Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tachypnea Medical Intervention
Tachypnea Medical Intervention
Uploaded by
Corinne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Tachypnea Medical Intervention.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesTachypnea Medical Intervention
Tachypnea Medical Intervention
Uploaded by
CorinneCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
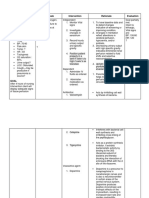
Medical Intervention
Drug Classification Indication Action Dosage Nursing Implication
Ampicillin Antibiotics Used for 48 hours after Destroys bacteria by 50 mg/kg IV Watch for signs and
birth, until sepsis has inhibiting bacterial cell-wall over 30 symptoms of
been ruled out. synthesis during microbial minutes hypersensitivity reaction.
Broad spectrum multiplication Frequently measure the
antibiotic useful against patient’s temperature and
group B streptococcus, check for signs and
Listeria monocytogenes, symptoms of superinfection,
and susceptible E. coli especially oral or rectal
species candidiasis.
Monitor for bleeding
tendency or hemorrhage.
Gentamicin Antibiotics Antibiotics are often Destroys gram-negative 5 mg/kg IM Watch for signs and
used for 48 hours after bacteria by irreversibly q24hr symptoms of
birth until sepsis has binding to 30S subunit of hypersensitivity reactions.
been ruled out. bacterial ribosomes and Monitor CBC, BUN,
Proven neonatal sepsis blocking protein synthesis, creatinine level, and
(pneumonia, resulting in a misreading of creatinine clearance.
septicaemia, etc), with genetic code and separation
bacteria known to be of ribosomes from
sensitive messenger RNA
Other Intervention
Procedure Indication Nursing Responsibility
Oxygen Therapy Oxygen support may be required if pulse 1. Maintain the neonate’s clear airway and suction as
Oxygen Hood oximetry or ABG suggest hypoxemia per protocol.
Continuous Positive Babies with respiratory problems may 2. Administer oxygen to maintain SpO2 as per standing
Airway Pressure need to breathe increased amounts of orders. Alarm limits are set accordingly.
(CPAP) oxygen to get normal levels of oxygen in
3. Change SpO2 lead position every four hours.
4. Check oxygen level and document
(including the amount of supplemental oxygen and SpO2
levels):
at nursing handover (beginning of each shift)
hourly if the baby on CPAP or ventilated
2 - 3 hourly if baby receiving LF O2 / incubator O2
their blood. Oxygen therapy provides 5. Notify medical staff if a baby’s oxygen requirement
babies with extra oxygen. increases consistently by 10% or more.
6. Calibrate oxygen analyzer at the beginning of each
shift,
7. The oxygen analyzer is calibrated to:
air if baby receiving <60% O2
100% O2 if baby receiving >60% O2
8. Provide humidification appropriate to oxygen
delivery at all times
Regular analysis of ABG levels in neonates 1. Define and describe the blood test to the mother
with respiratory problems until signs of 2. State the purpose and explain the procedure
respiratory distress have resolved. 3. Monitor patient’s vital signs
Blood Test (ABG) (Arterial blood gases give an estimate of
4. Assess the patient’s physical condition
oxygen and carbon dioxide content, which
5. Document and report the findings to the patient’s
can assist in determining the pH as well as
metabolic abnormalities.) doctor.
1. Initiate fluid therapy at 60-80 ml/kg/d with D10W
2. Observe the intravenous site closely for extravasation
Larger preterm and sick term newborns in (leakage).
Intravenous Nutrition whom it is anticipated that full enteral 3. Measure urine output.
feedings will be delayed longer than 3-5 days. 4. Palpate and inspect the site for puffiness, redness,
blanching, and skin temperature.
5. Assess IV site hourly (at a minimum), and document.
Enteral Feeding Newborn with a high respiratory rate for 1. Ensure the tube remains in the correct position.
Check before first feed on each shift with pH strips.
2. Visually check the position of the tube before each
feed. If in doubt aspirate to check position.
3. Aspirate routinely 6 hourly or PRN as ordered or if
more than a few hours. uncertain of placement.
4. Observe for abdominal distension.
(This will help give the baby more nutrition
5. Ensure the infant has their tubes on free drainage
without the risk of breathing in food from the
mouth into the lungs.) with the free end of the tube draining into a
specimen pot.
6. Replace tubes every 2 weeks. (note if the gastric tube
is not to be removed)
7. Document date, time, and depth of insertion on
observation chart and care map.
References:
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn. (n.d.). Retrieved September 29, 2020, from https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?
id=transient-tachypnea-of-the-newborn-90-P02420
Oxygen Therapy- Nursing Responsibilities. (n.d.). Retrieved September 29, 2020, from
http://www.adhb.govt.nz/newborn/Guidelines/Respiratory/Oxygen/OxygenTherapyNursingResponsibilities.htm
You might also like
- Baby 411Document1,101 pagesBaby 411Raycharles100% (1)
- New Approach On The Protocol of Babesiossis in Dog'sDocument2 pagesNew Approach On The Protocol of Babesiossis in Dog'sDocNo ratings yet
- 09 2019 Pediatric Neonatology LAYOUT R2Document50 pages09 2019 Pediatric Neonatology LAYOUT R2khalid alharbiNo ratings yet
- PICU ProtocolDocument13 pagesPICU ProtocolRania SaadNo ratings yet
- Prado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Document52 pagesPrado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Catherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Case Study of AppendicitisDocument9 pagesCase Study of AppendicitisJustin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Intervention Rationale EvaluationHerald Jones LamirezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 9 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationMariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- Prince NCPDocument9 pagesPrince NCPALVARADO, KRISTINE JOYNo ratings yet
- Human Clinical TrialDocument1 pageHuman Clinical TrialWobik HopeNo ratings yet
- Blosensors: Applications For Dairy Food Industry: Edward R. Richter Silliker Laboratories Columbus, OH 43212Document4 pagesBlosensors: Applications For Dairy Food Industry: Edward R. Richter Silliker Laboratories Columbus, OH 43212ARATHI PMPMNo ratings yet
- Rationale The Presence ofDocument24 pagesRationale The Presence ofPia CadornaNo ratings yet
- NCP PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNCP PneumoniaMerliah LofrancoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianeDocument13 pagesPneumonia: Romero, Pamela Sanchez, DianePam RomeroNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1323893022000120 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S1323893022000120 MainValeria BoomNo ratings yet
- Your Big IdeaDocument12 pagesYour Big Ideaapi-380169571No ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan Asuhan Keperawatan Bayi Dengan BBLR Di Ruang Cempaka 1 Neonatus Rsup SanglahDocument20 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Asuhan Keperawatan Bayi Dengan BBLR Di Ruang Cempaka 1 Neonatus Rsup SanglahSutariniNo ratings yet
- 10 Communicable Disease Control Program IDocument9 pages10 Communicable Disease Control Program IJennica JaoNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Urinary Tract InfectionDocument21 pagesCase Study: Urinary Tract InfectionRania Sh AzzehNo ratings yet
- Abg Demo BDocument6 pagesAbg Demo Bsaai saaiNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock: Supervisor: DR Ali Haedar, Sp. EM FAHA Dinisa Novaurahmah Nanin Aprilia PutriDocument42 pagesSeptic Shock: Supervisor: DR Ali Haedar, Sp. EM FAHA Dinisa Novaurahmah Nanin Aprilia PutriMutia Larasati AlbarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG: STGDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STG: STGLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Applican F Enzymes N Diary IndDocument4 pagesApplican F Enzymes N Diary Indrajeshbabu2007No ratings yet
- Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Fertility: No Impact On Ovarian Reserve in Premenopausal WomenDocument5 pagesAntiphospholipid Antibodies and Fertility: No Impact On Ovarian Reserve in Premenopausal WomenForuz53 ForuzNo ratings yet
- Faraj Medical Case Study Mksl5 1Document30 pagesFaraj Medical Case Study Mksl5 1MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 2 Simpo - Amnion - Sepsis Purpuralis Fix1Document29 pages2 Simpo - Amnion - Sepsis Purpuralis Fix1Rezky Faried HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1 Acid Fast Staining (Exercise 9)Document1 pageLab 3.1 Acid Fast Staining (Exercise 9)Miguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Status AsthmaticusDocument6 pagesStatus AsthmaticusMae Azores100% (1)
- Rot 2 Darunday Drug Study Als 5Document17 pagesRot 2 Darunday Drug Study Als 5Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Final Protocol Full and Final (72030)Document13 pagesFinal Protocol Full and Final (72030)Nido MalghaniNo ratings yet
- FMPCR Art 42286-10Document4 pagesFMPCR Art 42286-10Sebastian Jaén Vinueza SoteloNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis G3Document12 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis G3Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For Adults 2018 PDFDocument58 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For Adults 2018 PDFAhmad RizqiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dian Kusumaningrum - PRESENTASI JCCA-ANTIBIOTIC DOSING IN CRITICALLY ILLDocument31 pagesDr. Dian Kusumaningrum - PRESENTASI JCCA-ANTIBIOTIC DOSING IN CRITICALLY ILLRestu TriwulandaniNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientDocument4 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco100% (1)
- BCB 411 - Lec 5Document10 pagesBCB 411 - Lec 5NaushinKhanNo ratings yet
- Oleh: DR - Octariany, M.ked (Paru), SP.PDocument15 pagesOleh: DR - Octariany, M.ked (Paru), SP.PbennyrolandnababanNo ratings yet
- Day 2 BSV MDR Infections - HensonDocument37 pagesDay 2 BSV MDR Infections - HensonRye CalderonNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Therapy of Streptococcal Pneumonia in A CatDocument3 pagesCase Report: Therapy of Streptococcal Pneumonia in A CatMuhammad Fernanda DanuartaNo ratings yet
- Askep Ri September WulandariDocument9 pagesAskep Ri September Wulandariwulandari ketutNo ratings yet
- Rot 3 - Darunday SicDocument9 pagesRot 3 - Darunday SicEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Paper-1 QBDocument38 pagesMicrobiology Paper-1 QBPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- SKILL STATION Management of Critically Ill Patient With Septic Shock Provider GuideDocument27 pagesSKILL STATION Management of Critically Ill Patient With Septic Shock Provider GuidesrinidhiNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. (MED.) : AffectDocument3 pagesB.Sc. (MED.) : AffectEdemson NavalesNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Concept MapDocument1 pagePneumonia Concept MapsekwetNo ratings yet
- Ivermectin Potential Candidate For The Treatment of Covid 19Document3 pagesIvermectin Potential Candidate For The Treatment of Covid 19glenwell sentosaNo ratings yet
- Medical Mycology Case ReportsDocument3 pagesMedical Mycology Case ReportsReza FaisalNo ratings yet
- Vibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter, and Campylobacter-Like SpeciesDocument19 pagesVibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter, and Campylobacter-Like SpeciesPrinces MaeNo ratings yet
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic RiDocument4 pagesSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objective: Bt-38.5 C HR - 114 BPM BP - 110/70 MMHG RR - 28 BPM Diaphoretic Ristrawberrykate26No ratings yet
- RHU Case Analysis - Patient XYZDocument17 pagesRHU Case Analysis - Patient XYZaasimon2466cabNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Study SheetDocument50 pagesBacteriology Study Sheetvishal_life27100% (5)
- Pediatric Tuberculosis: Specimen Collection For Analysis Sputum Specimens - Used in OlderDocument3 pagesPediatric Tuberculosis: Specimen Collection For Analysis Sputum Specimens - Used in OldernadiahNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of PlagueDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of PlagueAhmad Zulhilmi YusofNo ratings yet
- Protracted Bacterial BronchitisDocument7 pagesProtracted Bacterial BronchitisDr. Sarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics - A Rational ApproachDocument49 pagesAntibiotics - A Rational ApproachMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Name: Cyrill Alexandria G. Tolentino Drug Study Date: Level & Section: BSN 2BDocument1 pageName: Cyrill Alexandria G. Tolentino Drug Study Date: Level & Section: BSN 2BCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- The Aga Khan University Hospital Pediatric SCU Course Final Exam Test Paper Name: - UnitDocument5 pagesThe Aga Khan University Hospital Pediatric SCU Course Final Exam Test Paper Name: - UnitUmar RashidNo ratings yet
- Kyle 2004Document24 pagesKyle 2004Sam Steven Hernandez JañaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient: Strategies for ManagementFrom EverandPulmonary Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient: Strategies for ManagementCarlos AgustiNo ratings yet
- Ethico Moral Case ActivityDocument2 pagesEthico Moral Case ActivityCorinneNo ratings yet
- Gerontologic Health Promotion ActivityDocument3 pagesGerontologic Health Promotion ActivityCorinne50% (2)
- Subjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: "Sumikip Ang Dibdib Ko at Hindi Ako Makahinga NG Maayos" As IndependentCorinneNo ratings yet
- Health Statistics and Epidemiology QuestionsDocument2 pagesHealth Statistics and Epidemiology QuestionsCorinneNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit QuestionsDocument6 pagesFluid Volume Deficit QuestionsCorinneNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure and Colloid Osmotic Pressure QuestionsDocument2 pagesHydrostatic Pressure and Colloid Osmotic Pressure QuestionsCorinneNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesMuscular SystemCorinneNo ratings yet
- Death Trauma ViolenceDocument14 pagesDeath Trauma Violencejoylizz14No ratings yet
- Immunization CTP March 2021 4-Per-PageDocument71 pagesImmunization CTP March 2021 4-Per-PageAssal Al JanabiNo ratings yet
- Who Ban Covid 19Document3 pagesWho Ban Covid 19xakilNo ratings yet
- The Treatment of Small-Pox by Application of Tincture of IodineDocument2 pagesThe Treatment of Small-Pox by Application of Tincture of IodinefrankNo ratings yet
- (19330693 - Journal of Neurosurgery) Evaluation of Surgical Treatment For Neuropathic Pain From Neuroma in Patients With Injured Peripheral NervesDocument6 pages(19330693 - Journal of Neurosurgery) Evaluation of Surgical Treatment For Neuropathic Pain From Neuroma in Patients With Injured Peripheral NervesGeorgios StathisNo ratings yet
- ASM 345 - Disease and Human EvolutionDocument53 pagesASM 345 - Disease and Human EvolutionCynthia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Dispatch Eedition 9-20-20Document20 pagesCommercial Dispatch Eedition 9-20-20The DispatchNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Stenosis: Ehud Arbit, MD and Susan Pannullo, MDDocument7 pagesLumbar Stenosis: Ehud Arbit, MD and Susan Pannullo, MDBudhiNo ratings yet
- 2022 1 Sim Enem-03-04 Linguag e Cien Humanas Resolvido-3-26Document34 pages2022 1 Sim Enem-03-04 Linguag e Cien Humanas Resolvido-3-26André FilhoNo ratings yet
- Micro Levinson QuestionsDocument30 pagesMicro Levinson QuestionsadehkordiNo ratings yet
- Mouhamadou Lamine Sarr CPC 1B MR Brunson Peace 2 Semester English TestDocument3 pagesMouhamadou Lamine Sarr CPC 1B MR Brunson Peace 2 Semester English TestLamine SarrNo ratings yet
- SPC - Ma130 00201Document6 pagesSPC - Ma130 00201Cassia FistulaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Mindfulness Meditation On Serum Cortisol of Medical StudentsDocument7 pagesEffects of Mindfulness Meditation On Serum Cortisol of Medical StudentsPatriciaFarcaşNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument2 pagesMedical TerminologyChrystel Mae PañaresNo ratings yet
- Elective II FinalsDocument15 pagesElective II FinalsAljon Dofeliz LlamasNo ratings yet
- Chrysalis Crack BookletDocument9 pagesChrysalis Crack BookletHhhNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment: Sequence of ExamDocument7 pagesAbdominal Assessment: Sequence of ExamCristine SyNo ratings yet
- Post-Test For Unit 8: Biological Periodontal TherapyDocument6 pagesPost-Test For Unit 8: Biological Periodontal TherapyDavidNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery in Feline Epilepsy Including Clinicopatholo - 2022 - The VeterinarDocument10 pagesNeurosurgery in Feline Epilepsy Including Clinicopatholo - 2022 - The VeterinarGNo ratings yet
- Project On MSWDocument88 pagesProject On MSWSukhdev SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Light From Computer Monitors On MelaDocument7 pagesThe Impact of Light From Computer Monitors On MelaYosefNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals On Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Divya Mehrotra Download 2024 Full ChapterDocument47 pagesFundamentals On Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Divya Mehrotra Download 2024 Full Chapterantoinette.doil874100% (9)
- Thesis Protocol For M.S. Degree (Ophthalmology)Document31 pagesThesis Protocol For M.S. Degree (Ophthalmology)zebaNo ratings yet
- Furin Cleavage Virus Strain 10032020Document38 pagesFurin Cleavage Virus Strain 10032020Ravishankar PolisettyNo ratings yet
- Accidente Ofidico NEJMDocument11 pagesAccidente Ofidico NEJMNicole IriarteNo ratings yet
- Icd-10 Codes For Orthodontics: Introduction - Kirt E. Simmons, DDS, PHDDocument10 pagesIcd-10 Codes For Orthodontics: Introduction - Kirt E. Simmons, DDS, PHDmsk adiwiryaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care Plan and Documentaion of Pharmacotherapy Intervention (MTM)Document67 pagesPharmaceutical Care Plan and Documentaion of Pharmacotherapy Intervention (MTM)CAROL ANN PATITICONo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Head and SwellingDocument41 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Head and Swellingmachine318No ratings yet
- Standard Five Term - II ScienceDocument38 pagesStandard Five Term - II ScienceJigna PatelNo ratings yet