Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cabhydrates
Uploaded by
Pretut VillamorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cabhydrates
Uploaded by
Pretut VillamorCopyright:
Available Formats
Glucose- a simple sugar which is an important energy source in living organisms and
is a component of many carbohydrates.
Fructose- a crystalline sugar sweeter and more soluble than glucose.
Ribose- a sugar of the pentose class which occurs widely in nature as a constituent
of nucleosides and several vitamins and enzymes.
Glucosamine- a crystalline compound which occurs widely in connective tissue,
especially as a component of chitin.
Galactose- a simple sugar that is normally transformed in the liver before being
used up as energy. This sugar is quite abundant in human diets and helps in a
number of functions.
Maltose- malt sugar is the least common disaccharide in nature. It is present in
germinating grain, in a small proportion in corn syrup, and forms on the partial
hydrolysis of starch. It is a reducing sugar.
Sucrose- a compound which is the chief component of cane or beet sugar.
Lactose- a sugar present in milk. It is a disaccharide containing glucose and
galactose units.
Lactulose- a synthetic sugar with laxative properties. It is a disaccharide
consisting of glucose and fructose units.
Chitobiose- A disaccharide amino sugar composed of two glucosamine residues.
Raffinose- a sugar present in sugar beet, cotton seed, and many grains. It is a
trisaccharide containing glucose, galactose, and fructose units.
Stachyose- a sweet crystalline tetrasaccharide sugar C24H42O21 that yields glucose,
fructose, and galactose on hydrolysis.
Verbascose- a pentasaccharide (galactose-galactose-galactose-glucose-fructose),
found in many legumes, that is metabolized by intestinal flora.
Maltotriose- is a trisaccharide (three-part sugar) consisting of three glucose
molecules linked with a-1,4 glycosidic bonds. It is most commonly produced by the
digestive enzyme alpha-amylase (a common enzyme in human saliva) on amylose in
starch.
HMO (Human Milk Oligosaccharide)-also known as human milk glycans, are sugar
molecules, that are part of the oligosaccharides group and which can be found in
high concentrations exclusively in human breast milk.
Amylose- the crystallizable form of starch, consisting of long unbranched
polysaccharide chains.
Amylopectin- the noncrystallizable form of starch, consisting of branched
polysaccharide chains.
Maltodextrins- dextrin containing maltose, used as a food additive.
Glycosaminoglycan- any of a group of compounds occurring chiefly as components of
connective tissue. They are complex polysaccharides containing amino groups.
Monostarch phosphate- is a modified starches. These are not absorbed intact by the
gut, but are significantly hydrolysed by intestinal enzymes and then fermented by
intestinal microbiota.[1]
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Immortality of Eating MeatDocument7 pagesImmortality of Eating MeatSumit KapoorNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Mind Blowing Magic Collection PDFDocument41 pagesMind Blowing Magic Collection PDFjules629450% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Biology Revision Notes Part3Document10 pagesBiology Revision Notes Part3volvanskyNo ratings yet
- Physical Development Personal Development ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysical Development Personal Development ReviewerPretut VillamorNo ratings yet
- Biological Science PreboardDocument19 pagesBiological Science PreboardMark de Jesus0% (2)
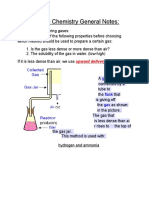
- Paper 6 Chemistry General NotesDocument5 pagesPaper 6 Chemistry General NotesMiran El-MaghrabiNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy Is by DR Gireesh Kumar K PDocument16 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy Is by DR Gireesh Kumar K PAETCM Emergency medicineNo ratings yet
- Site Selection Criteria For Coal Power PlantsDocument7 pagesSite Selection Criteria For Coal Power Plantsmrizvi33No ratings yet
- JINGLEDocument4 pagesJINGLEPretut VillamorNo ratings yet
- Perdev ReviewerDocument9 pagesPerdev ReviewerPretut VillamorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 PerdevDocument2 pagesLesson 8 PerdevPretut Villamor75% (4)
- Anesthesia: Essays and Researches General Anesthesia in Tetanus Patient Undergoing Emergency Surgery: A Challenge For AnesthesiologistDocument4 pagesAnesthesia: Essays and Researches General Anesthesia in Tetanus Patient Undergoing Emergency Surgery: A Challenge For AnesthesiologistEnrico StefanelliNo ratings yet
- Soalan Upk1Document2 pagesSoalan Upk1Kak Long IntanNo ratings yet
- T NG Ôn 2-HandoutDocument14 pagesT NG Ôn 2-HandoutHà HườngNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive ElementsDocument10 pagesActive and Passive Elements1234 5678No ratings yet
- Cake Makers GuidanceDocument16 pagesCake Makers GuidancegenebabaNo ratings yet
- Lifespan Development Lives in Context 1st Edition Kuther Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesLifespan Development Lives in Context 1st Edition Kuther Solutions Manualgiangdoankqb1rc100% (34)
- Dt. NestleDocument9 pagesDt. NestleQytyku BoranaNo ratings yet
- Water PotentialDocument2 pagesWater PotentialsmellybottomNo ratings yet
- Turnstile Design SheetDocument6 pagesTurnstile Design SheetArmstrongMasengaNo ratings yet
- Vendor PerformanceDocument38 pagesVendor PerformanceManojNo ratings yet
- Till Saxby Electric Pallet Truck Egv 10-12-0240 0242 0300 0302 Workshop ManualDocument22 pagesTill Saxby Electric Pallet Truck Egv 10-12-0240 0242 0300 0302 Workshop Manualmichaelfisher030690fgaNo ratings yet
- Tyler Resume Updated 3 23 17Document1 pageTyler Resume Updated 3 23 17api-285213449No ratings yet
- Astm g21 g22Document7 pagesAstm g21 g22ENZO CORSI0% (1)
- (PDF) Concrete Cracks Repair Using Epoxy ResinDocument18 pages(PDF) Concrete Cracks Repair Using Epoxy ResinAakanksha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 2012-02-01 FWGIDR 9 Checklist For The Qualification of Computed Radiography SystemsDocument19 pages2012-02-01 FWGIDR 9 Checklist For The Qualification of Computed Radiography SystemsDeepak DasNo ratings yet
- Latsol Pat Ing - 11 Ipa Mei 2023Document3 pagesLatsol Pat Ing - 11 Ipa Mei 2023primagama sragenNo ratings yet
- 4099 0002Document4 pages4099 0002kikeecpNo ratings yet
- Esec 2100 XP Esec 2100 XP: Plus PlusDocument2 pagesEsec 2100 XP Esec 2100 XP: Plus PlusЧарли FrogNo ratings yet
- 1) Gobar Danga Model: Purpose of Visit: To IntroduceDocument6 pages1) Gobar Danga Model: Purpose of Visit: To IntroduceArun BiswasNo ratings yet
- ASTM Hydrometers: Standard Specification ForDocument12 pagesASTM Hydrometers: Standard Specification FordawoodNo ratings yet
- Aipmt-Neet Cutoff 2012Document178 pagesAipmt-Neet Cutoff 2012rahuldayal90No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument6 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 7 Human Nutrition - CIE Biology IGCSEImran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 8662Document8 pages86628662No ratings yet