Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HACVD Patho
Uploaded by
Angel Filoteo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageOriginal Title
102939917-HACVD-patho.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageHACVD Patho
Uploaded by
Angel FiloteoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
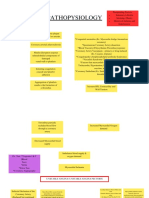
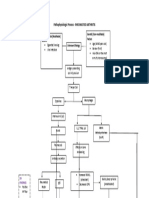
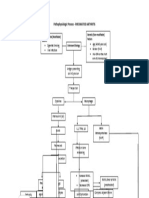
Pathophysiology HACVD LDL and Tryglycerides
Damage to intimal endothelial cells
Platelets and Monocytes adhere to injured site
Abnormal proliferation of smooth muscles and connective tissue
Inflammation of blood vessels
Migration of monocytes beneath the endothelium and become macrophage
Permeability of endothelium
Formation of Atherosclerotic plaque (CXR: Atherosclerosis of thoracic aorta)
Narrowing of the blood vessel lumen
Blood flow Plaque hemmorrhage/rupture Vascular resistance
Afterload
Preload
Compensatory Mechanism: Myocardial Hypertrophy
Cardiomegaly
Increased O2 demands
Failure of O2 compensation
Cardiac Tissue Ischema
Cardiac Tissue Injury
Cardiac tissue Infarction
Decreased functioning contractile tissue
Cardiac output
Perfusion/Hypoperfusion
Systemic Hypoxia
Multiorgan Failure
Death
You might also like
- Penilaian Awal Pasien SyokDocument33 pagesPenilaian Awal Pasien SyokatikaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Leucemia: Desde la mutación genética inicial hasta el apoyo para la supervivenciaFrom EverandFast Facts: Leucemia: Desde la mutación genética inicial hasta el apoyo para la supervivenciaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfarctionSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Ccu Patho AcsDocument2 pagesCcu Patho AcsSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Atherosclerosis and Myocardial InfarctionSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram On The 4 Types of ShockDocument5 pagesSchematic Diagram On The 4 Types of Shockgodgiven25100% (5)
- Pathophysiology STEMIDocument2 pagesPathophysiology STEMIMary SutingcoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AppendicesDocument2 pagesCardiovascular System AppendicesKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Factors and Causes of Acute Myocardial Infarction (IMADocument1 pageFactors and Causes of Acute Myocardial Infarction (IMAFhicholy Davied VanrioNo ratings yet
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoNo ratings yet
- Sindrom Koroner Akut.ADocument55 pagesSindrom Koroner Akut.AwidiyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument55 pagesPathophysiology and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery DiseaseShirinNo ratings yet
- Asinas Shairabsn3aDocument28 pagesAsinas Shairabsn3aJoshua ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) vs. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Document37 pagesCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) vs. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Grace IgnacoNo ratings yet
- PathopysiologyDocument5 pagesPathopysiologyAnnie GutualNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiologynursing concept maps67% (3)
- Pa Tho Physiology of M.IDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of M.Inica_nyxNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio - Stemi - FinalDocument4 pagesPathophysio - Stemi - FinalPrincessDianneNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm, Hypertension & StrokeDocument20 pagesAneurysm, Hypertension & StrokeSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Shock: Coass Anestesi Periode 12 Desember 2017 - 13 Januari 2018Document18 pagesShock: Coass Anestesi Periode 12 Desember 2017 - 13 Januari 2018iqbalNo ratings yet
- Increased Cardiac Workload: Ossible DX: Cranial CT Scan, DopplerDocument2 pagesIncreased Cardiac Workload: Ossible DX: Cranial CT Scan, DopplerMari LynNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Goals in The Postoperative Period of Cardiovascular SurgeryDocument78 pagesResuscitation Goals in The Postoperative Period of Cardiovascular SurgeryRicardo Poveda JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Schematic Pathophysiology of Stroke (CVADocument3 pagesSchematic Pathophysiology of Stroke (CVAmizzybaylonNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument18 pagesCardiomyopathyDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis in an Overweight 70-Year-Old FemaleDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Atherosclerosis in an Overweight 70-Year-Old FemaleCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Zhao Mingyao BMC - Zzu. 2004-3-8Document30 pagesZhao Mingyao BMC - Zzu. 2004-3-8api-19916399No ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentDocument7 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology ofDocument2 pagesThe Pathophysiology ofMelanie Moises JavierNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 EditedDocument336 pagesBiology 1 EditedEmperor GooseNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument12 pagesMyocardial InfarctionRifka Meilinda Putri IINo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy in ICU: Dr. Basuki Rahmat SP - AnDocument84 pagesFluid Therapy in ICU: Dr. Basuki Rahmat SP - AndianNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis for Cardiac, Pulmonary, Hematological, and Neurological PresentationsDocument32 pagesDifferential Diagnosis for Cardiac, Pulmonary, Hematological, and Neurological PresentationsSom Lakhani100% (2)
- Kuliah Blok 2 Gangguan Hemodinamik Trombosis Dan ShockDocument37 pagesKuliah Blok 2 Gangguan Hemodinamik Trombosis Dan ShockAnonymous N2PHMnTIYLNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument1 pageAngina PectorisAlissa MaghopoyNo ratings yet
- LP Stemi PujaDocument25 pagesLP Stemi PujaPuja Oktavia100% (1)
- Precipitating Factors:: Myocardial Cell Death (NecrosisDocument2 pagesPrecipitating Factors:: Myocardial Cell Death (NecrosisLean Ashly MacarubboNo ratings yet
- Atherero 1 Doc Raquid 2021Document50 pagesAtherero 1 Doc Raquid 2021orea0% (1)
- Dr. Eka - CAD and It's Renal ComplicationDocument34 pagesDr. Eka - CAD and It's Renal Complicationlab adjidarmoNo ratings yet
- 11-Heart Failure-0604-Dinggao 18 - 4 - 06Document46 pages11-Heart Failure-0604-Dinggao 18 - 4 - 06api-19916399No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseNursesLabs.comNo ratings yet
- DR Anuj Raj BijukchheDocument95 pagesDR Anuj Raj BijukchheMUHAMMAD JAWAD HASSANNo ratings yet
- (5+6) PATH - Cerebrovascular AccidentsDocument16 pages(5+6) PATH - Cerebrovascular AccidentsNader NURESNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Stroke HemorraghicDocument126 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Stroke HemorraghicHerna PattakitaNo ratings yet
- Syok, Demam, DiareDocument101 pagesSyok, Demam, Diarepss rsjrwNo ratings yet
- Final Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesFinal Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology PDFDave JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Essential of Special Patholog by DR Zair Hassan: December 2015Document271 pagesEssential of Special Patholog by DR Zair Hassan: December 2015pdf pediatriNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAnne SedanzaNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument54 pagesFinalsAndrea Love PalomoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCYUSRIL ZUMADINSYAHNo ratings yet
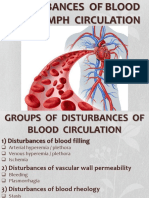
- Disturbances of Blood CirculationDocument59 pagesDisturbances of Blood Circulationсветлый поповNo ratings yet
- Cvs Lec 1Document43 pagesCvs Lec 1data4fourgNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)Document4 pagesPathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)jhonkivenNo ratings yet
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroDocument12 pagesTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Blood Vessels: - ANTERIOSCLEROSISDocument4 pagesDisorders of The Blood Vessels: - ANTERIOSCLEROSISJack KayatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- FORMAT (Case Study PPS 3)Document2 pagesFORMAT (Case Study PPS 3)Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Key Issues Desired Outcome Independent Intervention Actual Outcome March 5, 2015Document4 pagesKey Issues Desired Outcome Independent Intervention Actual Outcome March 5, 2015Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Or Sample ChartingDocument3 pagesOr Sample ChartingPrincess Sarey88% (8)
- Filoteo, Angel Hannah A. BSN 3B: Pathophysiologic Process - RHEUMATOID ARTHRITISDocument1 pageFiloteo, Angel Hannah A. BSN 3B: Pathophysiologic Process - RHEUMATOID ARTHRITISAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument2 pagesStudyAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- PRJ prj0000253Document30 pagesPRJ prj0000253Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Death Can Occur From The Misuse of Cough and Cold Medicines in Very Young ChildrenDocument4 pagesDeath Can Occur From The Misuse of Cough and Cold Medicines in Very Young ChildrenAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Name: Filoteo, Angel Hannah A. Date: Sept. 7,2020Document3 pagesName: Filoteo, Angel Hannah A. Date: Sept. 7,2020Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Caring for older adults after ischemic attack or strokeDocument4 pagesCaring for older adults after ischemic attack or strokeAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- WritingDocument44 pagesWritingAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Research-4 Otter - AiDocument1 pageResearch-4 Otter - AiAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Safety and Safe MedicationDocument92 pagesSafety and Safe MedicationAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Coa 1 - Otter - AiDocument6 pagesNeuro Coa 1 - Otter - AiAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Caring for older adults after ischemic attack or strokeDocument4 pagesCaring for older adults after ischemic attack or strokeAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Aging on the Nervous System: Symptoms and PreventionDocument51 pagesEffects of Aging on the Nervous System: Symptoms and PreventionAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Research-5 Otter - AiDocument2 pagesResearch-5 Otter - AiAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Coa 1 - Otter - AiDocument6 pagesNeuro Coa 1 - Otter - AiAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Safety and Safe MedicationDocument92 pagesSafety and Safe MedicationAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Safety and Safe MedicationDocument92 pagesSafety and Safe MedicationAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Rest and Sleep: Week 4 Mr. Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSNDocument80 pagesRest and Sleep: Week 4 Mr. Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSNAngel Filoteo100% (1)
- WritingDocument44 pagesWritingAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- PTE Homework FiloteoDocument1 pagePTE Homework FiloteoAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Aging Skin and Common ConditionsDocument89 pagesAging Skin and Common ConditionsAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument45 pagesReadingAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- ListeningDocument64 pagesListeningAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- 4 Cardiovascular HealthDocument79 pages4 Cardiovascular HealthAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System/ Movement: Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSNDocument85 pagesMusculoskeletal System/ Movement: Mark Ebony C. Sumalinog, RN MSNAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28: Virology: Poxvirus Herpes Virus Adenovirus Papovavirus Hepatitis BDocument2 pagesChapter 28: Virology: Poxvirus Herpes Virus Adenovirus Papovavirus Hepatitis BAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet