yet
- Makerere University: Business SchoolDocument6 pagesMakerere University: Business Schoolkitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- Moh 21 LT 174Document1 pageMoh 21 LT 174romano sartoriNo ratings yet
- Proclamation 649.ae PDFDocument53 pagesProclamation 649.ae PDFeph93% (14)
- Difference Between EDI and ALEDocument1 pageDifference Between EDI and ALEdjmastNo ratings yet
- Cobit SoalDocument36 pagesCobit SoalYANI ANJANI 1No ratings yet
- Group Risk Management Policy May2021.pdf - DownloadassetDocument6 pagesGroup Risk Management Policy May2021.pdf - DownloadassetMg MgNo ratings yet
- Lebone College of Emergency Care LearnershipDocument7 pagesLebone College of Emergency Care LearnershipPiko AhNo ratings yet
- Rubine Store: Shop Rubine Malaysia Service CenterDocument1 pageRubine Store: Shop Rubine Malaysia Service CenterChristy WongNo ratings yet
- Chartered Professional Accountants of Ontario Act, 2017: S.O. 2017, CHAPTER 8 S 3Document23 pagesChartered Professional Accountants of Ontario Act, 2017: S.O. 2017, CHAPTER 8 S 3susan thomasNo ratings yet
- Flutter Prelims Statement 2022 Final FinalDocument66 pagesFlutter Prelims Statement 2022 Final Finalzereabrham mulugetaNo ratings yet
- BSBFIM601 Manage Finances: ASSESSMENT 1 - Written QuestionsDocument41 pagesBSBFIM601 Manage Finances: ASSESSMENT 1 - Written QuestionsPriyanka Aggarwal75% (4)
- Pricing Model For A Credit-Linked Note On A CDX TrancheDocument6 pagesPricing Model For A Credit-Linked Note On A CDX TranchechertokNo ratings yet
- Uniform CPA Examination May 1983-May 1987 Selected Questions &Document675 pagesUniform CPA Examination May 1983-May 1987 Selected Questions &Abdelmadjid djibrineNo ratings yet
- CHAP 9. Materiality and RiskDocument28 pagesCHAP 9. Materiality and RiskNoroNo ratings yet
- MR Evans Is A Wholesaler Who Buys and Sells ADocument2 pagesMR Evans Is A Wholesaler Who Buys and Sells AAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- TNEB Online PaymentDocument1 pageTNEB Online PaymentveerNo ratings yet
- Lifted From BAR Exam Questions & QuizzersDocument9 pagesLifted From BAR Exam Questions & QuizzersAira Jaimee GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument2 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceReema KhatiNo ratings yet
- Ics 2210 System Analysis and Design 2Document3 pagesIcs 2210 System Analysis and Design 2123 321No ratings yet
- Benefit Illustration: UIN: 104N116V02 Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesBenefit Illustration: UIN: 104N116V02 Page 1 of 3Ravindar aNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: November 2018Document14 pagesMark Scheme: November 2018BethanyNo ratings yet
- United Construction P.L.C - Ethiopian ConstructionDocument2 pagesUnited Construction P.L.C - Ethiopian Constructionermias asalifNo ratings yet
- AIDA Model - ExplanationDocument4 pagesAIDA Model - ExplanationQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Group Project On "Bloop" Ice-Cream MKT 460 Strategic Marketing Mr. Rafsan ElahiDocument23 pagesGroup Project On "Bloop" Ice-Cream MKT 460 Strategic Marketing Mr. Rafsan ElahiRifat ChowdhuryNo ratings yet