Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Biology (STM 007)
Uploaded by
Irish Barte0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesGeneral Biology (STM 007)
Uploaded by
Irish BarteCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
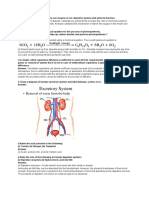
2nd ACHIEVEMENT EXAM REVIEWER resisting pressure and shock.
GENERAL BIOLOGY (STM 007) III.1 Extra Cellular Matrix
Day 10 a.1 Protein Fibers
TISSUES- are group of cells that have a similar structure and act together to perform a Collagen
specific function. Elastin
a.2 Ground Substances - supports the cells and fibers
I. Epithelial Tissue- mostly in linings of airways, reproductive tract and GI tract.
Types of Connective Tissue:
Types of Epithelial Tissue: A. Loose/Areolar Connective Tissue - fastens down the skins, binds muscles
A. Simple Epithelial- consist of one layer of cells together and fill spaces in between organs.
a.1) Simple Squamous
B. Dense Connective Tissue - mostly found in tendons (bone to muscle),
flattened cells
ligaments (bone to bone). Poorly vascularized - wound healing is slow.
found in linings of lungs, blood vessels and capillary walls
it allows diffusion C. Adipose/Fat Tissue - it provides heat and it is the storage of nutrient and fat.
a.2) Simple Cuboidal D. Osseous Connective Tissue- bone and living tissue
cube cells
found in kidney tubules and ducts of ovaries IV. Vascular Tissue - carry blood and its components
for secretion and absorption Types of Blood Cells:
A. Red Blood Cell/Erythrocytes - disk-shaped cell, no nucleus. They carry much
a.3) Simple Columnar
oxygen.
Column like/elongated cells
Found in linings of stomach and intestines B. White Blood Cell/Leukocytes - lesser in number, bigger in size. It fights
against infection.
a.4) Cillated Epithelium
Type of White Blood Cell:
Either cuboidal or columnar
1. Agranulocytes- without granules in the cytoplasm
Hair like called CILIA- found in nose, nasal cavity
1.a Lymphocytes- smallest white blood cells, lymphatic vessels
B. Stratified Epithelium - multiple layers of cells 1.b Monocytes- largest white blood cell with huge appetites
2. Granulocytes
II. Muscular Tissue- contraction and relaxation of muscles. It consists of cells called
2.a Neutrophils - phagocytes during bacterial infection
MUSCLE FIBER.
2.b Eosinophils - active during allergic reaction
1. Membrane (sarcolemma)
2.c Basophils - histamine containing granules
2. Cytoplasm (sarcoplasm)
a. Miyofribrils C. Thrombocytes - are platelets. It is responsible for blood clotting
Actin & Myosin - proteins responsible for contraction and
relaxation. V. Nervous Tissue- responsible in receiving and transmitting stimuli in the form of
b. Mitochondria nerve impulses. Dendrites - carries impulses
Types of Muscular Tissue: towards the cell body
A. Based on location
a.1) Skeletal - attached to bones. Ex. Biceps, triceps and pectoralis Axon- carries impulses away from
a.2) Visceral/Smooth- walls of hollow organs, stomach and intestines the cell body
a.3) Cardiac-located at your heart Terminal Dendrites- connected to
dendrites of another neurons
B. Based on Appearance
b.1) Striated- there is stripes seen Cell Body- called soma. It
b.2) Unstriated- there is none stripes seen connects to the dendrites that
brings information to the neuron
C. Based on Neural Control
Node of Ranvier- a small gap in
c.1) Voluntary- you have control
the between the myelin sheath
c.2) Involuntary- you cannot control the movement
Schawann Cell- a glial cell that
wraps around the nerve fiber
Myelin Sheath- insulating covering
III. Connective Tissue - it gives form and shape. It forms rigid structures capable of that surround an axon
Day 11 Day 13
PLANT TISSUES Cellular Modification
1. Protective Tissue - it covers the surface of your leaves and living cells of roots and Newly formed cell undergo structural modification
stems. In order to adapt and respond to the changes in the environment
a. Epidermis - secretes a coating called CUTICLE- helps the plant to retain water
ANIMALS
b. Periderm- bark. It consists of cork cells that protects the plant from pathogens. 1. MICROVILI
It prevents excessive loss of water and provides insulation. Cellular modification happens in plasma membrane
Epithelial cells
2. Meristematic Tissue - region where rapid production of cell is happening
Found in hollow organs
a. Apical Meristem- primary growth (vertical growth)
Found in stomach, SI, kidney tubules, inner ear, cells of the taste buds,
b. Lateral Meristem- secondary growth (horizontal growth)
olfactory receptor cells.
b.1 Vascular Cambium- increasing the thickness/girth of plants
It increases surface area for absorption, secretion and cellular
b.2 Cork Cambium- only for woody plants
adhesion.
c. Intercalary Meristem - grass, bamboo. It has apical meristem, doesn’t have
lateral meristem 2. CILIA
Whip-like extensions that more substances along the surface
3. Mechanical/Ground Tissue
Types:
a. Parenchyma - most abundant cell type. They are vital in repairing tissue
a. Motile Cilia - more substances, sweeper. Accumulation of dirt and dusts.
damage
Found in lining of trachea.
a.1 Chlorenchyma- parenchyma cell that has a lot of chloroplast.
b. Non-motile Cilia - found in eyes and nose. Its function is to trap dirt.
a.2 Aerenchyma- parenchyma cell that loosely packed together with
Nose: acts as olfactory senses (tells the brain what is it)
connected air spaces. (Ex. Water lily)
b. Collenchyma - found beneath the epidermis. It provides flexible support. (Ex. 3. STEREO CILIA
Celery) Mechano sensing organelles that respond to fluid pressure in ears
c. Sclerenchyma- embedded with LIGNIN- very important ingredient in making To maintain hearing and balance
cell wall
4. MUSCLES
4. Conducting Tissue- vascular tissue of plants For contraction (coordination of muscles & produce movement)
a. Xylem- water conducting tissue It needs a lot of mitochondria
b. Phloem- food conducting tissue. It responsible for distributing glucose
5. RBC/RED BLOOD CELLS
Biconcave shaped without nucleus
5. Specialized Tissue
Red pigment called HEMOGLOBIN
a. Stomata- found underside of the leaves/leaf and where carbon enters the
leaves
PLANTS
b. Trichomes- the one who prevents excessive evaporation from the leaves. It
1. ROOT HAIR CELLS
regulates stomata.
Found in epidermis roots
Surface area for the absorption of water and nutrients in the soil
2. TRICHOMES
They closes the stomata if they feel increase of water
Regulates water evaporation
3. GUARD CELLS
Values open and close the pores in response to changes in the
temperature of environment
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Photosynthesis and Respiration (Hopkins W.G., 2006)Document177 pagesPhotosynthesis and Respiration (Hopkins W.G., 2006)Houssein Ya Mazloum100% (3)
- Quantitative Sample ResearchDocument41 pagesQuantitative Sample ResearchIrish Barte96% (24)
- R1 Designing A School Public ToiletDocument18 pagesR1 Designing A School Public ToiletIrish Barte100% (1)
- Plumbing 1Document1 pagePlumbing 1Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Revision NoteDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesis Revision NoteUsman Mukhtar AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of A LeafDocument25 pagesInternal Structure of A LeafAri Pitoyo50% (2)
- AP Biology Free Response Questions Through 2010Document44 pagesAP Biology Free Response Questions Through 2010Bob100% (1)
- Biology M4 PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesBiology M4 PhotosynthesisDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- P001 Plumbing Layout IsometricDocument1 pageP001 Plumbing Layout IsometricIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- FINALS Lecture Part 1Document24 pagesFINALS Lecture Part 1Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- Portfolio ContentDocument8 pagesPortfolio ContentIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- R3 Designing A KitchenDocument10 pagesR3 Designing A KitchenIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- A003 Ground Second Floor PlanDocument1 pageA003 Ground Second Floor PlanIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- 7 - Annex C-3 UP MDP Restroom Design Standards 2018Document103 pages7 - Annex C-3 UP MDP Restroom Design Standards 2018Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- Requirements To Complete The IPMA Philippines OJTDocument13 pagesRequirements To Complete The IPMA Philippines OJTIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Final ReviewerDocument7 pagesDay 2 Final ReviewerIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- R3 Benefits of Natural Lights Lighting in BuildingsDocument9 pagesR3 Benefits of Natural Lights Lighting in BuildingsIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- R2 Different Types of KitchenDocument12 pagesR2 Different Types of KitchenIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Heliodon StudiesDocument2 pagesHeliodon StudiesIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Proposed Construction of Two Storey Building With Basement For Provincial Satellite Auditing Office PSAO Rizal Sitio Cabading Barangay Inarawan Antipolo City RizalDocument50 pagesProposed Construction of Two Storey Building With Basement For Provincial Satellite Auditing Office PSAO Rizal Sitio Cabading Barangay Inarawan Antipolo City RizalIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Barte. Module 2, S.A. 1 To 3Document2 pagesBarte. Module 2, S.A. 1 To 3Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- Practical Research (APP 006)Document5 pagesPractical Research (APP 006)Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- English Acad (APP 002)Document1 pageEnglish Acad (APP 002)Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- App 004 EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesApp 004 EntrepreneurshipIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- SSP (SSP 003)Document1 pageSSP (SSP 003)Irish BarteNo ratings yet
- KolehiyoDocument1 pageKolehiyoIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant and Sustainable BuildingDocument4 pagesEarthquake Resistant and Sustainable BuildingIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- Twenty One Twenty One: - Joshua's - Joshua'sDocument2 pagesTwenty One Twenty One: - Joshua's - Joshua'sIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- A Position Paper On The Death Penalty in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageA Position Paper On The Death Penalty in The PhilippinesIrish BarteNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Plant Structure and Growth: Topic 9: Plant Science (HL)Document6 pages9.1 Plant Structure and Growth: Topic 9: Plant Science (HL)Morgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Plant Agronomic Performance and Selection For Green Roofs Under Mediterranean and Maritime Climate ConditionsDocument160 pagesPlant Agronomic Performance and Selection For Green Roofs Under Mediterranean and Maritime Climate ConditionsPoly LitoikairoiNo ratings yet
- June 2011 (v1) MS - Paper 2 CIE Biology IGCSEDocument11 pagesJune 2011 (v1) MS - Paper 2 CIE Biology IGCSESriyashas KalluriNo ratings yet
- Biomimicry Architecture Project Seminar by A.S.Amizhdhan 18CE02016Document15 pagesBiomimicry Architecture Project Seminar by A.S.Amizhdhan 18CE02016AMIZHDHAN A SNo ratings yet
- Floriculture: Fundamentals and PracticesDocument529 pagesFloriculture: Fundamentals and Practicesnutescu.alexNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 3: Name: Class: DateDocument6 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 3: Name: Class: DateTeng Pei ErNo ratings yet
- Padlet H8xipv2kpjqkDocument2 pagesPadlet H8xipv2kpjqkapi-264373083No ratings yet
- X Bio Masterkey Differences 22 - 234Document40 pagesX Bio Masterkey Differences 22 - 234Varenayam editzNo ratings yet
- Biology Practical Class Xi 2023Document2 pagesBiology Practical Class Xi 2023Himanshu GautamNo ratings yet
- Characterizing Agronomic Response of Rice Genotypes To Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease in Uganda - IJAARDocument10 pagesCharacterizing Agronomic Response of Rice Genotypes To Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease in Uganda - IJAARInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Remedial StudentsDocument5 pagesAssignment For Remedial StudentsPoul GonaNo ratings yet
- Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLLDocument50 pagesMelc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLLphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - BIOACCUMULATION AND BIODISPOSITION OF TOXICANTS - Dec 2020Document57 pagesCHAPTER 3 - BIOACCUMULATION AND BIODISPOSITION OF TOXICANTS - Dec 2020Adam Zachary Mohd FaizalNo ratings yet
- Student Worksheet On StomataDocument2 pagesStudent Worksheet On StomataScribd_is_GreatNo ratings yet
- Structureoftheleaf Complete LessonDocument28 pagesStructureoftheleaf Complete Lessonjerylle25No ratings yet
- Anatomical Study of Sansevieria Zeylanica Leaf Affected by Vehicular EmissionsDocument35 pagesAnatomical Study of Sansevieria Zeylanica Leaf Affected by Vehicular EmissionsLowie Soriano Bacunot100% (1)
- Plant Nutrition Chapter-1: Review QuestionsDocument17 pagesPlant Nutrition Chapter-1: Review QuestionsRajeevSangam100% (1)
- Cbse LP RevisionDocument18 pagesCbse LP RevisionKanak ChhajerNo ratings yet
- Let Review QuestionsDocument12 pagesLet Review QuestionsMarvin V. Rubia50% (2)
- Final Quality ControlDocument36 pagesFinal Quality ControlRajeswari Rajarammurthy R100% (1)
- ORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFDocument3 pagesORDONEZ ERALAINE G. Photosynthesis Reading and Questions PDFRaine OrdonezNo ratings yet
- Hawassa University College of AgricultureDocument31 pagesHawassa University College of Agriculturehilina workuNo ratings yet
- CLASS X (2020-21) Science (Code 086) Sample Paper-10: Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument9 pagesCLASS X (2020-21) Science (Code 086) Sample Paper-10: Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80 General InstructionsRD's EducationNo ratings yet
- Monitoreo BiosferaDocument37 pagesMonitoreo BiosferaHéctor W Moreno QNo ratings yet
- 83 e - RR - 511 A PDFDocument12 pages83 e - RR - 511 A PDFArmaan MujjuNo ratings yet