Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - Postgresql
Uploaded by
TiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - Postgresql
Uploaded by
TiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoCopyright:
Available Formats
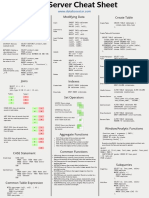
SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgreSQL - www.databasestar.
com
SELECT Modifying Data MERGE:
INSERT INTO table_name (col1, col2...)
SELECT col1, col2
INSERT: VALUES (val1, val2)...
FROM table
INSERT INTO tablename (col1, col2...) ON CONFLICT (identifier_column) (DO
WHERE condition
VALUES (val1, val2); UPDATE
GROUP BY cols
SET col2 = EXCLUDED.val2|DO NOTHING)
HAVING condition INSERT From Table:
ORDER BY col; INSERT INTO tablename (col1, col2…) Joins
SELECT col1, col2…
Order of Processing SELECT t1.*, t2.*
UPDATE: FROM t1
1. FROM
UPDATE tablename SET col1 = val1 join_type t2 ON t1.col = t2.col;
2. JOIN
3. WHERE WHERE condition;
INNER JOIN: show all matching records in both
4. GROUP BY tables.
DELETE:
5. HAVING
DELETE FROM tablename WHERE condition;
6. SELECT LEFT JOIN: show all records from left table, and any
7. DISTINCT TRUNCATE: matching records from right table.
8. ORDER BY TRUNCATE TABLE tablename;
9. LIMIT RIGHT JOIN: show all records from right table, and
UPDATE with Join: any matching records from left table.
SELECT Keywords UPDATE t
FULL JOIN: show all records from both tables,
SET col1 = val1
DISTINCT: Removes duplicate results whether there is a match or not.
FROM tablename t
INNER JOIN table x ON t.id = x.tid CROSS JOIN: show all combinations of records from
BETWEEN: Matches a value between two other
WHERE condition; both tables.
values (inclusive)
INSERT Multiple Rows: SELF JOIN: join a table to itself. Used for hierarchical
IN: Matches a value to one of many values
INSERT INTO tablename (col1, col2…) data.
LIKE: Performs partial/wildcard matches VALUES (valA1, valB1), (valA2, valB2), SELECT p.*, c.*
(valA3, valB3); FROM yourtable p
INNER JOIN yourtable c ON p.id =
c.parent_id;
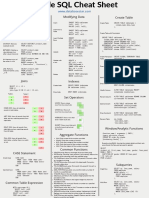
SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgreSQL - www.databasestar.com
Create Table Modify Column Set Operators
ALTER TABLE tablename ALTER COLUMN
Create Table:
columnname TYPE newdatatype; UNION: Shows unique rows from two result sets.
CREATE TABLE tablename (
column_name data_type Rename Column UNION ALL: Shows all rows from two result sets.
); ALTER TABLE tablename RENAME COLUMN
currentname TO newname; INTERSECT: Shows rows that exist in both result
Create Table WIth Constraints: sets.
CREATE TABLE tablename ( Add Constraint
column_name data_type NOT NULL, ALTER TABLE tablename ADD CONSTRAINT EXCEPT: Shows rows that exist in the first result set
CONSTRAINT pkname PRIMARY KEY (col), constraintname constrainttype (columns); but not the second.
CONSTRAINT fkname FOREIGN KEY (col)
REFERENCES Drop Constraint Analytic Functions
other_table(col_in_other_table), ALTER TABLE tablename DROP function_name ( arguments ) OVER (
CONSTRAINT ucname UNIQUE (col), constraint_type constraintname; [query_partition_clause]
CONSTRAINT ckname CHECK (conditions) [ORDER BY order_by_clause
); Rename Table
[windowing_clause] ] )
ALTER TABLE tablename RENAME TO
Drop Table: newtablename; Example using RANK, showing the student details
DROP TABLE tablename; and their rank according to the fees_paid, grouped by
Indexes gender:
Create Temporary Table:
Create Index: SELECT
CREATE TEMP TABLE tablename (colname
CREATE INDEX indexname ON tablename student_id, first_name, last_name,
datatype);
(cols); gender, fees_paid,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY gender ORDER
Drop Index: BY fees_paid) AS rank_val
Alter Table
DROP INDEX indexname; FROM student;
Add Column
ALTER TABLE tablename ADD COLUMN CASE Statement
columnname datatype;
Simple Case:
Drop Column CASE name
ALTER TABLE tablename DROP COLUMN WHEN 'John' THEN 'Name John'
columnname; WHEN 'Steve' THEN 'Name Steve'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
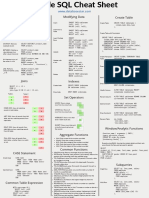
SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgreSQL - www.databasestar.com
Searched Case:
CASE Aggregate Functions REPLACE(whole_string, string_to_replace,
WHEN name='John' THEN 'Name John' replacement_string): Replaces one string inside the
WHEN name='Steve' THEN 'Name Steve' SUM: Finds a total of the numbers provided whole string with another string.
ELSE 'Unknown'
COUNT: Finds the number of records SUBSTRING(string, [start_pos], [length]): Returns
END
part of a value, based on a position and length.
AVG: Finds the average of the numbers provided
With Clause/Common Table Expression
WITH queryname AS ( MIN: Finds the lowest of the numbers provided
SELECT col1, col2
MAX: Finds the highest of the numbers provided
FROM firsttable)
SELECT col1, col2..
Common Functions
FROM queryname…;
LENGTH(string): Returns the length of the provided
Subqueries string
Single Row:
SELECT id, last_name, salary POSITION(string IN substring): Returns the position
FROM employee of the substring within the specified string.
WHERE salary = (
CAST(expression AS datatype): Converts an
SELECT MAX(salary)
expression into the specified data type.
FROM employee
); NOW: Returns the current date, including time.
Multi Row CEIL(input_val): Returns the smallest integer greater
SELECT id, last_name, salary than the provided number.
FROM employee
WHERE salary IN ( FLOOR(input_val): Returns the largest integer less
SELECT salary than the provided number.
FROM employee
WHERE last_name LIKE 'C%' ROUND(input_val, [round_to]): Rounds a number to a
); specified number of decimal places.
TRUNC(input_value, num_decimals): Truncates a
number to a number of decimals.
You might also like
- ScholarshipDocument17 pagesScholarshipharindramehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - QuizDocument10 pagesChapter 8 - QuizTrang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Hyper-Grace - The Doctrine of The DevilDocument47 pagesHyper-Grace - The Doctrine of The DevilTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotosho75% (4)
- Best Practices For Bucketing in Spark SQL - by David Vrba - Towards Data ScienceDocument27 pagesBest Practices For Bucketing in Spark SQL - by David Vrba - Towards Data ScienceSekhar SahuNo ratings yet
- Shireesha Resume SFDCDocument8 pagesShireesha Resume SFDCramu_uppadaNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - MysqlDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - MysqlHenrique PeixotoNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - OracleDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - OracleSagar Rao CrNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet: Select JoinsDocument3 pagesSQL Cheat Sheet: Select JoinsAvaya Swain100% (1)
- Select Joins: SQL Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesSelect Joins: SQL Cheat SheetAYMANE EL ANSARI100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet PostgresqlDocument1 pageCheat Sheet PostgresqlyagaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SqlserverDocument1 pageCheat Sheet SqlserveryagaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet MysqlDocument1 pageCheat Sheet MysqlPranav TanejaNo ratings yet
- SQL 20Document4 pagesSQL 20ttt100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet OracleDocument1 pageCheat Sheet OracleyagaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SqlserverDocument1 pageCheat Sheet SqlserverPranav TanejaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet OracleDocument1 pageCheat Sheet OraclePranav TanejaNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet MysqlDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet MysqlAnxious ZhouNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet SqlserverDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet Sqlservershirleyn22225No ratings yet
- Oracle 11gDocument3 pagesOracle 11gMatthew CoxNo ratings yet
- SQL Statement 2Document17 pagesSQL Statement 2Thao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL: Manipulation CheatsheetDocument2 pagesLearn SQL: Manipulation CheatsheetKaylan AchongNo ratings yet
- Mysql Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMysql Cheat SheetAnil PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Forgotten T-SQL Cheat Sheet: L P O Select XML T: L DDocument1 pageForgotten T-SQL Cheat Sheet: L P O Select XML T: L DJivan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Writing and PrintDocument115 pagesRdbms Writing and PrintsornammalchennappanNo ratings yet
- 8 SQLDocument73 pages8 SQLOnn ChueNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SQLDocument59 pagesIntroduction To SQLVidhi ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Commands: SQL, 'Structured Query Language', Is A ProgrammingDocument4 pagesCommands: SQL, 'Structured Query Language', Is A ProgrammingCyrill Joyce Santelices EgualNo ratings yet
- Rebellabs SQL Cheat Sheeasdasdasd55555555Document1 pageRebellabs SQL Cheat Sheeasdasdasd55555555cuevaNo ratings yet
- Section 1 - Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageSection 1 - Cheat Sheet PDFseb devNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick RefDocument2 pagesSQL Quick RefAudiseshareddy100% (1)
- Fetttobse SqliteDocument1 pageFetttobse SqliteAntiaNo ratings yet
- You Can Also Do The Same by Substituting Unwanted Values by NULLDocument2 pagesYou Can Also Do The Same by Substituting Unwanted Values by NULLDYK DUDESNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet: Basic QueriesDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet: Basic QueriesrwurdigNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet: Basic QueriesDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet: Basic QueriesArturvillegasNo ratings yet
- Rams SQLDocument2 pagesRams SQLram_somalaNo ratings yet
- Complete SQL SyntaxDocument3 pagesComplete SQL SyntaxMuhammad Azeem Raza ShahNo ratings yet
- SQL - Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesSQL - Quick ReferenceBCONo ratings yet
- Oracle PLSQL Quick Reference CardDocument3 pagesOracle PLSQL Quick Reference CardgongoracNo ratings yet
- MariaDB SQL Quick Reference GuideDocument16 pagesMariaDB SQL Quick Reference Guidechristianpaul.cudalNo ratings yet
- Database Commands - Class 12Document9 pagesDatabase Commands - Class 12JeevanNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesSQL Cheat SheetAaryanNo ratings yet
- Book 16Document2 pagesBook 16salesNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL - Manipulation Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument2 pagesLearn SQL - Manipulation Cheatsheet - CodecademysuujaanNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick Reference: SQL Syntax Statement SyntaxDocument2 pagesSQL Quick Reference: SQL Syntax Statement SyntaxKowshik KunduNo ratings yet
- Quickref)Document3 pagesQuickref)rajinbangetNo ratings yet
- Essential Mysql Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesEssential Mysql Cheat Sheet: by ViaEDU ArtefaktNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesSQL Cheat SheetAkshaya Priya JanarthanNo ratings yet
- Hand Notes On SQL Namrata NagpalDocument3 pagesHand Notes On SQL Namrata NagpalJesmine GandhiNo ratings yet
- PL SQL CheatsheetDocument3 pagesPL SQL CheatsheetAnuj Vikal100% (2)
- Data Integrity Constraints-Lab-2 NotesDocument20 pagesData Integrity Constraints-Lab-2 Noteschauhansumi143No ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ExamDocument3 pagesDBMS Lab ExamKomal nadakuditiNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL CheatsheetDocument2 pagesOracle SQL CheatsheetGiova RossiNo ratings yet
- Manipulation: Column ConstraintsDocument2 pagesManipulation: Column ConstraintsZeyad AlodatNo ratings yet
- MySQL Commands Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMySQL Commands Cheat SheetSiddique RanaNo ratings yet
- SQL Commands: Prepared by Pandeeswari MDocument32 pagesSQL Commands: Prepared by Pandeeswari MShadab malik shahNo ratings yet
- SQL CheatSheetDocument17 pagesSQL CheatSheetCarlos Garcia CatalanNo ratings yet
- My SQLDocument2 pagesMy SQLJuan AráozNo ratings yet
- SQL CheatSheetDocument57 pagesSQL CheatSheetmynenianupamaNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Graphs with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")From EverandGraphs with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- GCK Ikorodu IMPACT ProgramDocument2 pagesGCK Ikorodu IMPACT ProgramTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- 06 Workshop 18july2020 Working With StakeholdersDocument4 pages06 Workshop 18july2020 Working With StakeholdersTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- DLCF Digital Skills Bootcamp - Microsoft Excel 1-6Document26 pagesDLCF Digital Skills Bootcamp - Microsoft Excel 1-6TiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- 05 Workshop 04july2020 Machine Learning 2Document5 pages05 Workshop 04july2020 Machine Learning 2TiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Artificial Intelligence and Machine LearningDocument8 pagesCurriculum Guide: Artificial Intelligence and Machine LearningTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- 04 Workshop 04july2020 Machine Learning 1Document6 pages04 Workshop 04july2020 Machine Learning 1TiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- DLCF Digital Skills Bootcamp - Microsoft Excel - OMOTOSHODocument15 pagesDLCF Digital Skills Bootcamp - Microsoft Excel - OMOTOSHOTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- UCT PG Applicant GuideDocument32 pagesUCT PG Applicant GuideTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- And He Hath On His Vesture and On His Thigh A Name Written, KING OF KINGS, AND LORD OF LORDSDocument2 pagesAnd He Hath On His Vesture and On His Thigh A Name Written, KING OF KINGS, AND LORD OF LORDSTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Preface To Sixth Edition: Dimensionless AnalysisDocument2 pagesPreface To Sixth Edition: Dimensionless AnalysisTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- History of Genetic EngineeringDocument1 pageHistory of Genetic EngineeringTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- How Does Modern Business Influence Information Systems?: New Products and ServicesDocument4 pagesHow Does Modern Business Influence Information Systems?: New Products and ServicesTeja MullapudiNo ratings yet
- Power Exchange Interfaces For Power CenterDocument227 pagesPower Exchange Interfaces For Power CenterPreeti VNo ratings yet
- R12 - List of Obsolete Tables and ColumnsDocument35 pagesR12 - List of Obsolete Tables and Columnscpsharma_vnsNo ratings yet
- Presentation - 2018 - Microsoft SSAS SQL Server 2016&2017Document31 pagesPresentation - 2018 - Microsoft SSAS SQL Server 2016&2017Alberto KontadorNo ratings yet
- DBMS Chap 3Document13 pagesDBMS Chap 3Harsh OjhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 SerializabilityDocument24 pagesUnit 6 SerializabilitySonalS NaikNo ratings yet
- ACCTG432 by Jemela Del ValleDocument3 pagesACCTG432 by Jemela Del ValleJemela del ValleNo ratings yet
- ICT Grade 11-ExamDocument10 pagesICT Grade 11-ExamEndash HaileNo ratings yet
- Bcs Higher Education Qualifications BCS Level 4 Certificate in ITDocument5 pagesBcs Higher Education Qualifications BCS Level 4 Certificate in ITdasdNo ratings yet
- Python Data File Handling XII CS 2022-23 As On 28-10-2022Document62 pagesPython Data File Handling XII CS 2022-23 As On 28-10-2022Mayank KashyapNo ratings yet
- Model Practical Examination QuestionsDocument7 pagesModel Practical Examination QuestionsBolt FFNo ratings yet
- Mensagem de Erros Spectrum ProtectDocument368 pagesMensagem de Erros Spectrum ProtectrctrctNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Annotated CRFS: Pharmasug 2020 - Paper Ds-248Document5 pagesBest Practices For Annotated CRFS: Pharmasug 2020 - Paper Ds-248Khaja rameezNo ratings yet
- Sai Prakash - JAVADocument5 pagesSai Prakash - JAVAHARSHANo ratings yet
- 2 - Electronic Record and Document Management System (Edms)Document34 pages2 - Electronic Record and Document Management System (Edms)Ibrahim Samsoni ChristianNo ratings yet
- Mi Microservices Eap 7 Reference Architecture 201606 enDocument153 pagesMi Microservices Eap 7 Reference Architecture 201606 enCarlosArturoQuirogaNo ratings yet
- SAP CPI: Integration Process & Exception HandlingDocument6 pagesSAP CPI: Integration Process & Exception HandlingshubhamNo ratings yet
- Extend Configuration Software SCTask User ManualDocument33 pagesExtend Configuration Software SCTask User Manualsugeng wahyudiNo ratings yet
- ADMS 2320 Chapter 2 Questions PDFDocument4 pagesADMS 2320 Chapter 2 Questions PDFpranta sahaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 1.3 Dbms Sarthak Verma Lab (20bcs3950)Document8 pagesWorksheet - 1.3 Dbms Sarthak Verma Lab (20bcs3950)SarthakNo ratings yet
- C ADO - NET. Building Secure and Scalable Data Access 2023 (Theophilus Edet)Document275 pagesC ADO - NET. Building Secure and Scalable Data Access 2023 (Theophilus Edet)madeingodNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of A JSP Page: Server-Side Servlet Sun HTMLDocument36 pagesThe Life Cycle of A JSP Page: Server-Side Servlet Sun HTMLPankaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Predictive Machine Learning Applying Cross Industry Standard Process For Data Mining For The Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document14 pagesPredictive Machine Learning Applying Cross Industry Standard Process For Data Mining For The Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2IAES IJAINo ratings yet
- Decision Sheet CALGARY DROP IN CENTREDocument2 pagesDecision Sheet CALGARY DROP IN CENTREarun babuNo ratings yet
- Dbms Worksheet-3: Name: - Praduman Kumar Section: - 20ITB5 UID: - 20BCS9446Document10 pagesDbms Worksheet-3: Name: - Praduman Kumar Section: - 20ITB5 UID: - 20BCS9446Raja RajNo ratings yet
- Declared Foreign and Primary Keys in RDM Embedded SQLDocument6 pagesDeclared Foreign and Primary Keys in RDM Embedded SQLSarah KhanNo ratings yet