Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pregnancy Trimesters & SIgns of Pregnancy
Uploaded by
Jewell PascualCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy Trimesters & SIgns of Pregnancy
Uploaded by
Jewell PascualCopyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy
1. First trimester
The first trimester is the most crucial to the baby's development. During this period, the baby's
body structure and organ systems develop. Most miscarriages and birth defects occur during this
period.
The body also undergoes major changes during the first trimester. These changes often cause a
variety of symptoms, including nausea, fatigue, breast tenderness and frequent urination.
Although these are common pregnancy symptoms, every woman has a different experience. For
example, while some may experience an increased energy level during this period, others may
feel very tired and emotional.
2. Second Trimester
The second trimester of pregnancy is often called the "golden period" because many of the
unpleasant effects of early pregnancy disappear. During the second trimester, you're likely to
experience decreased nausea, better sleep patterns and an increased energy level. However, you
may experience a whole new set of symptoms, such as back pain, abdominal pain, leg cramps,
constipation and heartburn.
Somewhere between 16 weeks and 20 weeks, you may feel the baby's first fluttering movements
3. Third Trimester
The mother may feel more uncomfortable now as she continues to gain weight and begins to
have false labor contractions (called Braxton-Hicks contractions).
During the third trimester of pregnancy, fetus development continues to grow in size and weight.
The lungs are still maturing and the fetus begins to position itself head-down. By the end of the
third trimester, the fetus is about 19 to 21 inches long and weighs, on average, six to nine
pounds.
Fetal development during the third trimester includes:
The fetus can see and hear.
The brain continues to develop.
The kidneys and lungs continue to mature.
By the 36th week, the head may "engage" (drop into the pelvic area) - a process
called "lightening."
The bones of the skull remain soft to make it easier to pass through the birth canal.
For many babies, the irises of the eyes are slate blue. The permanent eye color will
not appear until several days or weeks after birth.
The fetus can suck its thumb and has the ability to cry.
By 38 to 40 weeks, the fetus' lanugo has disappeared almost completely.
By 38 to 40 weeks, the lungs have matured completely.
The baby is covered in vernix caseosa (or simply called vernix), a creamy, protective
coating on the skin.
The head will usually turn downward during the last couple of weeks of pregnancy.
Changes in the mother's body
In the third trimester of pregnancy, some women become increasingly uncomfortable as their due
date nears. As the fetus grows in size and crowds the abdominal cavity, some mothers-to-be have
difficulty taking deep breaths or getting comfortable at night for sleep, while others are free from
any discomfort as they anxiously await the arrival of their new son or daughter.
List of changes and symptoms experiencd during the third trimester and includes:
Increased skin temperature as fetus radiates body heat, causing the mother to feel hot.
Increased urinary frequency returns due to increased pressure placed on bladder.
Blood pressure may decrease as the fetus presses on the main vein that returns blood
to the heart.
Swelling of the ankles, hands and face may occur (called edema), as the mother
continues to retain fluids.
Hair may begin to grow on a woman's arms, legs, and face due to increased hormone
stimulation of hair follicles. Hair may also feel coarser.
Leg cramps may become more frequent.
Braxton-Hicks contractions (false labor) may begin to occur at irregular intervals in
preparation for childbirth.
Stretch marks may appear on the abdomen, breast, thighs and buttocks.
Colostrum (a fluid in the breasts that nourishes the baby until the breast milk becomes
available) may begin to leak from the nipples.
Dry, itchy skin may persist, particularly on the abdomen, as the skin continues to
grow and stretch.
A woman's libido (sexual drive) may decrease.
Skin pigmentation may become more apparent, especially dark patches of skin on the
face.
Constipation, heartburn and indigestion may continue.
Increased white-colored vaginal discharge (leukorrhea) which may contain more
mucus.
Backaches may persist and increase in intensity.
Hemorrhoids may persist and increase in severity.
Varicose veins in the legs may persist and increase.
Signs of Pregnancy
1. Presumptive Signs of Pregnancy (Subjective)
Least indicative of pregnancy
Taken as single entities, could easily indicate other conditions.
Experienced by the woman but cannot be documented by an examiner.
2. Probable Signs of Pregnancy
Objective and can be documented by an examiner.
More reliable than presumptive signs, they still are not positive or true diagnostic
findings.
Laboratory Tests
Commonly used: based on detecting the presence of human chorionic
gonadotropin (hCG).
hCG - a hormone created by the chorionic villi of the placenta, in the
urine or blood serum of the pregnant woman
All laboratory tests for pregnancy are accurate in diagnosing pregnancy only
95% to 98% of the time, positive results from these tests are considered probable
rather than positive signs.
Home Pregnancy Tests
Most based on immunologic reactions are available over the counter.
Have high degree of accuracy (about 97%) if the instructions are followed
exactly.
3. Positive Signs of Pregnancy
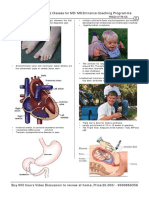
Demonstration of a fetal heart separate from the mother’s
- Fetal heart has been beating since the 24th day after conception.
- Fetal heart rate usually ranges between 120 and 160 beats per minute
Fetal heart beat
Detected on Echocardiography as early as 5 weeks.
Detected on ultrasound as early as 6th to 7th week of pregnancy.
Detected by auscultation of the abdomen with an ordinary stethoscope
at about 18 to 20 weeks.
Fetal heart sounds
- Difficult to hear if a woman’s abdomen has a great deal of subcutaneous fat or
if a larger than normal amount of amniotic fluid is present (hydramnios).
- Heard best when the position of the fetus is determined by palpation and the
stethoscope is placed over the area of the fetus’s back.
Detected through Doppler Technique early as the 10th to 12th week of
gestation.
Fetal movements felt by an examiner
- May be felt by a woman as early as 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Those felt by an objective examiner are considered much more reliable.
(movement can be mistaken by mother as movement of gas)
Can be felt by an examiner at the 20th to 24th week unless extremely obese.
Visualization of the fetus by ultrasound
A characteristic ring, indicating the gestational sac, will be revealed on an
oscilloscope screen as early as the fourth to sixth week of pregnancy
By the eighth week, a fetal outline can be seen so clearly within the sac that the
crown-to-rump length can be measured to establish the gestational age of the
pregnancy
- Also gives information about the site of implantation and whether a multiple
pregnancy exists.
4. Danger Signs of Pregnancy
a) Vaginal Bleeding
Serious bleeding complications of pregnancy begin with only slight spotting.
If discovered on toilet paper following a bowel movement, she is probably reporting
spotting from hemorrhoids.
Until the bleeding is found to be innocent all women with spotting need further
evaluation.
b) Persistent Vomiting
- depletes the nutritional supply available to a fetus so is a danger to the
pregnancy.
Vomiting more than once or twice a day.
Vomiting that continues past the 12th week of pregnancy is also extended vomiting.
c) Chills and Fever
May indicate an intrauterine infection (serious complication for woman and fetus)
A woman cannot make a definite determination about the cause of a fever, further
evaluation by a health care provider is necessary.
d) Sudden Escape of Clear Fluid From the Vagina
Means the membranes have ruptured and mother and fetus are now both
threatened, because the uterine cavity is no longer sealed against infection.
- If a fetus is small so the head does not fit snugly into the cervix, the umbilical
cord may prolapse following membrane rupture.
- If the cord is then compressed by the fetal head, oxygenation is compromised
and a fetus will be in immediate and grave danger.
Alerting a health care provider to any sudden escape of fluid is crucial so a safe
and controlled birth can be planned.
Occasionally, a woman confuses stress incontinence (involuntary loss of urine on
coughing or sneezing or lifting a heavy object) for this.
- In this situation, vaginal examination typically reveals that the membranes are
still intact.
e) Abdominal or Chest Pain
Report it immediately.
Health teaching: A pregnant uterus normally expands painlessly.
Possible complications implicated by abdominal pain:
- Tubal (ectopic) pregnancy
- Separation of the placenta
- Preterm labor
- Appendicitis
- Ulcer
- Pancreatitis.
Chest pain may indicate a pulmonary embolus
- A complication that can follow thrombophlebitis.
f) Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension (PIH)
Refers to a potentially severe and even fatal elevation of blood pressure that
occurs during pregnancy.
Must not have occurred prior to pregnancy.
Several symptoms signal that PIH is developing:
- Rapid weight gain (over 2 lb per week in the second trimester, 1 lb per week in
the third trimester)
- Swelling of the face or fingers
- Flashes of light or dots before the eyes
- Dimness or blurring of vision
- Severe, continuous headache
- Decreased urine output
Some edema of the ankles during pregnancy is normal (if it occurs after a woman
has been on her feet for a long period)
Edema indicated by swelling of the hands or face
cerebral edema or acute hypertension – signalled by visual disturbances or a
continuous headache
g) Increase or Decrease in Fetal Movement
An unusual increase or decrease in movement compared to the fetus’ usual may
suggest that a fetus is responding to a need for oxygen.
- Ask a woman about typical fetal movements and any increase or decrease in
this rate. If there has been a change, she is a candidate for further testing and
follow-up.
You might also like
- The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS) To Transform Our WorldDocument7 pagesThe 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS) To Transform Our WorldJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- LorealDocument13 pagesLorealJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS) To Transform Our WorldDocument10 pagesThe 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS) To Transform Our WorldJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- Health HistoryDocument10 pagesHealth HistoryJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- Binalbal Festival: Presented By: Jewell PascualDocument5 pagesBinalbal Festival: Presented By: Jewell PascualJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem: SourcesDocument1 pageStatement of The Problem: SourcesJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Notes Second QuarterDocument7 pages21st Century Literature Notes Second QuarterJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- Globalization As An IdeologyDocument4 pagesGlobalization As An IdeologyJewell PascualNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Student Study Guidde ECE AND REPDocument39 pagesStudent Study Guidde ECE AND REPKareem Abo WardaNo ratings yet
- Oo GenesisDocument20 pagesOo GenesisDinar Yudistira FirdausNo ratings yet
- 4 6041841339799176725 PDFDocument159 pages4 6041841339799176725 PDFFaez ArbabNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding TPDocument3 pagesBreastfeeding TPAndrea Mae SanchezNo ratings yet
- MTHFR 97d077a0a2e9 20200116170647 PDFDocument31 pagesMTHFR 97d077a0a2e9 20200116170647 PDFOpen PrizesNo ratings yet
- Right To Abortion: Justified or Not? Yashaswi Singh & Ashutosh VermaDocument10 pagesRight To Abortion: Justified or Not? Yashaswi Singh & Ashutosh VermaShakshi MehtaNo ratings yet
- 1 Perinatal Mental Health Azlan Luk TARGET Session 22092016Document34 pages1 Perinatal Mental Health Azlan Luk TARGET Session 22092016Anny AunNo ratings yet
- FrazierDocument41 pagesFrazierJosh ZiveNo ratings yet
- How Dey Spent 2 DaysDocument10 pagesHow Dey Spent 2 DaysARAZRP KASHNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rujukan 2022Document11 pagesLaporan Rujukan 2022Sansan Volly BallNo ratings yet
- SF2 - 2022 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - AUSTENDocument3 pagesSF2 - 2022 - Grade 10 (Year IV) - AUSTENArthur LegaspinaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Infants Children and Adolescents 8th Edition Berk Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Infants Children and Adolescents 8th Edition Berk Solutions Manual PDFtopchainburdenerp2z5m100% (7)
- Coumba Kebe - Scan - Jschmidt - 2021-05-06-07-25-02Document8 pagesCoumba Kebe - Scan - Jschmidt - 2021-05-06-07-25-02Coumba KebeNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy & ChildbirthDocument12 pagesPregnancy & Childbirthrobert tambuliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology & NeurobiologyDocument14 pagesRespiratory Physiology & NeurobiologyRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- January 2009 MS - Unit 2 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDocument14 pagesJanuary 2009 MS - Unit 2 Edexcel Biology A-LevelHulk AlamNo ratings yet
- ST 2 Gr. 5 Science With TosDocument4 pagesST 2 Gr. 5 Science With TosEG Bitong-AlamaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Adnexal MassesDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Adnexal MassesSebastianNo ratings yet
- Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Is A Type of Brain Damage That Occurs When An Infant's Brain Doesn't Receive Enough Oxygen and BloodDocument6 pagesHypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Is A Type of Brain Damage That Occurs When An Infant's Brain Doesn't Receive Enough Oxygen and BloodTheresa MendoncaNo ratings yet
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy ActDocument27 pagesMedical Termination of Pregnancy ActMehkar KhanNo ratings yet
- Abortion Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesAbortion Reflection PaperMorvinNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The AbdomenDocument35 pagesAssessment of The AbdomenariannethereseNo ratings yet
- NCP On Preterm LaborDocument2 pagesNCP On Preterm Laborinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Dr. Murali Bharadwaz Classes For MD/MS Entrance Coaching ProgrammeDocument20 pagesDr. Murali Bharadwaz Classes For MD/MS Entrance Coaching ProgrammeskNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Physical Assessment: Observation /inspection Palpation Percussion AuscultationDocument56 pagesTechniques of Physical Assessment: Observation /inspection Palpation Percussion AuscultationAnna Fayeziah YussophNo ratings yet
- Jospeh Cicy PDFDocument125 pagesJospeh Cicy PDFRana VandanaNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument1 pageDaftar PustakaDwi sarwindahNo ratings yet
- Abortion Reversal Pill - August 15 2020Document2 pagesAbortion Reversal Pill - August 15 2020api-271968502No ratings yet
- MCN Menstrual Cycle LatestDocument8 pagesMCN Menstrual Cycle LatestsophienNo ratings yet