Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dissonant:: Dissonant Intervals Are Those That Cause Tension and
Dissonant:: Dissonant Intervals Are Those That Cause Tension and
Uploaded by
suriyaprakash0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThis document discusses dissonant musical intervals such as minor seconds, major seconds, minor sevenths, and major sevenths. It notes that dissonant intervals cause tension and desire resolution to consonant intervals. However, dissonance does not always need to be resolved, and perception of dissonance can be subjective. Dissonances are divided into sharp and soft types, and some intervals like tritones are considered neutral in certain musical styles like jazz.
Original Description:
Original Title
Dissonant intervals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses dissonant musical intervals such as minor seconds, major seconds, minor sevenths, and major sevenths. It notes that dissonant intervals cause tension and desire resolution to consonant intervals. However, dissonance does not always need to be resolved, and perception of dissonance can be subjective. Dissonances are divided into sharp and soft types, and some intervals like tritones are considered neutral in certain musical styles like jazz.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageDissonant:: Dissonant Intervals Are Those That Cause Tension and
Dissonant:: Dissonant Intervals Are Those That Cause Tension and
Uploaded by
suriyaprakashThis document discusses dissonant musical intervals such as minor seconds, major seconds, minor sevenths, and major sevenths. It notes that dissonant intervals cause tension and desire resolution to consonant intervals. However, dissonance does not always need to be resolved, and perception of dissonance can be subjective. Dissonances are divided into sharp and soft types, and some intervals like tritones are considered neutral in certain musical styles like jazz.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
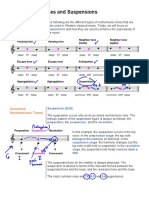
On the other hand these intervals are considered
dissonant:
• minor second - For example from C - Db
• major second - For example from C to D
• minor seventh - For example from C to Bb
• major seventh - For example from C to B
• tritone - For example from C to F#, tritone is
also known as an augmented 4th or diminished
fifth and it has an interval of 3 whole steps.
Most often dissonance is resolved by moving to a
consonant chord. This makes the initial feeling of
tension created by dissonant chords to reach a
resolution. The common term for this is tension
and release. However, dissonance doesn't
always need to be resolved, also perceiving
chords as dissonant tends to be subjective.
Dissonant intervals are those that cause tension and
desire to be resolved to consonant intervals. These
descriptions relate to harmonious intervals.
Dissonances can be divided into sharp and soft
dissonances. This division relates mainly to atonal
music. Minor second and major seventh are sharp
dissonances. In tonal music, non-diatonic intervals
(diminished and augmented) are usually dissonances,
but in jazz and other African-American music, the
tritone is "neutral", in other words it does not require
resolution to a consonance.
You might also like
- Music Composition For Film & TV Berklee Lalo SchifrinDocument169 pagesMusic Composition For Film & TV Berklee Lalo SchifrinsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- J.S. Bach's Clavier Figured Bass InstructionsDocument10 pagesJ.S. Bach's Clavier Figured Bass InstructionsDWCason100% (15)
- Tritone - Diabolus in MusicaDocument8 pagesTritone - Diabolus in MusicaEduardo BertainaNo ratings yet
- An Understandable Guide to Music Theory: The Most Useful Aspects of Theory for Rock, Jazz, and Blues MusiciansFrom EverandAn Understandable Guide to Music Theory: The Most Useful Aspects of Theory for Rock, Jazz, and Blues MusiciansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Composition & Orchestration PDFDocument30 pagesComposition & Orchestration PDFsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- HarmonyDocument14 pagesHarmonyReynaldo Rene PacolorNo ratings yet
- Musc1600 Week 2 Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesMusc1600 Week 2 Lecture Noteslanijeffries84No ratings yet
- Nonharmonic Tones and SuspensionsDocument8 pagesNonharmonic Tones and SuspensionsHazim Suhadi100% (1)
- Theory 2 Unit 2Document16 pagesTheory 2 Unit 2api-594920205No ratings yet
- Nonchord Tone - WikipediaDocument28 pagesNonchord Tone - WikipediaivanNo ratings yet
- Consonance and Dissonance - WikipediaDocument25 pagesConsonance and Dissonance - WikipediaDiana Ghius100% (1)
- Major and Minor - WikipediaDocument6 pagesMajor and Minor - WikipediaAla2 PugaciovaNo ratings yet
- Consonance and DissonanceDocument2 pagesConsonance and DissonanceTanish PruthiNo ratings yet
- Music TheoryDocument5 pagesMusic TheoryNJSchandlerNo ratings yet
- Sve Vrste ModulacijaDocument10 pagesSve Vrste ModulacijaNikolina ArapovićNo ratings yet
- Interval Size:: Dr. Barbara Murphy University of Tennessee School of MusicDocument5 pagesInterval Size:: Dr. Barbara Murphy University of Tennessee School of Musiczatanna10No ratings yet
- Mus 210 Some Elements 2019 SpringDocument2 pagesMus 210 Some Elements 2019 SpringWissam ZgheibNo ratings yet
- GED 303 Concept of Music Musical Content On Harmony and TextureDocument12 pagesGED 303 Concept of Music Musical Content On Harmony and TextureAngela GamayonNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art AuditoryDocument10 pagesElements of Art AuditoryMendoza Robin I.No ratings yet
- Manual of The Art of Tuning Your Own Piano Yourself: by C. MontalDocument15 pagesManual of The Art of Tuning Your Own Piano Yourself: by C. MontalMarcelo BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Tech ConferenceDocument9 pagesTech ConferenceMika BurgerNo ratings yet
- Week 9 - Suspensions LectureDocument13 pagesWeek 9 - Suspensions Lecturestuff mateNo ratings yet
- Music Theory - Notes ReadingDocument9 pagesMusic Theory - Notes ReadingDev PushNo ratings yet
- Pieces, The Second Symphony, The Young Maiden, and Bluebird's CastleDocument2 pagesPieces, The Second Symphony, The Young Maiden, and Bluebird's CastleAustin FenisNo ratings yet
- Art App Janel RealDocument6 pagesArt App Janel Realzylas lcNo ratings yet
- Guitarist's Dictionary Glossary: What Does It Mean? Musical Terms Defined For Guitar TeachersDocument12 pagesGuitarist's Dictionary Glossary: What Does It Mean? Musical Terms Defined For Guitar TeachersBretBrecunierNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 3Document152 pagesIlovepdf Merged 3Efe SönmezNo ratings yet
- Hepsine YakınDocument169 pagesHepsine YakınEfe SönmezNo ratings yet
- Music Finals (Notes)Document11 pagesMusic Finals (Notes)NELIAN DELA PEÑANo ratings yet
- Piston Harmony CheatsheetDocument13 pagesPiston Harmony CheatsheetAnonymous TBwEsioWNo ratings yet
- Chorale Writing TipsDocument8 pagesChorale Writing TipsvijayNo ratings yet
- Berklee Harmony ReviewDocument13 pagesBerklee Harmony ReviewulgenyNo ratings yet
- Reharmonization & Stella by Starlight PDFDocument19 pagesReharmonization & Stella by Starlight PDFMariángeles Guerrero100% (1)
- Arlene Shrut: Ten Simple Truths About Singing MozartDocument3 pagesArlene Shrut: Ten Simple Truths About Singing MozartVirginiaNATSNo ratings yet
- Meeting 13 - Nonharmonic Tones (II)Document8 pagesMeeting 13 - Nonharmonic Tones (II)Hazim SuhadiNo ratings yet
- Two-Voice CounterpointDocument2 pagesTwo-Voice CounterpointГлеб ЧепуровNo ratings yet
- Blues Music Scales Chart For Jazz ImprovisationDocument15 pagesBlues Music Scales Chart For Jazz ImprovisationJordan Galleguillos100% (3)
- Music 1 - Chapter 3Document12 pagesMusic 1 - Chapter 3Mark Ian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Non-Chord Tones (NCTS)Document4 pagesNon-Chord Tones (NCTS)Yban RykoNo ratings yet
- KHJBDLJF 999Document1 pageKHJBDLJF 999bampecruze21No ratings yet
- JHJHDHJGJKDDocument1 pageJHJHDHJGJKDbampecruze21No ratings yet
- Dominant Family: Dominant Chord Type PDFDocument12 pagesDominant Family: Dominant Chord Type PDFBicho GarciaNo ratings yet
- Music Theory - Tonal Degrees and Degree TendenciesDocument3 pagesMusic Theory - Tonal Degrees and Degree TendenciesDavid BumphisNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries For Part-Writing: HarmonyDocument15 pagesPreliminaries For Part-Writing: Harmonymuhidin100% (1)
- Fundamentals of MusicDocument19 pagesFundamentals of MusicClint Dexter SolomonNo ratings yet
- Swing Feel WikipediaDocument4 pagesSwing Feel Wikipediachrisbluescat7522No ratings yet
- Determine Your Voice TypeDocument7 pagesDetermine Your Voice Typeterrance moyoNo ratings yet
- Y12 Harmony Lesson 3 Student SheetDocument2 pagesY12 Harmony Lesson 3 Student SheetJonathan ScottNo ratings yet
- Intervals For The GuitarDocument7 pagesIntervals For The GuitarE. Goldstajn100% (2)
- Melody and Non-Chordal Tones - Page !1Document3 pagesMelody and Non-Chordal Tones - Page !1Jason JungNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Harmony - Intervals - Oscar Van DillenDocument5 pagesBuilding Blocks of Harmony - Intervals - Oscar Van DillenMusicalite MusicaliteNo ratings yet
- Jazz Improvisation 15 Tips For Getting StartedDocument2 pagesJazz Improvisation 15 Tips For Getting StartedBob Hinz100% (1)
- Musical Terminology: Creative MusicianshipDocument28 pagesMusical Terminology: Creative MusicianshipOFNS MusicNo ratings yet
- Theory of Tonal MusicDocument9 pagesTheory of Tonal MusicSamiam666No ratings yet
- Gutierrez V Finalpaper 2columnsDocument8 pagesGutierrez V Finalpaper 2columnsapi-560586406No ratings yet
- Music 100 Week 2 Lesson 2a MelodyDocument15 pagesMusic 100 Week 2 Lesson 2a MelodyziahNo ratings yet
- Arranging For AcapellaDocument24 pagesArranging For AcapellaGandhi Wasuvitchayagit100% (4)
- Orchestral String Runs - Notes - Orchestral Tools HelpdeskDocument8 pagesOrchestral String Runs - Notes - Orchestral Tools HelpdesksuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Layering Tips PDFDocument5 pagesLayering Tips PDFsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Audio Media Reflective ReportDocument3 pagesAudio Media Reflective ReportsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- SA StudioBrassPro UserManual v1.1 PDFDocument27 pagesSA StudioBrassPro UserManual v1.1 PDFsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Woodwinds ManualDocument59 pagesWoodwinds ManualsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Eastwest/Quantum Leap Hollywood Brass Virtual Instrument: Diamond EditionDocument65 pagesEastwest/Quantum Leap Hollywood Brass Virtual Instrument: Diamond EditionsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Hollywood Orchestral Percussion Virtual Instrument: Diamond EditionDocument55 pagesHollywood Orchestral Percussion Virtual Instrument: Diamond EditionsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Diploma 1 Timetable Monday Tuesday Wednesdaythursday FridayDocument1 pageDiploma 1 Timetable Monday Tuesday Wednesdaythursday FridaysuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Mutes Transposition RangesDocument1 pageMutes Transposition RangessuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Instrumental TechniquesDocument1 pageInstrumental TechniquessuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Orchestra SizeDocument1 pageOrchestra SizesuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Petrushka Analysis PDFDocument1 pagePetrushka Analysis PDFsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- SYMPHONY SERIES STRING ENSEMBLE Manual PDFDocument90 pagesSYMPHONY SERIES STRING ENSEMBLE Manual PDFsuriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Orchestration Style Sheet 2Document1 pageOrchestration Style Sheet 2suriyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Orchestration Style Sheet 1Document1 pageOrchestration Style Sheet 1suriyaprakashNo ratings yet