100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology
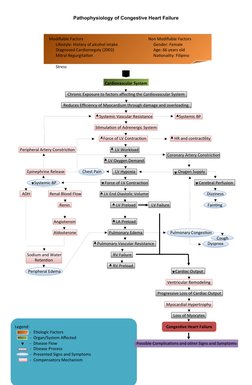
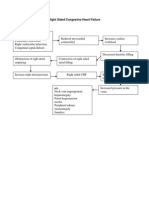
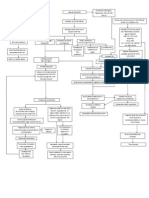
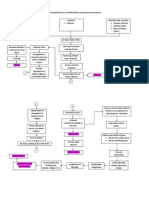
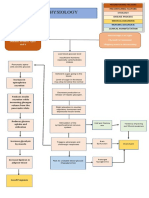
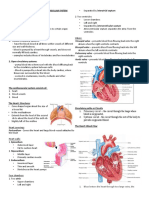
Chronic exposure to modifiable and non-modifiable factors that affect the cardiovascular system can reduce the efficiency of the myocardium through damage and overloading. This stimulates the adrenergic system and increases heart rate, contractility, and systemic vascular resistance, raising blood pressure and the workload on the left ventricle. Over time, this leads to left ventricular hypoxia, failure, and remodeling with progressive loss of cardiac output and the development of congestive heart failure. Without treatment, congestive heart failure can result in complications that affect the cardiovascular, respiratory, cerebrovascular, and urinary systems.
Uploaded by
tinaykoCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology
Chronic exposure to modifiable and non-modifiable factors that affect the cardiovascular system can reduce the efficiency of the myocardium through damage and overloading. This stimulates the adrenergic system and increases heart rate, contractility, and systemic vascular resistance, raising blood pressure and the workload on the left ventricle. Over time, this leads to left ventricular hypoxia, failure, and remodeling with progressive loss of cardiac output and the development of congestive heart failure. Without treatment, congestive heart failure can result in complications that affect the cardiovascular, respiratory, cerebrovascular, and urinary systems.
Uploaded by
tinaykoCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure
- Systemic Effects and Symptoms