Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Military Organization
Uploaded by
hanna lynn tillamaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Military Organization
Uploaded by
hanna lynn tillamaCopyright:
Available Formats
MILITARY ORGANIZATION
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE AFP
The origin of the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP) could be traced to the Tejeros
Convention in 1897-where the revolutionary government of General Emilio Aguinaldo created
the Philippine Army under Captain General Artemio Ricarte. This Army was the off-shoot of
the Revolutionary Forces, which took arms against the Spanish Government from August 30,
1896 up to December 10, 1898 when the treaty of Paris was entered into by the United States
of America and Spain. The same Army engaged the Americans during the hostilities between
the Philippines and the United States which began on the night of February 4, 1899 and
lasted up to September 25, 1903 - when the last of Filipino Generals, General Simeon Ola
surrendered to the Americans. After the Filipino-American war, the country's armed forces
organized through the promulgation of the National Defense Act in 1935 which created the
Philippine Army, with the off-shore patrol and Army Air Corps as its major components. The
Philippine Constabulary, was then existing under the Department of Interior.
MISSION OF THE AFP
Following are the mission of the Armed Forces of the Philippines:
1. To uphold the sovereignty, support the constitution and defend the territory of the Republic
of the Philippines against all enemies foreign and domestic.
2. To advance the national aims and policies.
3. To effectively plan for the organization, maintenance, development and employment of its
regular and citizen reserve forces for national security.
4. To perform such other functions as the President may direct.
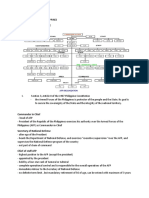
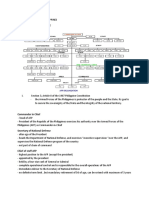
CHAIN OF COMMAND (Commander-in-chief, DND, AFP)
“The President shall be the Commander-in-Chief of all Armed Forces of the Philippines and
whenever it becomes necessary, he may call out such Armed Forces to prevent and suppress
lawless violence, invasion or rebellion.” (Art VII, Sec 18).
The Secretary of National Defense exercises supervision and control over the Armed Forces of
the Philippines. Charge with the responsibility of directing, planning and supervising the National
Defense program. The Chief of Staff, AFP is the highest military officer in the AFP. He has
command and control over all the elements of the AFP. He executes the President’s command
functions in relation to military strategy, tactics and operations and acts as the immediate
adviser to the Secretary of National Defense.
COMPONENTS OF THE AFP
As provided for in the National Defense Act, as amended, the Armed Forces of the Philippines
shall be composed of the Regular Force and Reserve Force components.
1. The Regular Force
- the permanent military organization which is maintained in the time of peace and war. In
time of peace, the authorized active commissioned officer and enlisted personnel of the
Regular Force is determined every year by the annual general and special Appropriation
Act. This strength however, does not only include those officers and EP who are
permanently commissioned or serving under voluntary enlistment in the Regular Force, but
also those officer and reservist assigned for duty with the different services of the Regular
Force.
PROPERTY OF SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY ROTC UNIT ©SMUROTC2020
2. The Reservist Force
- the military organization that will come to physical existence only upon mobilization as
may be called upon by the Commander-in-Chief due to state of national emergency such
as war or widespread disorder. Units of the Reserved Force are “paper” organizations
which come to being to augment the Regular Force in comforting the threat to the Nation.
The Reserved Force Organization includes the commissioned Reserved Officers and all
citizens who have completed the prescribed trainee instructions as provided by the National
Defense Act and who are assigned as reservists to the organizations of the Reserved
Force.
THE THREE (3) MAJOR SERVICES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS A. THE PHILIPPINE ARMY
Is responsible for the preparation of land forces necessary for the effective prosecution
of war except as otherwise assigned and in accordance with integrated mobilization
plans for expansion of the peace time components of the Army to meet the needs of
war.
Functions:
a. To organize, train and equip army forces for the conduct of prompt and sustained
combat operations on land – especially forces to defeat enemy land forces and to
seize, occupy and defend land areas.
b. To develop doctrine, procedures, tactics and techniques, organization and
equipment peculiar to the Army for un-service operations.
c. To develop in coordination with other major services, doctrines, procedures,
tactics, and techniques and equipment of interest to the Army for joint operations.
d. To provide and organization capable of furnishing adequate, timely and reliable
intelligence for the Army.
e. To organize, train, and equip all Army reserve units.
f. To perform such other task functions as the President may direct.
B. PHILIPPINE AIR FORCE
Is responsible for the preparation of air forces necessary for the effective prosecution of war
except as otherwise assigned in accordance with integrated mobilization plans, for the
expansion of the peacetime components of the Air Force to meet the needs of war.
Function:
a. To organize, train and equip air forces for prompt and sustained operations in the
air, especially forces to defend the Philippines against air attacks, to gain and
maintain air superiority and to control vital air areas.
b. To organize, train and equip Air Forces, forces for close support of surface
forces.
c. To develop doctrines, procedures, tactics and techniques, organization and
equipment peculiar to the Air Forces for un-service operation.
d. To develop in coordination with the other major services, doctrines, procedures,
tactics and techniques and equipment of interest to the Air Forces for joint
operation.
e. To provide an organization capable of furnishing adequate, timely and reliable
intelligence for the Air Forces
C. THE PHILIPPINE NAVY
The Philippine navy is responsible for the preparation of Navy Forces effective for
prosecution of war except as otherwise assigned, in accordance with integration
PROPERTY OF SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY ROTC UNIT ©SMUROTC2020
mobilization plans for the expansion for the peacetime components of the Navy to meet
the needs of war.
Function:
a. To organize, train, equip, maintain and operate naval air crafts, necessary to
provide water borne support to assistance required of the AFP in the
accomplishment of its mission.
b. To assist the proper government agencies in the enforcement of the Laws and
regulation pertaining to navigation, immigration, custom revenue, opium,
quarantine, fishing and neutrality in the territorial and contiguous waters of the
Philippines Archipelago.
c. To develop doctrine, procedure, tactics and techniques, organization and
equipment peculiar to the Navy for unit-service operations.
d. To develop, in coordination with the other major service, doctrines procedure,
tactics and techniques and equipment and interest to the reconnaissance,
antisubmarine welfare and protection of shipping.
e. To perform such as other function the President may direct
Operations:
The Philippine Fleet, the Philippine Coast guard and the Philippine Marines are the
operating forces of the Philippine Navy. These forces are the vital components of the
Navy to accomplished its function for naval defense, law enforcement and
maintenance of peace and order, national development and country insurgency
1. The Philippine Fleet.
The core of Philippine Navy is the Philippine Navy fleet, since the ships are
assembled into a completely prepared and integrated systems to composed the
fleet that is thoroughly and collective trained as the naval fighting force. Its
mission is to man, train and maintain operationally ready sub-surface, air and
amphibious forces in order that they can be deployed to conduct prompt
operations, support of the National Interest.
2. The Philippine Coast Guard
The mission of the Philippine Coast Guard is to enforce or assist in to the
enforcement of maritime laws, to promulgate and administered regulation for the
safety of life and property at sea, and to develop, establish, maintain and
operate, with due to requirements of National Defense, aids to maritime
navigation and sea rescue facilities.
3. The Philippine Maritime
Missions:
a. To provides force of combined arms and to serve with the naval forces
in the conduct of such amphibious or special operations as may be
essential to the prosecution of naval campaign.
b. To provides security abroad naval bases, vessels, stations and other
government installation.
c. To develop in coordination with other services of doctrine, tactics,
techniques and equipment by landing forces in amphibious operation.
d. To maintain a force in readiness for internal contingencies and
fulfillment commitments of the country.
e. To participate in socio –economic development and assist in time of
national calamities and disasters.
PROPERTY OF SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY ROTC UNIT ©SMUROTC2020
f. To perform such other duties as the Flag Officer in Command,
Philippine Navy may direct
PROPERTY OF SAINT MARY’S UNIVERSITY ROTC UNIT ©SMUROTC2020
You might also like
- Promissory NoteDocument2 pagesPromissory NoteMario Ryan Lauzon91% (23)
- Military Science - 2: Reserve Officers Training CorpsDocument167 pagesMilitary Science - 2: Reserve Officers Training CorpsBailawan Watamama83% (6)
- Philippine Air Force - PAF OrganizationDocument40 pagesPhilippine Air Force - PAF Organizationjb2ookworm78% (9)
- Republic Act No. 7898Document8 pagesRepublic Act No. 7898Hib Atty TalaNo ratings yet
- Afp Organization 2Document18 pagesAfp Organization 2Joy CabatoNo ratings yet
- Military OrganizationDocument7 pagesMilitary Organizationjohn mark pampoNo ratings yet
- Ra 7898Document7 pagesRa 7898Roda CatindinNo ratings yet
- Afp OrgnizationDocument2 pagesAfp OrgnizationKenneth Albaran (6)No ratings yet
- B. Military OrganizationDocument5 pagesB. Military OrganizationXtream TvwatchNo ratings yet
- 3@ - NSTP1 Module 6 Military OrientationDocument23 pages3@ - NSTP1 Module 6 Military OrientationSharmaine Martirez100% (1)
- NSTP Afp OrgDocument4 pagesNSTP Afp OrgAllyn BalabatNo ratings yet
- Test IV - Module 1Document5 pagesTest IV - Module 1Mary LouiseNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities of The 3 Major Services of The AFPDocument2 pagesResponsibilities of The 3 Major Services of The AFPDestor, Justin AndreNo ratings yet
- 516 Nrotc Unit: Subject: The Afp OrganizationDocument6 pages516 Nrotc Unit: Subject: The Afp Organizationikki kuroganeNo ratings yet
- AFP OrganizationDocument2 pagesAFP OrganizationElijah Dave BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Commander in ChiefDocument4 pagesCommander in Chiefxyji mave ingosanNo ratings yet
- The Afp OrganizationDocument3 pagesThe Afp OrganizationMarichou BarongNo ratings yet
- Afp Mandate, Mission, Function and OrganizationDocument3 pagesAfp Mandate, Mission, Function and OrganizationAnastacio H Echavez II67% (3)
- Afp OrganizationDocument29 pagesAfp OrganizationGrace Ann Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- 2nd Military OrganizationDocument7 pages2nd Military OrganizationFrancis Valdez LopezNo ratings yet
- Military Science - 2: Reserve Officers Training CorpsDocument12 pagesMilitary Science - 2: Reserve Officers Training CorpsJaren QueganNo ratings yet
- Basic Organisation of Armed ForcesDocument25 pagesBasic Organisation of Armed ForcesVenushreeNo ratings yet
- Afp-Mandate, Mission, Organization, and Function - BalagoDocument23 pagesAfp-Mandate, Mission, Organization, and Function - BalagoAlthea Lei Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vision: Philippine MarinesDocument2 pagesVision: Philippine MarinesMa. Carla Dianne EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Four Major Command of Armed Forces of The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesFour Major Command of Armed Forces of The PhilippinesMeagan Manibo100% (1)
- The AFP OrganizationDocument5 pagesThe AFP OrganizationWendell AgotNo ratings yet
- AFP ORGANIZATION MondDocument18 pagesAFP ORGANIZATION MondAllan HernandezNo ratings yet
- Rotc Reviewer 2ND SemDocument19 pagesRotc Reviewer 2ND SemNovilyn TendidoNo ratings yet
- 04-Afp OrganizationDocument8 pages04-Afp OrganizationKath CagmatNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Student Handout Afp Mandate, Mission, Function and Organization Afp MandateDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Student Handout Afp Mandate, Mission, Function and Organization Afp MandateBLOCK 8 / TAMAYO / K.No ratings yet
- Armed Forces of The PhilippinesDocument30 pagesArmed Forces of The Philippinestaguba luckyNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Military in Philippine PoliticsDocument23 pagesThe Role of The Military in Philippine PoliticsJim Paul ManaoNo ratings yet
- Afp OrganizationDocument12 pagesAfp OrganizationAustinEvansManaigNo ratings yet
- Commonwealth Act No. 1 - Official Gazette of The Republic of The PhilippinesDocument36 pagesCommonwealth Act No. 1 - Official Gazette of The Republic of The PhilippinesJANISE PANGILINAN CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Military OrganizationDocument95 pagesMilitary OrganizationCarl0217No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document19 pagesLesson 2Rexson Dela Cruz TagubaNo ratings yet
- Afp OrganizationDocument7 pagesAfp OrganizationArchie French100% (1)
- Module 2Document52 pagesModule 2Charice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Brief History ROTCDocument6 pagesBrief History ROTCAlyssa Tagle100% (1)
- Reviewer in RotcDocument37 pagesReviewer in RotcJoelar OndaNo ratings yet
- Afp Mandate Mission and Function and OrganizationDocument2 pagesAfp Mandate Mission and Function and Organizationserene.nyxxxNo ratings yet
- Assignment NoDocument1 pageAssignment Noariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cat 2Document31 pagesCat 2Doro WakitNo ratings yet
- REPUBLIC ACT No7077 NSTP NOTESDocument2 pagesREPUBLIC ACT No7077 NSTP NOTESHeaven RoyNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument22 pagesNSTPMark CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Functions Armed Forces of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesFunctions Armed Forces of The PhilippinesSyril Mae Montejo GelaNo ratings yet
- Armed Forces of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesArmed Forces of The Philippinesjb2ookworm91% (11)
- Afp History OrganizationDocument48 pagesAfp History OrganizationKeith Clifford RobleNo ratings yet
- Commander in ChiefDocument5 pagesCommander in Chiefxyji mave ingosanNo ratings yet
- Military-Science-1 Midterm Reviewer FullDocument58 pagesMilitary-Science-1 Midterm Reviewer Full10ruby.nagumroxanne15No ratings yet
- 03 AFP OrganizationDocument5 pages03 AFP OrganizationYob YnnosNo ratings yet
- MS 2 HandookDocument180 pagesMS 2 Handookissei dragneelNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1554336967466Document153 pagesOrca Share Media1554336967466Fernando Santos Vergonia100% (4)
- Quiz#1 Bravo 1stPltn LERONDocument3 pagesQuiz#1 Bravo 1stPltn LERONRia BarisoNo ratings yet
- ROTCDocument13 pagesROTCAltea Shane BalicotNo ratings yet
- Pa Basic DoctrineDocument6 pagesPa Basic DoctrineTheresa MendozaNo ratings yet
- R.A. 7077Document10 pagesR.A. 7077Jim CeeNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document158 pagesModule 2Shane PenuliarNo ratings yet
- Military Police Operations In The Okinawa CampaignFrom EverandMilitary Police Operations In The Okinawa CampaignNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned From Advising And Training The Republic Of South Vietnam’s Armed ForcesFrom EverandLessons Learned From Advising And Training The Republic Of South Vietnam’s Armed ForcesNo ratings yet
- The Twelfth US Air Force: Tactical And Operational Innovations In The Mediterranean Theater Of Operations, 1943-1944From EverandThe Twelfth US Air Force: Tactical And Operational Innovations In The Mediterranean Theater Of Operations, 1943-1944No ratings yet
- Free Download Here: Law of Contract by RK Bangia PDFDocument2 pagesFree Download Here: Law of Contract by RK Bangia PDFKritik Roshan RVNo ratings yet
- Regulation Crowdfunding - A Small Entity Compliance Guide For IssuersDocument7 pagesRegulation Crowdfunding - A Small Entity Compliance Guide For IssuersCrowdfundInsiderNo ratings yet
- Lohmann Rausher GMBH Vs Medisphere Marketing Pvt. Ltd. On 13 January, 2005Document7 pagesLohmann Rausher GMBH Vs Medisphere Marketing Pvt. Ltd. On 13 January, 2005Itish KakarNo ratings yet
- Company Law and AllotmentDocument6 pagesCompany Law and Allotmentmahesh145m100% (1)
- Obligations and Contracts Chapter 4 and Chapter 6 Problems AnswerDocument3 pagesObligations and Contracts Chapter 4 and Chapter 6 Problems AnswerNicole Allyson Aguanta100% (5)
- Greenberg, Zachary Complaint PDFDocument2 pagesGreenberg, Zachary Complaint PDFFox NewsNo ratings yet
- Purificacion G. Tabang vs. National Labor Relations Commission G.R. No. 121143 January 21, 1997 FactsDocument1 pagePurificacion G. Tabang vs. National Labor Relations Commission G.R. No. 121143 January 21, 1997 Factscarlo_tabangcura100% (1)
- G.R. No. 153675 DigestDocument2 pagesG.R. No. 153675 DigestK Manghi100% (1)
- TST Briefing - Investment Funds in Bahrain and OffshoreDocument23 pagesTST Briefing - Investment Funds in Bahrain and OffshoresjmpakNo ratings yet
- Milton Parness v. United States, 415 F.2d 346, 3rd Cir. (1969)Document2 pagesMilton Parness v. United States, 415 F.2d 346, 3rd Cir. (1969)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Melissa Montoya' Sentinel ClipsDocument12 pagesMelissa Montoya' Sentinel ClipsMontoyaMelissaNo ratings yet
- North Bergen OPRA Request FormDocument2 pagesNorth Bergen OPRA Request FormThe Citizens CampaignNo ratings yet
- Verbs That Take An InfinitiveDocument7 pagesVerbs That Take An InfinitiveRho CruzNo ratings yet
- GERMAN BASIC LAW: A Presentation.Document17 pagesGERMAN BASIC LAW: A Presentation.Princess Fathia NkrumahNo ratings yet
- Mx-Mex-Nmx: MexicoDocument2 pagesMx-Mex-Nmx: Mexicoalexis nicolas espejo ramosNo ratings yet
- Philippine Judges Association vs. Prado (G.R. No. 105371 November 11, 1993)Document2 pagesPhilippine Judges Association vs. Prado (G.R. No. 105371 November 11, 1993)Clayton ChambersNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Judiciary Prelims Cum Mains Syllabus 2022Document4 pagesUttarakhand Judiciary Prelims Cum Mains Syllabus 2022sabirNo ratings yet
- Professional Architectural Consulting ServicesDocument8 pagesProfessional Architectural Consulting ServicesZaimin YazNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of BD With Comments N Case Laws by Latifur RahmanDocument275 pagesThe Constitution of BD With Comments N Case Laws by Latifur RahmanMd Ahsan-Ul- KabirNo ratings yet
- Cybersquatting in IndiaDocument9 pagesCybersquatting in IndiaDivyanshu Gupta100% (1)
- FINAL - Notice of Nullification Cancellation of RBM Purchase Agreement For Atty ChanDocument3 pagesFINAL - Notice of Nullification Cancellation of RBM Purchase Agreement For Atty ChanPending_nameNo ratings yet
- Zernik, J. "E-Government in Israel - Transformation Into The Post-Truth Era" - European Conference On Digital Government PP 270-9 (2017)Document14 pagesZernik, J. "E-Government in Israel - Transformation Into The Post-Truth Era" - European Conference On Digital Government PP 270-9 (2017)Human Rights Alert - NGO (RA)100% (1)
- San Miguel Brewery V Law Union Rock Insurance Company DigestDocument1 pageSan Miguel Brewery V Law Union Rock Insurance Company DigestCessy Ciar KimNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 164518Document19 pagesG.R. No. 164518Liz LorenzoNo ratings yet
- In Re Benjamin DacanayDocument4 pagesIn Re Benjamin Dacanayjeesup9No ratings yet
- The Writs of Amparo and Habeas Data - Anna Lorem Ramos PDFDocument25 pagesThe Writs of Amparo and Habeas Data - Anna Lorem Ramos PDFALEX ABITANNo ratings yet
- Commercial Business Security Agreement Template-49605Document11 pagesCommercial Business Security Agreement Template-49605Dubakoor86 DubakoorNo ratings yet
- 22.book Building & Green Shoe OptionDocument5 pages22.book Building & Green Shoe OptionmercatuzNo ratings yet
- B52 Information BulletinDocument3 pagesB52 Information BulletinrayrayrayyeungNo ratings yet