Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheat Sheet Oracle
Uploaded by
yagaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheat Sheet Oracle
Uploaded by
yagaCopyright:
Available Formats
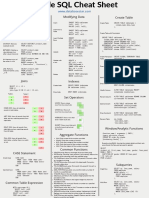
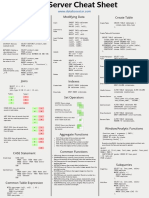
Oracle SQL Cheat Sheet
www.databasestar.com
SELECT Query Modifying Data Create Table
SELECT col1, col2
FROM table Insert INSERT INTO tablename Create Table CREATE TABLE tablename (
JOIN table2 ON table1.col = table2.col (col1, col2...) column_name data_type
WHERE condition VALUES (val1, val2); );
GROUP BY column_name Insert from a
HAVING condition INSERT INTO tablename
Table
ORDER BY col1 ASC|DESC; (col1, col2...) Create Table with Constraints
SELECT col1, col2...
CREATE TABLE tablename (
SELECT Keywords Insert Multiple
Rows
INSERT
INTO tablename (col1, col2) column_name data_type NOT NULL,
VALUES (valA1, valB1) CONSTRAINT pkname PRIMARY KEY (col),
DISTINCT: Removes SELECT DISTINCT product_name INTO tablename (col1, col2) CONSTRAINT fkname FOREIGN KEY (col)
duplicate results FROM product; VALUES (valA2, valB2) REFERENCES other_table(col_in_other_table),
SELECT * FROM dual; CONSTRAINT ucname UNIQUE (col),
CONSTRAINT ckname CHECK (conditions)
BETWEEN: Matches a SELECT product_name
Update UPDATE tablename );
value between two FROM product
other values (inclusive) WHERE price BETWEEN 50 AND 100; SET col1 = val1
WHERE condition;
Create Temporary CREATE GLOBAL TEMPORARY TABLE
SELECT product_name Table tablename (
IN: Matches to any of
FROM product Update with UPDATE t colname datatype
the values in a list
WHERE category IN a Join SET col1 = val1 ) ON COMMIT DELETE ROWS;
('Electronics', 'Furniture'); FROM tablename t
INNER JOIN table x Drop Table DROP TABLE tablename;
LIKE: Performs SELECT product_name ON t.id = x.tid
wildcard matches using FROM product WHERE condition;
_ or % WHERE product_name
Delete DELETE FROM tablename
Alter Table
LIKE '%Desk%";
WHERE condition;
Add Column ALTER TABLE tablename
ADD columnname datatype;
Joins Indexes
Drop Column ALTER TABLE tablename
Create Index CREATE INDEX indexname DROP COLUMN columnname;
SELECT t1.*, t2.*
ON tablename (cols);
FROM t1
join_type t2 ON t1.col = t2.col; Modify Column ALTER TABLE tablename MODIFY
Drop Index DROP INDEX indexname; columnname newdatatype;
Table 1 Table 2
A A
Set Operators Rename Column ALTER TABLE tablename RENAME COLUMN
currentname TO newname;
B B
C D UNION: Shows unique
Add Constraint ALTER TABLE tablename ADD
rows from two result sets. CONSTRAINT constraintname
INNER JOIN: show all matching A constrainttype (columns);
A
records in both tables. UNION ALL: Shows all
B B
rows from two result sets.
Drop Constraint ALTER TABLE tablename DROP
constraint_type constraintname;
LEFT JOIN: show all records from left A A
INTERSECT: Shows rows that
table, and any matching records from Rename Table sp_rename
B B exist in both result sets.
right table. 'old_table_name',
C
'new_table_name';
EXCEPT: Shows rows that exist
RIGHT JOIN: show all records from in the first result set but not
Window/Analytic Functions
A A
right table, and any matching records the second.
B B
from left table.
function_name ( arguments ) OVER (
Aggregate Functions
D
[query_partition_clause]
[ORDER BY order_by_clause
FULL JOIN: show all records from A A SUM: Finds a total of the numbers provided
[windowing_clause] ] )
both tables, whether there is a match COUNT: Finds the number of records
or not. B B AVG: Finds the average of the numbers provided
Example using RANK, showing the student details and their rank
C MIN: Finds the lowest of the numbers provided
according to the fees_paid, grouped by gender:
MAX: Finds the highest of the numbers provided
D
SELECT
Common Functions student_id, first_name, last_name, gender, fees_paid,
CASE Statement LENGTH(string): Returns the length of the provided string RANK() OVER (
INSTR(string, substring, [start_position], [occurrence]): Returns the PARTITION BY gender ORDER BY fees_paid
position of the substring within the specified string. ) AS rank_val
Simple Case CASE name TO_CHAR(input_value, [fmt_mask], [nls_param]): Converts a date FROM student;
WHEN 'John' THEN 'Name John' or a number to a string
WHEN 'Steve' THEN 'Name Steve' TO_DATE(charvalue, [fmt_mask], [nls_date_lang]): Converts a
ELSE 'Unknown'
END
string to a date value.
TO_NUMBER(input_value, [fmt_mask], [nls_param]): Converts a
Subqueries
string value to a number. SELECT id, last_name, salary
Single Row
Searched Case CASE ADD_MONTHS(input_date, num_months): Adds a number of FROM employee
WHEN name='John' THEN 'Name John' months to a specified date. WHERE salary = (
WHEN name='Steve' THEN 'Name Steve' SYSDATE: Returns the current date, including time. SELECT MAX(salary)
ELSE 'Unknown' CEIL(input_val): Returns the smallest integer greater than the FROM employee
END provided number. );
FLOOR(input_val): Returns the largest integer less than the
provided number.
Common Table Expression ROUND(input_val, round_to): Rounds a number to a specified
Multi Row SELECT id, last_name, salary
FROM employee
number of decimal places. WHERE salary IN (
WITH queryname AS ( TRUNC(input_value, dec_or_fmt): Truncates a number or date to a SELECT salary
SELECT col1, col2 number of decimals or format. FROM employee
FROM firsttable) REPLACE(whole_string, string_to_replace, [replacement_string]): WHERE last_name LIKE 'C%'
SELECT col1, col2.. Replaces one string inside the whole string with another string. );
FROM queryname...; SUBSTR(string, start_position, [length]): Returns part of a value,
based on a position and length.
You might also like
- 100+ SQL Queries Jet SQL for Microsoft Office AccessFrom Everand100+ SQL Queries Jet SQL for Microsoft Office AccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SQL 20Document4 pagesSQL 20ttt100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet OracleDocument1 pageCheat Sheet OraclePranav TanejaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet MysqlDocument1 pageCheat Sheet MysqlPranav TanejaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SqlserverDocument1 pageCheat Sheet SqlserveryagaNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet SqlserverDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet Sqlservershirleyn22225No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SqlserverDocument1 pageCheat Sheet SqlserverPranav TanejaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PostgresqlDocument1 pageCheat Sheet PostgresqlyagaNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet MysqlDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet MysqlAnxious ZhouNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - MysqlDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - MysqlHenrique PeixotoNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - OracleDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - OracleSagar Rao CrNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet: Select JoinsDocument3 pagesSQL Cheat Sheet: Select JoinsAvaya Swain100% (1)
- Select Joins: SQL Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesSelect Joins: SQL Cheat SheetAYMANE EL ANSARI100% (1)
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - SQL ServerTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Select Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgresqlDocument3 pagesSelect Modifying Data: SQL Cheat Sheet - PostgresqlTiwaladeIfeoluwaOmotoshoNo ratings yet
- Oracle 11gDocument3 pagesOracle 11gMatthew CoxNo ratings yet
- MariaDB SQL Quick Reference GuideDocument16 pagesMariaDB SQL Quick Reference Guidechristianpaul.cudalNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick RefDocument2 pagesSQL Quick RefAudiseshareddy100% (1)
- SQL Quick Reference: SQL Syntax Statement SyntaxDocument2 pagesSQL Quick Reference: SQL Syntax Statement SyntaxKowshik KunduNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageSQL Quick ReferencedimakikilalaNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick Reference by Tableau GurusDocument7 pagesSQL Quick Reference by Tableau GurusReza AhmadNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesSQL Cheat SheetAaryanNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesSQL Cheat SheetAkshaya Priya JanarthanNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick Reference From W3Schools: Previous (SQL - Func - Format - Asp) Next Chapter (SQL - Hosting - Asp)Document4 pagesSQL Quick Reference From W3Schools: Previous (SQL - Func - Format - Asp) Next Chapter (SQL - Hosting - Asp)Mateus Valgueiro TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL: Manipulation CheatsheetDocument2 pagesLearn SQL: Manipulation CheatsheetKaylan AchongNo ratings yet
- SQL Statement 2Document17 pagesSQL Statement 2Thao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL CheatsheetDocument2 pagesOracle SQL CheatsheetGiova RossiNo ratings yet
- Mysql Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMysql Cheat SheetAnil PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet PDF - Hackr - IoDocument25 pagesSQL Cheat Sheet PDF - Hackr - IoNguyễn Trung Hồng AnhNo ratings yet
- SQL CheatSheetDocument57 pagesSQL CheatSheetmynenianupamaNo ratings yet
- Oracle PLSQL Quick Reference CardDocument3 pagesOracle PLSQL Quick Reference CardgongoracNo ratings yet
- Complete SQL SyntaxDocument3 pagesComplete SQL SyntaxMuhammad Azeem Raza ShahNo ratings yet
- Commands: SQL, 'Structured Query Language', Is A ProgrammingDocument4 pagesCommands: SQL, 'Structured Query Language', Is A ProgrammingCyrill Joyce Santelices EgualNo ratings yet
- Rams SQLDocument2 pagesRams SQLram_somalaNo ratings yet
- My SQLDocument2 pagesMy SQLJuan AráozNo ratings yet
- SQL QueriesDocument2 pagesSQL QueriesUTSAH SINGHNo ratings yet
- SQL - Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesSQL - Quick ReferenceBCONo ratings yet
- Database Commands - Class 12Document9 pagesDatabase Commands - Class 12JeevanNo ratings yet
- Nimakarimian Sql-Cheatsheet - BWDocument7 pagesNimakarimian Sql-Cheatsheet - BWRushikesh Salunke PatilNo ratings yet
- CIS340-lab#3-part 2Document31 pagesCIS340-lab#3-part 2iwvb.31No ratings yet
- SQL Simple Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesSQL Simple Cheat Sheetjingamadalina77No ratings yet
- SQL Cheat SheetDocument16 pagesSQL Cheat Sheetdiceplayaa0% (1)
- Mysql MemoDocument2 pagesMysql MemoPetar GolubovicNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet: By: Ika PurnamasariDocument2 pagesSQL Cheat Sheet: By: Ika PurnamasarividdychristoNo ratings yet
- Essential SQL Commands Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesEssential SQL Commands Cheat SheetDennis DubeNo ratings yet
- Fetttobse SqliteDocument1 pageFetttobse SqliteAntiaNo ratings yet
- Manipulation: Column ConstraintsDocument2 pagesManipulation: Column ConstraintsZeyad AlodatNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL - Manipulation Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument2 pagesLearn SQL - Manipulation Cheatsheet - CodecademysuujaanNo ratings yet
- SQL Quick Reference From W3Schools: Previous NextDocument4 pagesSQL Quick Reference From W3Schools: Previous NextAshwerya NarulaNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL CheatsheetDocument2 pagesOracle SQL Cheatsheetsachin dixitNo ratings yet
- Quickref)Document3 pagesQuickref)rajinbangetNo ratings yet
- Book 16Document2 pagesBook 16salesNo ratings yet
- PL SQL CheatsheetDocument3 pagesPL SQL CheatsheetAnuj Vikal100% (2)
- SQLCODECADEMYDocument11 pagesSQLCODECADEMYJava ProjectNo ratings yet
- Manual de SQLDocument44 pagesManual de SQLMichelle CallesNo ratings yet
- Rdbms Writing and PrintDocument115 pagesRdbms Writing and PrintsornammalchennappanNo ratings yet
- CIS340-lab#3-part 3Document31 pagesCIS340-lab#3-part 3iwvb.31No ratings yet