Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philippine Science Education Initiatives
Uploaded by
Janea100%(5)100% found this document useful (5 votes)
6K views3 pagesScience education in the Philippines focuses on teaching scientific concepts, developing process skills, and preparing students for science careers. The government supports science education through scholarships and specialized schools like the Philippines Science High School System and Special Science Elementary Schools. These schools aim to identify gifted youth and provide them with enriched science and math curricula. Indigenous knowledge is also an important part of science education in the Philippines, as local communities have developed scientific understandings through daily observations and practices over generations.
Original Description:
Original Title
SCIENCE EDUCATION IN THE PHILIPPINES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentScience education in the Philippines focuses on teaching scientific concepts, developing process skills, and preparing students for science careers. The government supports science education through scholarships and specialized schools like the Philippines Science High School System and Special Science Elementary Schools. These schools aim to identify gifted youth and provide them with enriched science and math curricula. Indigenous knowledge is also an important part of science education in the Philippines, as local communities have developed scientific understandings through daily observations and practices over generations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(5)100% found this document useful (5 votes)
6K views3 pagesPhilippine Science Education Initiatives
Uploaded by
JaneaScience education in the Philippines focuses on teaching scientific concepts, developing process skills, and preparing students for science careers. The government supports science education through scholarships and specialized schools like the Philippines Science High School System and Special Science Elementary Schools. These schools aim to identify gifted youth and provide them with enriched science and math curricula. Indigenous knowledge is also an important part of science education in the Philippines, as local communities have developed scientific understandings through daily observations and practices over generations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
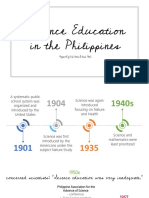
SCIENCE EDUCATION IN THE PHILIPPINES (STS)
Science education in the tertiary level also focuses
CONCEPT OF SCIENCE EDUCATION on the preparation of science teachers, scientist,
- Science Education focuses on teaching, learning, engineers and other professionals in field of
and understanding science. science.
-Exploring pedagogical theories and models
helping teachers teach scientific concept and The state provides scholarship to encourage more
processes effectively. students to pursue science courses.
-Understanding science implies developing and
applying science process skills and understanding SCIENCE SCHOOLS IN THE PHILIPPINES
the natural world and activities in everyday life.
Philippines Science High School System (PSHSS)
John Dewey ( 2001)
-Stressed the importance of utilizing the natural -The government program for gifted students in
environment to teach students. the Philippines.
-It's a serve institute of the Department of
Marx (1994) Science and Technology (DOST) whose mandate
-opines that science is going to be one of the most is to offer free scholarship basis for secondary
important school subject in the future. course with special emphasis on subjects
pertaining to the sciences, with the end-view of
Science education provides skills and knowledge preparing its students for science career
that are necessary for a person to live in what (Republic Act No. 3661).
Knight (1986) describes as the age of science and -The PHSS continues to pursue its vision to
to develop a citizenry that will meet the goals of develop Filipino science scholars with scientific
science in the society (Tilghman, 2005). minds and passion for excellence.
-PHSS students have brought honor to the
SCIENCE EDUCATION IN BASIC AND TERTIARY Philippines through their exemplary
EDUCATION achievements in various international
competitions and research circles.
Science education helps students learn important
concepts and facts that are related to everyday life Special Science Elementary Schools (SSES) Project
- ( Carale & Campo 2003 , Meador 2005; Worth &
Groliman, 2003) -SSES project is in pursuance to DepEd Order No.
73 and DepEd Order No. 51 s 2010
Including important skills such as process skills, -The project was piloted in SY 2007 – 2008 to
critical thinking skills and life skills that are needed selected 57 schools in 55 divisions in the 16
in coping up with daily life activities. regions particularly among the gifted and fast
-(chaille & Britain, 2002) learners classes in Special Education Centers and
regular schools.
Science education also develops positive attitude -Aims to develop Filipino children equipped with
such as the love for knowledge, passion for scientific and technological knowledge, skills, and
innovative things, curiosity to the study of nature values
and creativity. MISSION is to
-(Lind,1997). -provide a learning environment to science-
inclined children through a special curriculum that
In tertiary education, science education deals with recognizes the multiple intelligence of the learners
developing students’ understanding and -promote the development of lifelong learning
appreciation of science ideas and scientific works. skills
-foster the holistic development of the learners.
-Children enrolled in the program are identified
using set criteria and are primed to be Central Visayas Institute Foundation
mainstreamed to the Science and Technology High -The home and pioneer of the prominent school-
Schools. based innovation known as the Dynamic Learning
Program (DLP)
-SSES is a research and development project -DLP is a synthesis of classical and modern
designed to develop students with higher aptitude pedagogical theories adapted to foster and highest
for science and mathematics through the level of learning, creativity and productivity.
implementation of an enhanced science and -Takes pride in its Research Center Theoretical
mathematics curriculum at the elementary level. Physics (RCTP) established in 1992, which organizes
small international workshops to foster the
-The curriculum had a longer time compared to informal but intense exchange of ideas and
other subjects and also utilize different perspectives on outstanding problems in physics
instructional approaches that address the and math.
learning styles and needs of the learners like The original CVIF strategic plan
use of investigatory projects. (circa 1999) Focus on outcomes indexed by real
numbers: UPCAT passers, national
exams and, if possible, international
Quezon City Regional Science High School behavioral standards and assessments. And
(or to its students QueSci or Kisay) Leapfrog with increased math proficiency, then do
-Establish on Sept. 17,1967.( QCSHS) turn to broad front with language and science.
QCRSHS in 1999.
-Regional Science High School for the National 1960s- a group of biological educators at the
Capital Region. University of Philippines organized themselves into
-The school envisions to serve as a venue in a team to adapt the Biological Science Curriculum
providing maximum opportunities for science- Study (BSCS).
gifted students to develop spirit of inquiry and
creativity. R.A 5506- an Act establishing Science Education
-one of the prestigious sciences triumvirate of the Center (SEC) as a permanent unit of the University
Republic of the Philippines along with the of the Philippines.
Philippine Science High School and Manila Science This act earned marked 250,000 pesos annual from
High School. the national especial science fund for the support
of the center.
Manila Science High School
-establish on Oct. 1, 1963. 1st science high school in
the Philippines. by virtue of Municipal Resolution
426 signed by Mayor Antonio J. Villegas.
-Aims to produce scientist with souls. Humanities
courses and other electives are included in their
curriculum
-Manila Science High School Test (MSAT) an
entrance exam with five parts; aptitude in science,
aptitude test in math, problem-solving test in
science, pro-sol test in math, and proficiency in
English.
Indigenous Science and Technology in the Philippines (STS)
Indigenous Knowledge System
-Indigenous Knowledge embendded in daily life
experiences of young as they grow up. Parents and
other older folks served as their first teachers and their Scientific attitudes (Johnston 2000)
methods of teaching are very effective in transmitting 1. Motivating attitudes
cultural knowledge in their minds. 2. Cooperating attitudes
3. Practical attitudes
-The lesson they learned are intimately interwoven with 4. Reflective attitudes
their culture and the environment.
-Their views about nature and their reflections on their
experiences in daily life are evident in their stories, Concept of indigenous science (Pawilen, 2006)
poems and songs.
-Predicting weather conditions and seasons using INDIGENOUS
SCIENCE
knowledge in observing animal’s behavior and celestrial
bodies
-Using herbal medicine
-Preserving foods uses guided by composed by
-Classifying plants and animals into families and groups
based on cultural properties Science
Process Community
-Preserving and selecting good seeds for planting Culture and Traditional
Skills Knowledge
-Using indigenous technology in daily lives Values
-Building local irrigation systems
-Classifying different types of soil for planting based on
cultural properties
-Producing wines and juices from tropical fruits 1. Indigenous science uses science process skills such as
-Keeping the custom of growing plants and vegetables observing, comparing, classifying, measuring, problem
in the yard solving, inferring, communicating, and predicting
Indigenous Science 2. Indigenous science is guided by culture and
-Part of the indigenous knowledge system practiced by community values
different groups of people and early civilizations. - The land is the source of life.
- The Earth is revered as Mother Earth.
-It includes complex arrays of knowledge, expertise, - All living and non living things are interconnected and
practices, and representations that guide human interdependent with each other.
societies in their enumerable interactions with the -Human beings are stewards or trustee of the land and
natural milieu; agriculture, medicine, naming and natural resources.
explaining natural phenomena, and strategies for - Nature is a friend to human beings
coping with changing environments (Pawilen, 2005).
3. Indigenous science is composed of traditional
-Ogawa(1995) claimed that it is colletively lived in and knowledge practiced and valued by people and
experienced by the people of a given culture. communities such as ethno-biology , ethno-medicine,
indigenous farming methods, and folk astronomy.
-Cajete(2004) indigenous science includes everything
from metaphysics to philosophy and various practical “Indigenous science helped the people in
technologies practiced by inigenous peoples both past understanding the natural environment and coping
and present. with everyday life.”
-Iaccaeino (2003) elaborated this idea by explaining
that science is a part of culture, and how science is
done largely depends on the cultural practices of the
people.
You might also like
- Promoting Science Education in the PhilippinesDocument53 pagesPromoting Science Education in the PhilippinesThe Barking DogNo ratings yet
- Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument28 pagesScience Education in The PhilippinesJoshua Jonathan Dablo David80% (10)
- Science Education in The Philippines Major Development Programs in Science and Technology in The PhilippinesDocument17 pagesScience Education in The Philippines Major Development Programs in Science and Technology in The PhilippinesCatherine LaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.STSDocument36 pagesLesson 3.STSthe who75% (16)
- Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesScience Education in The PhilippinesShedina Dangle BalinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument43 pagesLesson 3 Science Education in The PhilippinesVinNo ratings yet
- Promoting Science Education in the PhilippinesDocument6 pagesPromoting Science Education in the PhilippinesDanylyn SampereNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 (Science Education in The Philippines)Document17 pagesLesson 3 (Science Education in The Philippines)Niñarita Fe Buot100% (1)
- Science Education in the Philippines: A Look at Key SchoolsDocument10 pagesScience Education in the Philippines: A Look at Key SchoolsJayson Temblor QuilatonNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument36 pagesPPTAlexandra Alyannah75% (4)
- Sts PDFDocument21 pagesSts PDFHeidi Rose Mendoza100% (3)
- Science Education in The Philippines and IndigenousDocument4 pagesScience Education in The Philippines and IndigenousCelia Theresa Delima100% (3)
- TECHNOLOGY AND HUMAN RIGHTSDocument5 pagesTECHNOLOGY AND HUMAN RIGHTSNorsaidin TungkagNo ratings yet
- Milestone 3 - CalculusDocument4 pagesMilestone 3 - CalculusSUNSHINE CATANNo ratings yet
- Sts ReviewerDocument17 pagesSts ReviewerAngel Joy CalisayNo ratings yet
- Module 9 The Information AgeDocument25 pagesModule 9 The Information AgeNanami100% (1)
- General Concepts and Historical DevelopmentsDocument29 pagesGeneral Concepts and Historical DevelopmentsJames ReyNo ratings yet
- Science Technology and Nation BuildingDocument4 pagesScience Technology and Nation BuildingCholophrex SamilinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Science, Technology, & Nation-BuildingDocument9 pagesLesson 2 - Science, Technology, & Nation-BuildingVijanes Beltrans100% (1)
- The Darwinian RevolutionDocument28 pagesThe Darwinian RevolutionckuxinvileNo ratings yet
- Government policies drive PH science advancementDocument20 pagesGovernment policies drive PH science advancementSittie Zuhaira KamidNo ratings yet
- Science Teachnology and Society Activity 1,2 and 3Document14 pagesScience Teachnology and Society Activity 1,2 and 3Ferliza Cudiamat Pacion100% (4)
- SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN THE PHILIPPINES: A HISTORICAL OVERVIEWDocument30 pagesSCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN THE PHILIPPINES: A HISTORICAL OVERVIEWMARIA100% (2)
- Indigenous Science and Technology in The PhilippinesDocument28 pagesIndigenous Science and Technology in The PhilippinesJoshua Dela Cruz Rogador67% (3)
- Intellectual Revolutions That Defined SocietyDocument2 pagesIntellectual Revolutions That Defined SocietyEds CarbonellNo ratings yet
- STS Lesson On Intellectual RevolutionsDocument57 pagesSTS Lesson On Intellectual RevolutionsGlencil Ariesga100% (2)
- Intellectual Revolutions that Changed SocietyDocument19 pagesIntellectual Revolutions that Changed SocietyJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesScience Education in The PhilippinesNita Teresa Bagara100% (1)
- Lesson 4 - Indigenous Science and Technology in The PhilippinesDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Indigenous Science and Technology in The Philippineskeen v0% (1)
- Intellectual Revolutions that Transformed SocietyDocument11 pagesIntellectual Revolutions that Transformed SocietyVijanes BeltransNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology and Nation-BuildingDocument37 pagesScience and Technology and Nation-Buildingrose belle garciaNo ratings yet
- How Technology Reveals the Human ConditionDocument18 pagesHow Technology Reveals the Human ConditionJohn Aibert Nicdao100% (3)
- 19 - The Human Condition Before Common EraDocument9 pages19 - The Human Condition Before Common EraZhainarra Raye BetonioNo ratings yet
- STS Chapter 1 Lesson 2,3,4Document34 pagesSTS Chapter 1 Lesson 2,3,4Rey Mark Bandala100% (2)
- Topic 1. General Concepts in Science, Technology & Society (STS) and Historical DevelopmentDocument5 pagesTopic 1. General Concepts in Science, Technology & Society (STS) and Historical DevelopmentJames Michael100% (2)
- Lesson 2 - SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, AND NATION-BUILDINGDocument6 pagesLesson 2 - SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, AND NATION-BUILDINGJermaine Gonzales100% (1)
- Science Technology Society. PPT 1Document47 pagesScience Technology Society. PPT 1Erika Mae Umali100% (2)
- LESSON 2 PPT Science, Technology and Nation Building v2Document39 pagesLESSON 2 PPT Science, Technology and Nation Building v2Owie Gee82% (11)
- Science and Technology and Nation Building Sts Presentation 2-3 WeeksDocument60 pagesScience and Technology and Nation Building Sts Presentation 2-3 WeeksJay AlbaytarNo ratings yet
- STS 1 Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesSTS 1 Midterm ExamJamaica DavidNo ratings yet
- STS INTELLECTUAL REVOLUTION EditedDocument18 pagesSTS INTELLECTUAL REVOLUTION EditedJoshua Dela Cruz Rogador100% (2)
- Philippine Presidents' Major S&T ProjectsDocument3 pagesPhilippine Presidents' Major S&T ProjectszelNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 2 STS and Nation BuildingDocument2 pagesQUIZ 2 STS and Nation BuildingOwie Gee100% (1)
- Test - Week 2 - Intellectual Revolutions That Defined Society - QuizletDocument3 pagesTest - Week 2 - Intellectual Revolutions That Defined Society - Quizletwinonna rocess100% (1)
- Three Intellectual Revolutions that Shaped SocietyDocument11 pagesThree Intellectual Revolutions that Shaped SocietyFINNI JEAN TAJANLANGITNo ratings yet
- Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesScience Education in The PhilippinesAndrea L.No ratings yet
- The Philippine Government Science & Technology AgendaDocument28 pagesThe Philippine Government Science & Technology AgendaBJ A. Isidro100% (1)
- Government Laws, Policies and Plans for Science and TechDocument24 pagesGovernment Laws, Policies and Plans for Science and TechDesiree Thea Tapar100% (1)
- Technology As A Way of RevealingDocument9 pagesTechnology As A Way of RevealingHajji Aficionado100% (6)
- GEC 007 Week 4 Gov PoliciesDocument23 pagesGEC 007 Week 4 Gov PoliciesRushane Garbosa71% (7)
- UuuuDocument6 pagesUuuuMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Historical Development in Science and TechnologyDocument31 pagesHistorical Development in Science and TechnologyMecaella Bondoc100% (7)
- Science and Technology in The Philippines: Group 3Document31 pagesScience and Technology in The Philippines: Group 3Elaine PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nation BuildingDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Nation BuildingAlly Capacio100% (1)
- Science, Technology and Society Chapter 2 - Intellectual RevolutionsDocument24 pagesScience, Technology and Society Chapter 2 - Intellectual RevolutionsJimboyAbisadoNo ratings yet
- Indigenous TechnologyDocument17 pagesIndigenous TechnologyRobert DaveNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Lesson 1, Human FlourishingDocument17 pagesGroup 4 - Lesson 1, Human FlourishingPrince Epal100% (3)
- Ge7 Exam ReviewerDocument6 pagesGe7 Exam ReviewerKae CeeNo ratings yet
- Hand Out 4Document3 pagesHand Out 4Mae TadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument27 pagesChapter 3 Science Education in The PhilippinesMelvin Earl AgdaNo ratings yet
- Why G10 Students Fear MathDocument5 pagesWhy G10 Students Fear MathElkniwt AinaretNo ratings yet
- English Language & Comprehension CLAT SyllabusDocument4 pagesEnglish Language & Comprehension CLAT SyllabusTopRankersNo ratings yet
- Ethics ModuleDocument80 pagesEthics ModuleMARIA MICHELLE A. HELARNo ratings yet
- Comparing Poems About Remembering the PastDocument2 pagesComparing Poems About Remembering the PastVirgilio FeliciaNo ratings yet
- HSC Part 1 Pre Engg ResultsDocument155 pagesHSC Part 1 Pre Engg ResultsZohaib IqbalNo ratings yet
- Grade5 Where We Are in Place and Time Sy14-15Document5 pagesGrade5 Where We Are in Place and Time Sy14-15api-25638227975% (8)
- Describe and Illustrates Parallel, Intersecting and Perpendicular Lines. (M4Ge-Iiia-12.2)Document5 pagesDescribe and Illustrates Parallel, Intersecting and Perpendicular Lines. (M4Ge-Iiia-12.2)Jade Ann II100% (1)
- Unt Geography Mini LessonDocument6 pagesUnt Geography Mini Lessonapi-350855342No ratings yet
- PROF Sudha SinghDocument14 pagesPROF Sudha SinghttpqueryNo ratings yet
- Graduate Attributes For 2020 and Beyond Recommendations For Australian Higher Education ProvidersDocument17 pagesGraduate Attributes For 2020 and Beyond Recommendations For Australian Higher Education Providersdcarter_907846No ratings yet
- Non-Refugee JKF ELIMU Application Form 2024Document7 pagesNon-Refugee JKF ELIMU Application Form 2024aqi69462No ratings yet
- 3204 s12 QP 2Document12 pages3204 s12 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Chandace Lesure Math Mathods Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesChandace Lesure Math Mathods Lesson Planapi-284401368No ratings yet
- Executive Summary-3Document12 pagesExecutive Summary-3Arjun Das100% (1)
- Project-ALPHA MatrixDocument2 pagesProject-ALPHA MatrixLobmosgam HaileyhanaelaineNo ratings yet
- Elementary Greek III SyllabusDocument3 pagesElementary Greek III Syllabusapi-232538409No ratings yet
- Weekly English KSSR scheme focuses musical instrumentsDocument4 pagesWeekly English KSSR scheme focuses musical instrumentsWan Amir Iskandar IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Degree Fpi Ism Pend - Awal - .Kanak2 BiDocument5 pagesDegree Fpi Ism Pend - Awal - .Kanak2 BianasirrrNo ratings yet
- CV Tax Accounting Grad Seeks JobDocument2 pagesCV Tax Accounting Grad Seeks JobgresyestepinaNo ratings yet
- Project Waste NewDocument27 pagesProject Waste Newcristina de marananNo ratings yet
- 3 strength stories in leadershipDocument2 pages3 strength stories in leadershipMuhammad shahbazNo ratings yet
- School of Theatre and Dance: By-LawsDocument5 pagesSchool of Theatre and Dance: By-LawsMartin NardoNo ratings yet
- Ee21 AnswersDocument59 pagesEe21 AnswersRETCHELLE TEJOSO PREMIANo ratings yet
- RPS English For TourismDocument4 pagesRPS English For TourismalifazahtoNo ratings yet
- Profed 109 Rosario Mark John Rey R. Module 7 1Document6 pagesProfed 109 Rosario Mark John Rey R. Module 7 1Jayacinth100% (1)
- Lucknow Admission BrochureDocument44 pagesLucknow Admission Brochureamit goswamiNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography (An Example For A Thesis)Document14 pagesAnnotated Bibliography (An Example For A Thesis)mariaNo ratings yet
- Telephone DirectoryDocument56 pagesTelephone Directorymann chalaNo ratings yet
- HandbookDocument60 pagesHandbookyachiru121No ratings yet
- Writing Project 2: Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesWriting Project 2: Annotated Bibliographyapi-356642645No ratings yet
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- STEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8From EverandSTEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Nature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetFrom EverandNature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasFrom EverandHow to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simple STEAM: 50+ Science Technology Engineering Art and Math Activities for Ages 3 to 6From EverandSimple STEAM: 50+ Science Technology Engineering Art and Math Activities for Ages 3 to 6No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- How Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksFrom EverandHow Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Nature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningFrom EverandNature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Interactive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8From EverandInteractive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsFrom EverandCool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)