Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Estimated Restoration Cost Must Be Discounted
Uploaded by
Ney Gasc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views2 pagesIntAcc
Original Title
Chapter 31
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntAcc
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views2 pagesThe Estimated Restoration Cost Must Be Discounted
Uploaded by
Ney GascIntAcc
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chapter 31
Depletion
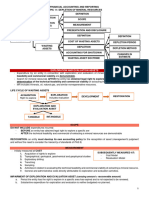
1. Define the term ‘’exploration and evaluation of mineral resources”
The search for mineral resources after the entity has obtained legal rights to explore in a specific
area as well as the determination of the technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting
the mineral resources.
Mineral resources include minerals, oil, natural gas and similar nonregenerative resources.
The expenditures incurred by an entity in connection with the exploration and evaluation of mineral
resources before the technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting a mineral resource
are known as exploration and evaluation expenditures.
Expenditures related to development of mineral resources, for example, preparation for
commercial production, such as building roads and tunnels, cannot be recognized as exploration and
evaluation expenditures.
2. What is the treatment of exploration and evaluation expenditures?
The exploration and evaluation expenditures may qualify as exploration and evaluation asset.
An entity must develop an accounting policy for the recognition of such asset.
An entity is permitted to continue to apply a previous accounting policy provided that the resulting
information is relevant and reliable.
An exploration and evaluation asset shall be measured initially at cost.
After initial recognition, an entity shall apply either the cost model or the revaluation model.
Exploration and evaluation asset is classified either as tangible asset or an intangible asset.
3. Define wasting assets.
These are material objects of economic value and utility to man produced by nature.
Wasting assets are actually natural resources, which usually include coal, oil, ore, precious metals
like gold and silver, and timber.
Wasting assets are so called because these are physically consumed, the wasting assets cannot be
replaced anymore.
If ever, the wasting assets can be replaced only by the process of nature. Natural resources cannot
be produced by man.
Wasting assets are physically consumed and irreplaceable.
4. Explain the cost of a wasting asset.
In general, it comprises acquisition cost, exploration cost, development cost and estimated
restoration cost.
Acquisition cost is the price paid to obtain the property containing the natural resource.
Unquestionably, this is the initial cost of the wasting asset.
If there is a residual land value after the extraction of the natural resource, the portion of the
acquisition cost applicable to the land should be deducted from the total cost to get the depletable
amount.
Exploration cost is the cost incurred in an attempt to locate the natural resource that can
economically be extracted or exploited.
Under the “successful effort” method, only the exploration cost directly related to the discovery of
commercially producible natural resource is capitalized as cost of the resource property.
Under the “full cost” method, all exploration costs, whether successful or unsuccessful, are
capitalized as cost of the successful resource discovery.
Development cost is the cost incurred to exploit or extract the natural resource that has been
located through successful exploration.
Development cost may be in the form of tangible equipment and intangible development cost.
Only intangible development cost is capitalized as cost of wasting asset.
The cost of tangible equipment is included in property, plant and equipment.
Estimated restoration cost is the cost to be incurred in order to bring the property to the original
condition as required by law or contract.
The estimated restoration cost must be discounted.
5. What is concept of depletion?
It is the removal, extraction or exhaustion of a natural resource or wasting asset.
As an accounting procedure, depletion is the systematic allocation of the depletable amount of a
wasting asset over the periods the natural resource is extracted or produced.
Normally, depletion is computed using the output or production method.
The depletable amount of the wasting asset is divided by the units estimated to be extracted to
obtain depletion rate per unit.
The depletion rate per unit is then multiplied by the units extracted during the year to arrive at the
depletion for the period.
Depletable amount equals cost of wasting asset minus residual land value.
6. What is the method used in computing depreciation of tangible equipment used in mining operations?
Generally, it is based on the life of the mining equipment or the life of the wasting asset, whichever is
shorter.
In the life of the mining equipment is shorter, the straight line method of depreciation is normally
used.
If the life of the wasting asset is shorter, the output method of depreciation is frequently used.
However, if the mining equipment is movable and can be used in future extractive project, the
equipment is depreciated over its useful life using the straight line method.
You might also like
- Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources Under PFRS 6Document2 pagesExploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources Under PFRS 6missyNo ratings yet
- Wasting AssetsDocument2 pagesWasting AssetsAdan NadaNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Exploration and EvaluationDocument2 pagesPFRS 6 Exploration and EvaluationEllen MaskariñoNo ratings yet
- 41 DepletionDocument5 pages41 DepletionjsemlpzNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Guide to Exploring Mineral ResourcesDocument1 pagePFRS 6 Guide to Exploring Mineral ResourcesAllaine ElfaNo ratings yet
- Audit of Wasting Assets Depletion and DepreciationDocument3 pagesAudit of Wasting Assets Depletion and DepreciationTrisha Mae RodillasNo ratings yet
- Depletion of Mineral Resources (Millan)Document3 pagesDepletion of Mineral Resources (Millan)didit.canonNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 - 1Document1 pagePFRS 6 - 1Ella MaeNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources With IllustrationsDocument31 pagesPFRS 6 Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources With IllustrationsHannah TaduranNo ratings yet
- CONFRACS - Module 8 - Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument8 pagesCONFRACS - Module 8 - Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesMatth FlorezNo ratings yet
- (1) EXPLORATION AND EVALUATION OF MINERAL RESOURCESDocument7 pages(1) EXPLORATION AND EVALUATION OF MINERAL RESOURCESJerome_JadeNo ratings yet
- Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources (PFRS 6)Document3 pagesExploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources (PFRS 6)Ragnar LothbrokNo ratings yet
- DepletionDocument3 pagesDepletioncheesequesoNo ratings yet
- (Intermediate Accounting 1B) : Lecture AidDocument12 pages(Intermediate Accounting 1B) : Lecture AidAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- IFRS 6 Exploration and Evaluation Asset DepletionDocument40 pagesIFRS 6 Exploration and Evaluation Asset DepletionJuliemar Frances PadilloNo ratings yet
- Depletion: Valix, C. T. Et Al. Intermediate GIC Enterprises & Co. IncDocument21 pagesDepletion: Valix, C. T. Et Al. Intermediate GIC Enterprises & Co. IncJoris YapNo ratings yet
- Revaluation of Property, Plant and Equipment ExplainedDocument1 pageRevaluation of Property, Plant and Equipment ExplainedAia SmithNo ratings yet
- Cpa Far - Study Unit 8 Property, Plant, Equipment, and Depletable Resources Core ConceptsDocument3 pagesCpa Far - Study Unit 8 Property, Plant, Equipment, and Depletable Resources Core ConceptsGAANo ratings yet
- Natural Resources - AccountingDocument2 pagesNatural Resources - AccountingAudrey Rose RagasajoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28: Depletion Pfrs/Ifrs 6: Financial Reporting For The Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesChapter 28: Depletion Pfrs/Ifrs 6: Financial Reporting For The Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Accounting For Plant Assets and Intangile Assets Revised 2011Document20 pagesChapter 3 Accounting For Plant Assets and Intangile Assets Revised 2011Biru EsheteNo ratings yet
- Plant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible AssetsDocument3 pagesPlant Assets, Natural Resources, and Intangible AssetsEva FransiscaNo ratings yet
- 02 Audit of Mining Entities PDFDocument12 pages02 Audit of Mining Entities PDFelaine piliNo ratings yet
- Property Plant and EquipmentDocument2 pagesProperty Plant and EquipmentdayanNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance - Mining Industries WORDDocument16 pagesAuditing and Assurance - Mining Industries WORDJazmine Hupp UyNo ratings yet
- Survey of Accounting 5Th Edition Edmonds Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesSurvey of Accounting 5Th Edition Edmonds Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFzanewilliamhzkbr100% (6)
- Survey of Accounting 5th Edition Edmonds Solutions ManualDocument65 pagesSurvey of Accounting 5th Edition Edmonds Solutions Manualmoriskledgeusud100% (20)
- Libby Financial Accounting Solution Manual Chapter 8 Entire VersionDocument5 pagesLibby Financial Accounting Solution Manual Chapter 8 Entire Versionmercy ko0% (1)
- Wasting Asset AnswerDocument3 pagesWasting Asset AnswerJessalyn DaneNo ratings yet
- FAR 11 Depletion of Mineral Resources (1)Document3 pagesFAR 11 Depletion of Mineral Resources (1)Shaira Mae DausNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Review Center (ARC) Student HandoutsDocument5 pagesAccountancy Review Center (ARC) Student HandoutsRNo ratings yet
- Plant Assets, Natural Resources and Intangible AssetsDocument11 pagesPlant Assets, Natural Resources and Intangible AssetsSamuel DebebeNo ratings yet
- Cornerstones of Financial Accounting Canadian 2nd Edition Rich Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesCornerstones of Financial Accounting Canadian 2nd Edition Rich Solutions Manualdariusba1op100% (22)
- 20 - Wasting AssetsDocument5 pages20 - Wasting AssetsYudna YuNo ratings yet
- Exploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources: Ifrs 6Document26 pagesExploration For and Evaluation of Mineral Resources: Ifrs 6Danna Claire100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Study GuideDocument9 pagesChapter 11 Study GuideAngelia TNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Accounting For Plant Assets and IntagiblesDocument20 pagesChapter 2, Accounting For Plant Assets and IntagiblesAbdi Mucee TubeNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Taxation of Business Entities 2017 8th Edition Spilker Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Taxation of Business Entities 2017 8th Edition Spilker Solutions Manual PDFquemefuloathableilljzf100% (10)
- Plant AssetsDocument38 pagesPlant AssetsYolowii XanaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Plant Assets, Natural Resources and Intangible AssetsDocument17 pagesCH 2 Plant Assets, Natural Resources and Intangible AssetsNigus AyeleNo ratings yet
- FuA II Chapter 2Document32 pagesFuA II Chapter 2YasinNo ratings yet
- Depletion Notes: Disclaimer: Not EntirelyDocument3 pagesDepletion Notes: Disclaimer: Not EntirelyRes GosanNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument26 pagesDepreciationBalu BalireddiNo ratings yet
- PVS Notes on Valuation Concepts, Principles and Market ValueDocument14 pagesPVS Notes on Valuation Concepts, Principles and Market ValueRob ClosasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Audit of Fixed AssetsDocument4 pagesUnit 5: Audit of Fixed AssetsTilahun S. KuraNo ratings yet
- Fixed AssetDocument25 pagesFixed AssetSisay Belong To JesusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsDocument46 pagesChapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsSimon MollaNo ratings yet
- PFRS 6 Acc For Exploration and Evaluating of Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesPFRS 6 Acc For Exploration and Evaluating of Natural ResourcesElaiza Jane CruzNo ratings yet
- Farm Management Chap 2Document42 pagesFarm Management Chap 2gedisha katola100% (1)
- MPD Assignment 1Document3 pagesMPD Assignment 1Maurielle John OcampoNo ratings yet
- Workbook 3 (July 2022)Document76 pagesWorkbook 3 (July 2022)Sansaar KandhroNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Accounting Acc614 - Intermediate Financial Accounting 2 Topic: Accounting For Extractive IndustriesDocument14 pagesBachelor of Accounting Acc614 - Intermediate Financial Accounting 2 Topic: Accounting For Extractive IndustriesGEORGINA KINIKANo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PpeDocument82 pagesUnit 2 PpeHirut GetachewNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Taxation of Business Entities 5th Edition Spilker Solutions Manual PDFDocument22 pagesDwnload Full Taxation of Business Entities 5th Edition Spilker Solutions Manual PDFquemefuloathableilljzf100% (10)
- Full Download Taxation of Business Entities 5th Edition Spilker Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Taxation of Business Entities 5th Edition Spilker Solutions Manualmateorivu100% (33)
- Chapter 6Document48 pagesChapter 6Nigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Depreciation: Prof. Bikash MohantyDocument63 pagesDepreciation: Prof. Bikash Mohantyacer_asd100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Solution of Fundamental of Financial Accouting by EDMONDS (4th Edition)Document118 pagesChapter 9 Solution of Fundamental of Financial Accouting by EDMONDS (4th Edition)Awais Azeemi67% (3)
- 2 Ass-02Document8 pages2 Ass-02mouniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Test BankDocument115 pagesChapter 09 Test BankaymangbaNo ratings yet
- Market TargetingDocument9 pagesMarket TargetingSrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lembar Siklus BerkahDocument34 pagesLembar Siklus BerkahSri Muji RahayuNo ratings yet
- Universal College Grade 11 Fundamentals of Accounting 2 Exam ReviewDocument7 pagesUniversal College Grade 11 Fundamentals of Accounting 2 Exam ReviewDin Rose Gonzales50% (2)
- Analisis Strategi Pemasaran Pabrik Roti Seleb BakeryDocument11 pagesAnalisis Strategi Pemasaran Pabrik Roti Seleb BakeryEva IndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument34 pagesBusiness Planjohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- (Q 16,17 PS3), (Q 1 PS4)Document4 pages(Q 16,17 PS3), (Q 1 PS4)asaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ AKM ACCOUNTINGDocument10 pagesQUIZ AKM ACCOUNTINGAlya Sufi IkrimaNo ratings yet
- Susquehanna Equipment Rentals (Group D) - PresentationDocument13 pagesSusquehanna Equipment Rentals (Group D) - PresentationNoman ANo ratings yet
- SH CO. NOTES-konti Na LangDocument15 pagesSH CO. NOTES-konti Na LangDare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- Defining Areas of Analysis: The Entrepreneur Will Want To Understand The Nature of The Industry He or She Is AnalyzingDocument27 pagesDefining Areas of Analysis: The Entrepreneur Will Want To Understand The Nature of The Industry He or She Is AnalyzingMohamed Farag MostafaNo ratings yet
- K-0120 (Paper-II) (Commerce)Document32 pagesK-0120 (Paper-II) (Commerce)sunil kumarNo ratings yet
- Internet Retailing: The Past, The Present and The Future: Neil F. Doherty and Fiona Ellis-ChadwickDocument26 pagesInternet Retailing: The Past, The Present and The Future: Neil F. Doherty and Fiona Ellis-ChadwickRavi kantNo ratings yet
- Winning Share and Customer Loyalty in Auto InsuranceDocument24 pagesWinning Share and Customer Loyalty in Auto Insurancemkiv74No ratings yet
- Case Econ08 PPT 09Document36 pagesCase Econ08 PPT 09Kristin Alice PonienteNo ratings yet
- MGKVP SyllabusDocument51 pagesMGKVP SyllabusAfreen RayeenNo ratings yet
- Vintage Human Capital Economics LectureDocument11 pagesVintage Human Capital Economics LecturekeyyongparkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: 7115/11 Business StudiesDocument12 pagesCambridge O Level: 7115/11 Business StudiesBACKYARD BOYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions EXERCISESDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Solutions EXERCISEScamd1290100% (1)
- ASES Chapter 1 Closure Summary & TimelineDocument21 pagesASES Chapter 1 Closure Summary & TimelineAnkit SainiNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On Strategic Management ModelDocument11 pagesAn Assignment On Strategic Management ModelAlinur IslamNo ratings yet
- Actuarial Corporate GovernanceDocument24 pagesActuarial Corporate Governancerohit_17No ratings yet
- New Product Development ProjectDocument14 pagesNew Product Development ProjectRakesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Accounting An Integrated Approach 6th Edition by AinsworthDocument6 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Accounting An Integrated Approach 6th Edition by Ainswortha755883752No ratings yet
- Lean Project ManagementDocument76 pagesLean Project ManagementAbel Quianga100% (1)
- Accounting Chapter 16 exercises and solutionsDocument10 pagesAccounting Chapter 16 exercises and solutionsAnonymous jrIMYSz9No ratings yet
- Economic TermsDocument5 pagesEconomic TermsMasniar MasniatNo ratings yet
- National Director Sales Business Development in Boston MA Resume Thomas FisherDocument2 pagesNational Director Sales Business Development in Boston MA Resume Thomas FisherThomasFisher2No ratings yet
- IndiGo Economic Analysis ReportDocument10 pagesIndiGo Economic Analysis ReportChandra Kiran100% (2)
- Seven Rules of International DistributionDocument11 pagesSeven Rules of International DistributionKhon LinNo ratings yet