Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Expenditure Cycle: Purchases and Cash Disbursements Procedures
Uploaded by
Anne Rose EncinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Expenditure Cycle: Purchases and Cash Disbursements Procedures
Uploaded by
Anne Rose EncinaCopyright:
Available Formats
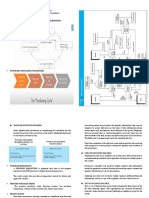
Chapter 5 The Expenditure Cycle Part 1: storeroom, Purchasing, Inventory Control, and
Purchases and Cash Disbursements Procedures Accounts Payable.
The Conceptual System
The Accounts Payable department has now
intended to be technology-neutral
received copies of the purchase requisition,
the sequence of activities through two of the
purchase order, and receiving report.
processes that constitute the expenditure cycle for
Upon receipt of the supplier’s invoice, Accounts
most retail, wholesale, and manufacturing
Payable reconciles all documents, posts to the
organizations
purchases journal, and records the liability in the
accounts payable subsidiary ledger.
Manual Purchases System
Periodically, the entries in the purchases journal
The purchases cycle begins in the Inventory
are summarized in a journal voucher which is
Control department when inventory levels drop to
sent to the General Ledger department.
reorder levels. A clerk prepares a purchase
requisition and sends copies to Purchasing and *UPDATE INVENTORY RECORDS
Accounts Payable. STANDARD COST SYSTEM. Carry their
inventories at a predetermined standard value
I. MONITOR INVENTORY RECORDS. regardless of the price actually paid to the vendor
Purchase requisition. When inventories drop to ACTUAL COST INVENTORY LEDGER.
a predetermined reorder point, the purchase cycle Requires additional financial information, such as
begins. The clerk prepares a purchase requisition a copy of the supplier’s invoice when it arrives.
and sends copies to Purchasing and Account
Payable. Journal Voucher. Prepared by Accounts
II. PREPARE PURCHASE ORDER. Payable and sent to the General Ledger
Purchase Order. The Purchasing department department. Accounts Payable also prepares a
prepares a purchase order for each vendor and cash disbursements voucher and posts it in the
sends copies to Inventory Control, Accounts voucher register.
Payable, Receiving (blind copy), and the vendor. The General Ledger Department:
o posts from the accounts payable journal
Valid Vendor Files. Supplied by the inventory
voucher to the general ledger
control function along with much of the routine o reconciles the inventory amount with the
ordering information that the purchasing account summary received from inventory
control
department needs directly from the inventory to
make the purchasing process efficient
Manual Cash Disbursement System
III. RECEIVE GOODS Periodically, usually daily, Accounts Payable
Upon receipt of the goods, the Receiving searches the open vouchers payable file for
Department counts and inspects the goods. items with payments due:
o One of the purposes of the blind copy of the o AP sends the voucher and supporting
purchase order is to force the workers to documents to Cash Disbursements
count the goods. o AP updates the accounts payable
Receiving Report. Prepared by the receiving subsidiary ledger
clerk pagtapos ng physical count and inspection.
The Cash Disbursements department:
Naglalaman ng quantity and condition ng
1. prepares the check
inventories Sends copies to the raw materials
2. records the information in a check register COMPUTER-BASED Expenditure Applications—
(cash disbursements journal) Purchases
3. returns paid vouchers to accounts payable,
Incorporates a data processing department which
mails the check to the supplier
4. sends a journal voucher to General Ledger performs many of the routine accounting tasks
Purchasing - a computer program
The General Ledger department receives: identifies inventory requirements and can
1. the journal voucher from cash disbursements use one of the following methods for
2. a summary of the accounts payable authorizing and ordering inventories
subsidiary ledger from Accounts Payable o the system prepares the POs and sends
The journal voucher is used to update the them to the Purchasing department for
review, signing, and distributing
general ledger.
o the system distributes the POs directly
The accounts payable control account is to the vendors and internal users,
reconciled with the subsidiary summary. bypassing the Purchasing department
o the system uses EDI and electronically
places the order
The Expenditure Cycle
The time lag splits the expenditure transaction
Other tasks performed by the computer:
cycle into two phases:
o Updates the inventory subsidiary file
o physical phase (purchasing cycle) from the receiving report and calculates
o financial phase (cash disbursements) batch totals for the general ledger
update procedure and then closes the
corresponding records in the open PO
file to the closed PO file
o A program validates the voucher
records against the valid vendor file,
adds them to the voucher register, and
prepares batch totals for posting to the
general ledger
o the system scans for vouchers currently
due
o prints checks for these vouchers
o records these checks in the check
register
o batch totals are prepared for the
general ledger update procedure
Levels of Automating and Re-Engineering Ordering
The Purchase Requisition. A need for an item starts the
Computer generates purchase requisition
expenditure cycle Purchase department manually generates
Manual: to initiate a credit purchase, someone in purchase order
Computer generates purchase order (no P.R.
the organization recognizes a need for a good or
needed)
service; an authorized person requests the good Not sent until manually reviewed
or service using a purchase requisition form. Computer-generated P.O. is automatically sent
Computerized: to initiate a credit purchase,
someone in the organization recognizes a need
for a good or service; an authorized person
requests the good or service using a terminal and
a purchase requisition screen.
INSPECTION OF ASSETS
packing slip - containing quantity information that could be
used to circumvent the inspection
*A supervisor should take custody of the packing slip while
receiving clerks count and inspect the goods
4. Accounting Records
To maintain an audit trail adequate for tracing a
transaction from its source document to the
financial statements.
The expenditure cycle employs the following
EXPENDITURE CYCLE CONTROLS accounting records:
1. Transaction Authorization o AP subsidiary ledger
o voucher register
PURCHASES SUBSYSTEM
o check register
o Unauthorized purchasing can result in o general ledger
excessive inventory levels for some 5. Access Controls
items DIRECT ACCESS. Direct access controls include
CASH DISBURSEMENTS SUBSYSTEM
locks, alarms, and restricted access to areas that
o A cash disbursements journal (check
contain inventories and cash.
register) containing the voucher number
authorizing each check provides an INDIRECT ACCESS. A firm must limit access to
audit trail for verifying the authenticity of documents that control its physical assets.
each check written.
6. Independent Verification
2. Segregation of Duties
Independent Verification by Accounts Payable
Segregation of Inventory Control from the
o Purchase requisitions, purchase orders,
Warehouse
receiving reports, and suppliers’ invoices
o Within the purchases subsystem, the must be checked and verified by Accounts
primary physical asset is inventory Payable.
o Inventory control keeps the detailed Independent Verification by the General Ledger
records of the asset, while the
Department
warehouse has custody
Segregation of the General Ledger and o the total obligations recorded equal the total
inventories received
Acc. payable from Cash Disbursements.
o the total reductions in accounts payable
o The asset subject to exposure in the equal the total disbursements of cash
cash disbursements subsystem is cash
REENGINEERING THE PURCHASES/CASH
3. Supervision
DISBURSEMENTS SYSTEM
In the expenditure cycle, the receiving
department is the area that most benefits CONTROL IMPLICATIONS. The Automated System
from supervision
Close supervision here reduces the chances 1. IMPROVED INVENTORY CONTROL
of two types of exposure: provide management with adequate summary
reports about inventory purchases, inventory
(1) failure to properly inspect the assets turnover, spoilage, and slow-moving items
and 2. BETTER CASH MANAGEMENT
(2) the theft of assets set a materiality threshold for check writing
3. TIME LAG
When sales clerks do not know the current
status of inventory, sales may be lost.
4. PURCHASING BOTTLENECK
In this automated system, the purchasing
department is directly involved in all
purchase decisions. For many firms this
creates additional work, which extends the
time lag in the ordering process.
5. EXCESSIVE PAPER DOCUMENTS.
The Reengineered System - improvements in this
Reengineered System are that
a. it uses real-time procedures and direct
access files to shorten the lag time in record
keeping
b. it eliminates routine clerical procedures by
distributing terminals to user areas
c. it achieves a significant reduction in paper
documents by using digital communications
between departments and by digitally storing
records.
*control implications of The Reengineered System
SEGREGATION OF DUTIES
system removes the physical separation
between authorization and transaction
processing
ACCOUNTING RECORDS AND ACCESS
CONTROLS
Advanced systems maintain accounting
records on digital storage media, with
little or no hard-copy backup
You might also like
- The Corporation Code Reviewer PDFDocument28 pagesThe Corporation Code Reviewer PDFJaja Ordinario Quiachon-Abarca89% (38)
- The Corporation Code Reviewer PDFDocument28 pagesThe Corporation Code Reviewer PDFJaja Ordinario Quiachon-Abarca89% (38)
- Sales (De Leon)Document737 pagesSales (De Leon)Bj Carido100% (7)
- Sales (De Leon)Document737 pagesSales (De Leon)Bj Carido100% (7)
- Case Carolina-Wilderness-Outfitters-Case-Study PDFDocument8 pagesCase Carolina-Wilderness-Outfitters-Case-Study PDFMira miguelito50% (2)
- Auditing and Assurance Principles Pre-Test ReviewDocument9 pagesAuditing and Assurance Principles Pre-Test ReviewKryzzel Anne JonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Exercises DeductionsDocument11 pagesChapter Exercises DeductionsShaine KeefeNo ratings yet
- 5.a in The Case That The AI Were To Have Made The Entries Themselves, It Would Ruin Their Function andDocument2 pages5.a in The Case That The AI Were To Have Made The Entries Themselves, It Would Ruin Their Function andAngeloNo ratings yet
- Heagy and Lehmann Accounting Information SystemDocument53 pagesHeagy and Lehmann Accounting Information SystemVal Mercury Faburada100% (1)
- Guzrev Revised Corporation Code Reviewer 2019Document6 pagesGuzrev Revised Corporation Code Reviewer 2019JehannahBarat100% (4)
- (Problems) - Audit of InventoriesDocument22 pages(Problems) - Audit of Inventoriesapatos40% (5)
- 2015-08-24 CapTrade Draft Response To Gulf Airlines CommentsDocument96 pages2015-08-24 CapTrade Draft Response To Gulf Airlines CommentscaptradeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Expenditure Cycle PDFDocument19 pagesLesson 4 Expenditure Cycle PDFJoshua JunsayNo ratings yet
- Ans To Exercises Stice Chap 1 and Hall Chap 1234 5 11 All ProblemsDocument188 pagesAns To Exercises Stice Chap 1 and Hall Chap 1234 5 11 All ProblemsLouise GazaNo ratings yet
- Audit of LiabsDocument2 pagesAudit of LiabsRommel Royce CadapanNo ratings yet
- Accounting For LaborDocument43 pagesAccounting For LaborAmy Spencer100% (1)
- Accounting For Branches and Combined FSDocument112 pagesAccounting For Branches and Combined FSyuaningtyasnvNo ratings yet
- Nfjpia Nmbe Far 2017 AnsDocument9 pagesNfjpia Nmbe Far 2017 AnsSamieeNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Expenditure CycleDocument1 pageQuestionnaire Expenditure Cycleleodenin tulangNo ratings yet
- Quiz I (Chapters 1 and 2Document5 pagesQuiz I (Chapters 1 and 2govt2No ratings yet
- CMA2011 CatalogDocument5 pagesCMA2011 CatalogDaryl DizonNo ratings yet
- Colegio de La Purisima Concepcion: School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas CityDocument5 pagesColegio de La Purisima Concepcion: School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas CityJhomel Domingo GalvezNo ratings yet
- Heats Corporation Current and Noncurrent LiabilitiesDocument1 pageHeats Corporation Current and Noncurrent LiabilitiesjhobsNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub Problems Solving Masdocx PDFDocument6 pagesEdoc - Pub Problems Solving Masdocx PDFReznakNo ratings yet
- 05GeneralInternalControl NotesDocument5 pages05GeneralInternalControl Notesjhaeus enajNo ratings yet
- T 01 PartnershipsDocument5 pagesT 01 PartnershipsCPMNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 1Document1 pageAssignment 7 1Eilen Joyce BisnarNo ratings yet
- Leocario, Melvette Ais TransactionsDocument11 pagesLeocario, Melvette Ais TransactionsMarion LeocarioNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 QuizDocument2 pagesUnit 7 QuizKimberly A AlanizNo ratings yet
- BAFINAR Quiz 6 R FinalDocument4 pagesBAFINAR Quiz 6 R FinalJemNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: SolutionDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: SolutionChris Jay LatibanNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Araneta UniversityDocument7 pagesDe La Salle Araneta UniversityBryent GawNo ratings yet
- Requirements:: Intermediate Accounting 3Document7 pagesRequirements:: Intermediate Accounting 3happy240823No ratings yet
- MQ1 - Topics FAR.2901 To 2915.Document7 pagesMQ1 - Topics FAR.2901 To 2915.Waleed MustafaNo ratings yet
- IT-Audit Team2Document1 pageIT-Audit Team2Von Andrei MedinaNo ratings yet
- Tina and KimDocument3 pagesTina and KimAngelli LamiqueNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 7Document2 pagesAIS Chapter 7Rosana CabuslayNo ratings yet
- Accounting Research EssayDocument4 pagesAccounting Research EssayInsatiable LifeNo ratings yet
- ACSTRAN - Realization and LiquidationDocument4 pagesACSTRAN - Realization and LiquidationDheine MaderazoNo ratings yet
- Partnership Dissolution ProblemsDocument2 pagesPartnership Dissolution ProblemsAilene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Modified Opinion, Emphasis of Matter Paragraph or Other Matter Paragraph in The Auditor's Report On The Entity's Complete Set of Financial StatementsDocument29 pagesModified Opinion, Emphasis of Matter Paragraph or Other Matter Paragraph in The Auditor's Report On The Entity's Complete Set of Financial Statementsfaye anneNo ratings yet
- ACC 211 Review AssignmentDocument5 pagesACC 211 Review Assignmentglrosaaa cNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - Corp Liqui and Installment SalesDocument8 pagesQuiz 2 - Corp Liqui and Installment SalesKenneth Christian WilburNo ratings yet
- Problem 3 5 6 Special TransactionDocument5 pagesProblem 3 5 6 Special TransactionBabyann BallaNo ratings yet
- Auditing 1 Final ExamDocument8 pagesAuditing 1 Final ExamEdemson NavalesNo ratings yet
- Stock Edited PDFDocument29 pagesStock Edited PDFCzarina PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Sales Chapter 13 Part II REPORTDocument50 pagesSales Chapter 13 Part II REPORTJeane Mae BooNo ratings yet
- Acc 118 Week 4 ModuleDocument10 pagesAcc 118 Week 4 ModuleChristine Joy SonioNo ratings yet
- Final Output in AudciseDocument4 pagesFinal Output in AudciseKean Brean GallosNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document7 pagesChap 4Christine Joy OriginalNo ratings yet
- Additional Data For The Period Were ProvidedDocument3 pagesAdditional Data For The Period Were Providedmoncarla lagon100% (1)
- Solution Manual Cornerstones of ManageriDocument12 pagesSolution Manual Cornerstones of ManageriZeenaNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities and ProvisionsDocument12 pagesCurrent Liabilities and ProvisionsRinkashizu TokimimotakuNo ratings yet
- P100,000 ÷ P1,000,000 = 10% Responsibility AccountingDocument3 pagesP100,000 ÷ P1,000,000 = 10% Responsibility AccountingKath LeynesNo ratings yet
- Ia FifoDocument5 pagesIa FifoNadine SofiaNo ratings yet
- Responsibility Accounting Concepts and CalculationsDocument5 pagesResponsibility Accounting Concepts and CalculationsRenNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other EntitiesDocument38 pagesCH 01 Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other Entitiesosggggg67% (3)
- CHP 7Document3 pagesCHP 7rio octavianus yapieterNo ratings yet
- Ict 2 Finals Quiz 1Document2 pagesIct 2 Finals Quiz 1Dmzjmb SaadNo ratings yet
- CH 19 & 20 Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesCH 19 & 20 Practice QuestionsNCTNo ratings yet
- QUizzer 4 - Overall With AnswerDocument20 pagesQUizzer 4 - Overall With AnswerJan Elaine CalderonNo ratings yet
- Straight ProblemsDocument1 pageStraight ProblemsMaybelle100% (1)
- Ais Final ReviewerDocument3 pagesAis Final ReviewerIexenne FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Internal Controls Weaknesses in Expenditure CycleDocument3 pagesInternal Controls Weaknesses in Expenditure CyclePrecious Anne CantarosNo ratings yet
- Expenditure Cycle DatabaseDocument11 pagesExpenditure Cycle DatabaseSophia Marie BesorioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 5Document14 pagesReviewer 5Cyrene CruzNo ratings yet
- Expenditure Cycle NoteDocument2 pagesExpenditure Cycle NoteZara Jane DinhayanNo ratings yet
- Ra 8799 PDFDocument55 pagesRa 8799 PDFpretityn19No ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 1405Document27 pagesRepublic Act No. 1405Anne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Ra 8799 PDFDocument55 pagesRa 8799 PDFpretityn19No ratings yet
- Accounting Information System (Chapter 12)Document4 pagesAccounting Information System (Chapter 12)Rose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Taxation General Principles of TaxationDocument14 pagesGeneral Principles of Taxation General Principles of TaxationAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Law On Banking TransactionsDocument9 pagesLaw On Banking TransactionsAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) SystemsDocument2 pagesChapter 11 - Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) SystemsRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Quasi Contracts Articles Civil Code of The Phil PDFDocument6 pagesQuasi Contracts Articles Civil Code of The Phil PDFAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Law On Banking TransactionsDocument9 pagesLaw On Banking TransactionsAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AIS PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 1 AIS PDFRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Managing the SDLCDocument1 pageManaging the SDLCRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Law On Banking TransactionsDocument9 pagesLaw On Banking TransactionsAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Ra 8799 PDFDocument55 pagesRa 8799 PDFpretityn19No ratings yet
- SEC 8799 ExplainedDocument57 pagesSEC 8799 ExplainedBeth Diaz Laurente100% (1)
- Chapter 2 AISDocument3 pagesChapter 2 AISRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AISDocument3 pagesChapter 6 AISAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The Conversion Cycle: Batch Processing SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 7 The Conversion Cycle: Batch Processing SystemAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- ch10 PDFDocument5 pagesch10 PDFmaeleneNo ratings yet
- Strat Chapter 7 PDFDocument47 pagesStrat Chapter 7 PDFAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Revenue CycleDocument6 pagesChapter 4 The Revenue CycleRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The Conversion Cycle: Batch Processing SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 7 The Conversion Cycle: Batch Processing SystemAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Hu Jintao pro-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesHu Jintao pro-WPS OfficeAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document2 pagesLesson 4Anne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- A Twisty Tales: (Hair Braiding)Document14 pagesA Twisty Tales: (Hair Braiding)Anne Rose Encina0% (1)
- Guide Sa English 10Document4 pagesGuide Sa English 10Anne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Expense ManagementDocument4 pagesExpense Managementdemiss gebrieNo ratings yet
- Nestle Finance International LTD Fullyear Financial Report 2021 enDocument37 pagesNestle Finance International LTD Fullyear Financial Report 2021 enT.k.e.dNo ratings yet
- OJT Case Study 2017 VVCDocument32 pagesOJT Case Study 2017 VVCRyan Joseph DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Veritas Partner Force Distribution Program GuideDocument30 pagesVeritas Partner Force Distribution Program GuideHebaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Terminology GuideDocument4 pagesAccounting Terminology GuideFaye BelenNo ratings yet
- Blake MorrisonDocument4 pagesBlake MorrisonAnonymous jF8rU5No ratings yet
- Introduction - Fusion Accounting Hub FundamentalsDocument50 pagesIntroduction - Fusion Accounting Hub FundamentalsRai Prashant Kumar Rai83% (6)
- CFAP SYLLABUS SUMMER 2023Document31 pagesCFAP SYLLABUS SUMMER 2023shajar-abbasNo ratings yet
- Example Engagement Letter PDFDocument3 pagesExample Engagement Letter PDFCharmaigne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Phar MoreDocument25 pagesPhar MoreAlexandrei OrioNo ratings yet
- 38 Executive SummaryDocument2 pages38 Executive SummaryJill SandersNo ratings yet
- Fraud Prevention Strategies ArticleDocument18 pagesFraud Prevention Strategies ArticleTsitsi NhekairoNo ratings yet
- Osh PlanDocument11 pagesOsh PlanjookapleeNo ratings yet
- Singapore Salary BankingDocument5 pagesSingapore Salary BankingMartin JpNo ratings yet
- Data Screening - StatWikiDocument6 pagesData Screening - StatWikiDaniel JCNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-5Document49 pagesChap 1-5Angel RubiosNo ratings yet
- Worldcom FraudDocument20 pagesWorldcom FraudAfdal SyarifNo ratings yet
- Invitation Government 2022aprilwebinarDocument2 pagesInvitation Government 2022aprilwebinarYom KiroNo ratings yet
- CAclubindia News - CSR - Auditors' Responsibility To Qualify in Audit ReportDocument2 pagesCAclubindia News - CSR - Auditors' Responsibility To Qualify in Audit ReportMahaveer DhelariyaNo ratings yet
- Activities/ Assessment:: Sky's The Limit: The China Sky Saga Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesActivities/ Assessment:: Sky's The Limit: The China Sky Saga Discussion QuestionsANH NGUYEN DANG QUENo ratings yet
- GST Returns: BackgroundDocument3 pagesGST Returns: BackgroundPrakash PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Accume Partners - Compliance Monthly - July 2014Document3 pagesAccume Partners - Compliance Monthly - July 2014Accume PartnersNo ratings yet
- Supplier-Tutorial Nadcap PDFDocument70 pagesSupplier-Tutorial Nadcap PDFRangaNo ratings yet
- PUP Citizens Charter October 2016 PDFDocument247 pagesPUP Citizens Charter October 2016 PDFJoseph Masangkay Lardizabal0% (1)
- CAAP Citizens Charter 2022 1st EditionDocument370 pagesCAAP Citizens Charter 2022 1st EditionCAD DEPARTMENTNo ratings yet
- LM300Document8 pagesLM300Sharma GokhoolNo ratings yet
- Professional Standards Learning Objectives: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2007Document15 pagesProfessional Standards Learning Objectives: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2007ZeabMariaNo ratings yet
- Tax - AssignmentDocument29 pagesTax - Assignmentjai_thakker7659No ratings yet