Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Definition: BIOTS: Useful For
Uploaded by
Saad KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Definition: BIOTS: Useful For
Uploaded by
Saad KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Definition: BIOTS
Biotinidase, S
Overview
Useful For
Preferred test for diagnosing biotinidase deficiency
Follow-up testing for certain organic acidurias
Genetics Test Information
Preferred test to rule-out biotinidase deficiency.
Second-tier molecular testing is available, see BTDZ / Biotinidase Deficiency, BTD Full Gene Analysis.
Highlights
Enzymatic testing for the diagnosis of biotinidase deficiency, usually in follow-up to an abnormal newborn screen.
Biotinidase deficiency is treatable with oral biotin supplements.
Individuals who are diagnosed presymptomatically (eg, by newborn screening) and who are treated with biotin
supplementation do not develop the associated clinical features of biotinidase deficiency.
Special Instructions
Informed Consent for Genetic Testing
Biochemical Genetics Patient Information
Informed Consent for Genetic Testing (Spanish)
Method Name
Colorimetric
NY State Available
Yes
Specimen
Specimen Type
Serum
Specimen Required
Collection Container/Tube:
Preferred: Red top
Acceptable: Serum gel
Submission Container/Tube: Plastic vial
Specimen Volume: 1 mL
Collection Instructions: Spin down immediately and remove serum.
Document generated August 7, 2020 at 11:04am CDT Page 1 of 4
Test Definition: BIOTS
Biotinidase, S
Forms
1. New York Clients-Informed consent is required. Document on the request form or electronic order that a copy
is on file. The following documents are available in Special Instructions:
-Informed Consent for Genetic Testing (T576)
-Informed Consent for Genetic Testing-Spanish (T826)
2. Biochemical Genetics Patient Information (T602) in Special Instructions.
3. If not ordering electronically, complete, print, and send an Inborn Errors of Metabolism Test Request (T798) with
the specimen.
Specimen Minimum Volume
0.5 mL
Reject Due To
Gross hemolysis Reject
Gross lipemia OK
Gross icterus OK
Specimen Stability Information
Specimen Type Temperature Time Special Container
Serum Frozen (preferred) 21 days
Refrigerated 5 days
Clinical and Interpretive
Clinical Information
Biotinidase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the biotinidase gene (BTD). Age of
onset and clinical phenotype vary among individuals depending on the amount of residual biotinidase activity.
Profound biotinidase deficiency occurs in approximately 1 in 137,000 live births and partial biotinidase deficiency
occurs in approximately 1 in 110,000 live births, resulting in a combined incidence of about 1 in 61,000. The carrier
frequency for biotinidase deficiency within the general population is about 1 in 120.
Untreated profound biotinidase deficiency typically manifests within the first decade of life as seizures, ataxia,
developmental delay, hypotonia, sensorineural hearing loss, vision problems, skin rash, and alopecia. Partial
biotinidase deficiency is associated with a milder clinical presentation, which may include cutaneous symptoms
without neurologic involvement. Certain organic acidurias, such as holocarboxylase synthase deficiency, isolated
carboxylase synthase deficiency, and 3-methylcrotonylglycinuria, present similarly to biotinidase deficiency. Serum
biotinidase levels can help rule out these disorders.
Treatment with biotin is successful in preventing the clinical features associated with biotinidase deficiency. In
symptomatic patients, treatment will reverse many of the clinical features except developmental delay, vision, and
Document generated August 7, 2020 at 11:04am CDT Page 2 of 4
Test Definition: BIOTS
Biotinidase, S
hearing complications. As a result, biotinidase deficiency is included in most newborn screening programs. This
enables early identification and treatment of presymptomatic patients.
Molecular tests form the basis of confirmatory or carrier testing. When biotinidase enzyme activity is deficient,
sequencing of the entire BTD gene (BTDZ / Biotinidase Deficiency, BTD Full Gene Analysis) allows for detection of
disease-causing mutations in affected patients. Identification of familial mutations allows for testing of at-risk family
members (FMTT / Familial Mutation, Targeted Testing).
While genotype-phenotype correlations are not well established, it appears that certain mutations are associated with
profound biotinidase deficiency, while others are associated with partial deficiency.
Reference Values
3.5-13.8 U/L
Interpretation
The reference range is 3.5 U/L to 13.8 U/L.
Partial deficiencies and carriers may occur at the low end of the reference range.
Values below 3.5 U/L are occasionally seen in specimens from unaffected patients.
Cautions
A diet high in biotin may result in normal clinical presentation even when the biotinidase level is low.
Clinical Reference
1. Zempleni J, Barshop BA, Cordonier EL, et al: Disorders of biotin metabolism. In The Online Metabolic and
Molecular Bases of Inherited Diseases. Edited by D Valle, AL Beaudet, B Vogelstein, et al. New York, McGraw-Hill
Book Company. Accessed February 20, 2018. Available at
http://ommbid.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=971§ionid=62646613
2. Wolf B: Biotinidase Deficiency. In GeneReviews Edited by MP Adam, HH Ardinger, RA Pagon, et al. University of
Washington, Seattle; 1993-2017. Updated 2016 Jun 9. Accessed February 20, 2018. Available at
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1322/
Performance
Method Description
Biotinidase activity is determined colorimetrically by measuring p-aminobenzoate liberation from N-biotinyl-p
-aminobenzoate at 546 nm. Activity is determined from a standard curve of p-aminobenzoic acid. Modified Sigma
substrate is used.(Wolf B, Grier RE, Allen RJ, et al: Biotinidase deficiency: the enzymatic defect in late-onset
carboxylase deficiency. Clin Chim Acta 1983;131:273-281)
PDF Report
No
Day(s) and Time(s) Test Performed
Monday, Thursday; set up at 8 a.m.
Analytic Time
4 days
Document generated August 7, 2020 at 11:04am CDT Page 3 of 4
Test Definition: BIOTS
Biotinidase, S
Maximum Laboratory Time
8 days
Specimen Retention Time
30 days
Performing Laboratory Location
Rochester
Fees and Codes
Fees
Authorized users can sign in to Test Prices for detailed fee information.
Clients without access to Test Prices can contact Customer Service 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Prospective clients should contact their Regional Manager. For assistance, contact Customer Service.
Test Classification
This test was developed and its performance characteristics determined by Mayo Clinic in a manner consistent with
CLIA requirements. This test has not been cleared or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
CPT Code Information
82261
LOINC® Information
Test ID Test Order Name Order LOINC Value
BIOTS Biotinidase, S 1982-8
Result ID Test Result Name Result LOINC Value
50666 Specimen 31208-2
50667 Specimen ID 57723-9
50668 Source 31208-2
50669 Order Date 82785-7
50670 Reason For Referral 42349-1
50671 Method 49549-9
50672 Biotinidase, S 1982-8
50673 Interpretation 59462-2
50674 Amendment 48767-8
50675 Reviewed By 18771-6
50676 Release Date 82772-5
Document generated August 7, 2020 at 11:04am CDT Page 4 of 4
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- Technical Standards and Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Biotinidase DeficiencyDocument7 pagesTechnical Standards and Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Biotinidase DeficiencySaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Absolute Final Biotinidase OptimizationDocument7 pagesAbsolute Final Biotinidase OptimizationSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Methods for Biotherapeutics: Discovery and Development ApplicationsFrom EverandBiophysical Methods for Biotherapeutics: Discovery and Development ApplicationsTapan K. DasNo ratings yet
- Bala Blood Report Ca, Uric, B12, D3Document3 pagesBala Blood Report Ca, Uric, B12, D3BALANo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval PotassiumDocument2 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval PotassiumGangapuram SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Panel: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument4 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Panel: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range Methodgsm2008No ratings yet
- Seema 1Document4 pagesSeema 1reenajanjadiaNo ratings yet
- 1-Liver Function Test - PO3921596584-773 - 230517 - 125136Document4 pages1-Liver Function Test - PO3921596584-773 - 230517 - 125136Moksh GujjarNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Interval MethodDocument2 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Interval MethodBapan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Nisha DeviDocument2 pagesNisha DeviSantan Lal DasNo ratings yet
- S62 - Lpl-Nagpur - 2 Plot No. 7, Ground Floor Hotel Sunny Int Besides Gujrati Samaj Bhavan, Dhantoli Nagpur 440012Document2 pagesS62 - Lpl-Nagpur - 2 Plot No. 7, Ground Floor Hotel Sunny Int Besides Gujrati Samaj Bhavan, Dhantoli Nagpur 440012prachi jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Biotin and Other Interferences in Immunoassays: A Concise GuideFrom EverandBiotin and Other Interferences in Immunoassays: A Concise GuideNo ratings yet
- LFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test NameDocument4 pagesLFT (Liver Function Test) : Biological Reference Results Units Test Namemetepraju0210No ratings yet
- SRL Format 2Document1 pageSRL Format 2haroon012023No ratings yet
- EGAC0401Document5 pagesEGAC0401bhanuprasadbkNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval TSH UltrasensitiveDocument5 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval TSH UltrasensitiveP Nagaraju RajuNo ratings yet
- Blood Tests ReportDocument7 pagesBlood Tests ReportLalith GoudNo ratings yet
- Uric Acid (Ua) Test Name Observed Values Units Biological Reference Intervals Uric Acid 10.5Document1 pageUric Acid (Ua) Test Name Observed Values Units Biological Reference Intervals Uric Acid 10.5seravanakumarNo ratings yet
- Biotinidase Deficiency ProposalDocument7 pagesBiotinidase Deficiency ProposalFaryalBalochNo ratings yet
- Final: Patient Name: Dummy 0002UG999999Document1 pageFinal: Patient Name: Dummy 0002UG999999abhimanyu kumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics BiotinaDocument10 pagesPharmacokinetics BiotinaneofherNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma GlucoseDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucosemasood syedNo ratings yet
- Uric Acid PDFDocument1 pageUric Acid PDFPulkit TalujaNo ratings yet
- Adipose Tissue in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandAdipose Tissue in Health and DiseaseTodd LeffNo ratings yet
- Report 516ce2e4Document6 pagesReport 516ce2e4Samruddhi RathiNo ratings yet
- Parameter Result Unit Biological Ref. Interval: Westergren (Manual)Document2 pagesParameter Result Unit Biological Ref. Interval: Westergren (Manual)Ashish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Report: FinalDocument1 pageDiagnostic Report: FinalAashyNo ratings yet
- Report GNDocument3 pagesReport GNPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)Document2 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)gsm2008No ratings yet
- 370 FullDocument1 page370 FulllorenadelherNo ratings yet
- Patient Profile FormDocument8 pagesPatient Profile FormShaRath KmNo ratings yet
- FTMREPORTDocument1 pageFTMREPORTMAYANK tecnooNo ratings yet
- 1-Frequent Pain Check Profile - PO2526765603-393Document8 pages1-Frequent Pain Check Profile - PO2526765603-393Satyendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ravinder Puri C-1Document14 pagesRavinder Puri C-1TasmiyaNo ratings yet
- Unlq6073 PDFDocument8 pagesUnlq6073 PDFSrinu VijayaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalDocument15 pagesBiochemistry: Investigation Observed Value Unit Biological Reference IntervalAshutoshNo ratings yet
- CpeptideDocument1 pageCpeptiderajanarora72No ratings yet
- Individual Variant Interpretation For Pathogenic MutationDocument3 pagesIndividual Variant Interpretation For Pathogenic MutationSukh SukhiNo ratings yet
- Intended Use: Form Catalog NoDocument6 pagesIntended Use: Form Catalog NoRafika RaraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: 19 Years / FemaleDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: 19 Years / Femalesneha sahaNo ratings yet
- For Success N Access 1022168537 - DBVE8685Document10 pagesFor Success N Access 1022168537 - DBVE8685vanam tejasviNo ratings yet
- Jasveen 2Document2 pagesJasveen 2rababkr23No ratings yet
- Blood TestDocument2 pagesBlood TestAll You NeedNo ratings yet
- Final: Patient Name: Dummy 0002UG999999Document1 pageFinal: Patient Name: Dummy 0002UG999999Sanket GuptaNo ratings yet
- Health ProfileDocument18 pagesHealth ProfileSahil HussainNo ratings yet
- Jinnah Central Lab: Jinnah Hospital & AIMC Lahore, PakistanDocument2 pagesJinnah Central Lab: Jinnah Hospital & AIMC Lahore, Pakistanafshan liaqatNo ratings yet
- HeaderDocument2 pagesHeader22sa010259No ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism (Iem) Summary Report: Sr. No. Test Methodology Result Test TypeDocument2 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism (Iem) Summary Report: Sr. No. Test Methodology Result Test TypeMallikharjunaRao medaNo ratings yet
- Applications of ZymographyDocument25 pagesApplications of ZymographyXênia SoutoNo ratings yet
- Optimasi Teknik Western Blot Untuk Deteksi Ekspresi Protein Tanaman Padi (Oryza Sativa L.)Document11 pagesOptimasi Teknik Western Blot Untuk Deteksi Ekspresi Protein Tanaman Padi (Oryza Sativa L.)Refhany AfidhaNo ratings yet
- WPPW9722Document3 pagesWPPW9722akumar_948771No ratings yet
- LFT ReportDocument3 pagesLFT Reportacer.tsk007No ratings yet
- This Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesDocument1 pageThis Is An Electronic Report & Not: To Be Used For Any Legal PurposesTauseef Taj KianiNo ratings yet
- Patient Name: Kunjamma KUNJF1207544155: FinalDocument5 pagesPatient Name: Kunjamma KUNJF1207544155: FinalPranay BhosaleNo ratings yet
- XIJU5502Document3 pagesXIJU5502Praveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jaswanth Redddy Sappp PDFDocument1 pageJaswanth Redddy Sappp PDFAnonymous VT75a3QNo ratings yet
- File PDFDocument1 pageFile PDFSabari PramanikNo ratings yet
- Pathology 22.04.2020 02.45.42.368Document3 pagesPathology 22.04.2020 02.45.42.368Small WondersNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportPawan MadhesiyaNo ratings yet
- Kit InsertDocument11 pagesKit InsertSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Elisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay: Syed Muhammad Khan Bshons. ZoologyDocument47 pagesElisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay: Syed Muhammad Khan Bshons. ZoologySaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Trace ElementsDocument182 pagesMinerals: Trace ElementsSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- The Aga Khan Hospital and Medical College, Karachi.: ConfidentialDocument1 pageThe Aga Khan Hospital and Medical College, Karachi.: ConfidentialSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- CH205 Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument30 pagesCH205 Atomic Absorption SpectrosSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- MTI (Path) : Medical Training Initiative in PathologyDocument18 pagesMTI (Path) : Medical Training Initiative in PathologySaad KhanNo ratings yet
- eMRCS Pathology 326 MCQsDocument101 pageseMRCS Pathology 326 MCQsSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Documents To Support Your Application: MTI (Path) Medical Training Initiative in PathologyDocument2 pagesDocuments To Support Your Application: MTI (Path) Medical Training Initiative in PathologySaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis C: DR Nosheen ZaidiDocument63 pagesHepatitis C: DR Nosheen ZaidiSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- DR Sarfraz Notes (Contoversial With Explanation)Document16 pagesDR Sarfraz Notes (Contoversial With Explanation)Saad KhanNo ratings yet
- Kaplan: Clinical Chemistry, 5 Edition: Clinical References - Methods of AnalysisDocument9 pagesKaplan: Clinical Chemistry, 5 Edition: Clinical References - Methods of AnalysisSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- FCPS PART 1 Study MaterialDocument1 pageFCPS PART 1 Study MaterialSaad Khan100% (1)
- eMRCS Pathology 326 MCQsDocument101 pageseMRCS Pathology 326 MCQsSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Biotinidase Deficiency QuestionnereDocument1 pageBiotinidase Deficiency QuestionnereSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Biotinidase Assay: Dr. Faryal Husnain Resident Clinical ChemistryDocument22 pagesOptimization of Biotinidase Assay: Dr. Faryal Husnain Resident Clinical ChemistrySaad KhanNo ratings yet
- eMRCS Microbiology 19 QuestionsDocument7 pageseMRCS Microbiology 19 QuestionsSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Excellent Important Pearls of Fcps Part1 Collection of Different Important PointsDocument18 pagesExcellent Important Pearls of Fcps Part1 Collection of Different Important PointsSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal MutationsDocument19 pagesChromosomal MutationsJanet BarcimoNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: AP BiologyDocument28 pagesChromosomal Abnormalities: AP BiologySuzy BaeNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret A KaryotypeDocument2 pagesHow To Interpret A KaryotypeLiberty NguyenNo ratings yet
- Karyotypes and Chromo Disorders NotesDocument19 pagesKaryotypes and Chromo Disorders NotesLester ParadilloNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument27 pagesChromosomal Abnormalitiessapu-98No ratings yet
- The Ishihara Color Test For Color BlindnessDocument13 pagesThe Ishihara Color Test For Color Blindnesslensi tirta tri buana100% (1)
- Recurrent Abortions and Chromosomal Defects - Edited 1 - Chrysantine ParamayudaDocument10 pagesRecurrent Abortions and Chromosomal Defects - Edited 1 - Chrysantine ParamayudaEndrianus Jaya PutraNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Information To Chapter 32: Inborn Errors of Metabolism General ConsiderationsDocument24 pagesSupplementary Information To Chapter 32: Inborn Errors of Metabolism General ConsiderationsAaron JoseNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Disorders in Childhood: Professor Kevin Dunne Department of Paediatrics RcsiDocument30 pagesNeuromuscular Disorders in Childhood: Professor Kevin Dunne Department of Paediatrics RcsiIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Worksheet Answer KeyDocument1 pagePedigree Worksheet Answer Keyapi-477608730100% (8)
- 3 - PorphyriasDocument14 pages3 - PorphyriasHamzehNo ratings yet
- Data Perbaikan Peserta KSN-K 2021: No Nama - Peserta NisnDocument10 pagesData Perbaikan Peserta KSN-K 2021: No Nama - Peserta NisnRianty LstNo ratings yet
- Clinical - Approach - To - The - Diagnosis IEM PDFDocument15 pagesClinical - Approach - To - The - Diagnosis IEM PDFVictor Lage de AraujoNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument17 pagesChromosomal DisordersJosh Rosenberg100% (1)
- ThalassemiaDocument10 pagesThalassemiaAmanda Scarlet100% (1)
- Errors in Meiosis QuizDocument3 pagesErrors in Meiosis QuizLorena ariateNo ratings yet
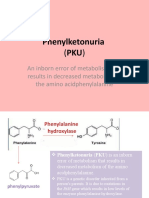
- Phenylketonuria: An Inborn Error of Metabolism That Results in Decreased Metabolism of The Amino AcidphenylalanineDocument8 pagesPhenylketonuria: An Inborn Error of Metabolism That Results in Decreased Metabolism of The Amino Acidphenylalanineელენე ბუჩუკურიNo ratings yet
- Sindrome de DownDocument27 pagesSindrome de DownKhissi BArzaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Muscular DystrophyDocument18 pagesCase Study - Muscular DystrophyJohn Rey BayoguingNo ratings yet
- Ukg Asahan - ExcelDocument124 pagesUkg Asahan - ExcelSutantoNo ratings yet
- Duchenne and Becker Muscular DystrophyDocument8 pagesDuchenne and Becker Muscular DystrophyRumela Ganguly ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Autosomal Recessive DisorderDocument17 pagesAutosomal Recessive DisorderAndrea Love PalomoNo ratings yet
- Muscular DystrophyDocument14 pagesMuscular Dystrophyapi-439738433No ratings yet
- Mutations and Genetic Disorders 4Document28 pagesMutations and Genetic Disorders 4MaleehaNo ratings yet
- SDR Hutchinson GilfordDocument22 pagesSDR Hutchinson GilfordVintilă BogdanNo ratings yet
- Babyshield TMS Fact SheetDocument399 pagesBabyshield TMS Fact SheetSunny RockyNo ratings yet
- ALKAPTONURIADocument15 pagesALKAPTONURIAJean Claude Balancio100% (1)
- Daftar Peserta FizDocument39 pagesDaftar Peserta FizFefin IriantiNo ratings yet
- Murder MysteryDocument13 pagesMurder Mysteryapi-451162079No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument69 pagesCell CycleJustine FariscalNo ratings yet