Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1-VLAN Design: Network Administration
Chapter 1-VLAN Design: Network Administration
Uploaded by
Rejean Isip0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesOriginal Title
NET-AD-CHAPTER-1-REVIEWER.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesChapter 1-VLAN Design: Network Administration
Chapter 1-VLAN Design: Network Administration
Uploaded by
Rejean IsipCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
NETWORK This is because it allows each layer
to implement specific functions,
ADMINISTRATION which simplifies the network design
Chapter 1- VLAN Design for easier deployment and
management.
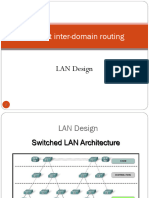
1.1 Campus Wired LAN Designs A hierarchical LAN design includes
three layers as shown in the figure:
A small company always has the
1. Access layer
tendency to grow along with their
2. Distribution layer
enterprise, that is why all enterprise
3. Core layer
networks must:
Some smaller enterprise networks
1. Support the exchange of
implement a two-tier hierarchical
various types of network
design and collapse the core and
traffic
distribution layers into one layer.
2. Support critical applications
3. Support converged network 1.3 (Expanding the Network) Design for
traffic Scalability
4. Support diverse business
needs The network designer must develop
5. Provide centralized a strategy to enable the network to
administrative control be available and scale easily and
effectively.
The LAN is the networking
infrastructure that provides access to Use expandable, modular equipment
network resources for end users or clustered devices that can be
over a single floor or a building. easily upgraded to increase
capabilities.
1.2 Hierarchical Design Model Design a hierarchical network to
include modules that can be added,
upgraded, and modified as needed.
Create an IPv4 or IPv6 address
strategy that is hierarchical.
Choose routers or multilayer
switches to limit broadcasts and filter
undesirable traffic from the network.
Implement redundant links between
critical devices and between access
and core layers.
1.4 Planning for Redundancy
Redundancy is an important part of
the network design for preventing
The campus wired LAN uses a disruption of network services.
hierarchical design model to break
the design up into modular layers.
Minimize the possibility of a single Switch Block Deployment
point of failure by recognizing these • Routers or multilayer
facts: switches are usually
1. Installing duplicate deployed in pairs with access
equipment and providing layer switches evenly divided
failover services for critical between them.
devices is necessary. • Each switch block acts
2. Redundant paths offer independently of the others,
alternate physical paths for which reduces the impact of
data to traverse the network. failures.
3. Spanning Tree Protocol
1.5 Increasing Bandwidth
(STP) is required with
redundant paths in a In a hierarchical network design,
switched Ethernet network to some links between access and
prevent Layer 2 loops. distribution layer switches may need to
STP provides a mechanism for process a greater amount of traffic than
disabling redundant paths in a switched other links do.
network until the path is necessary such As multiple links converge into a
as when a failure occurs. single link, it is possible for this link to
become a bottleneck.(point of
1.4 Failure Domains
congestion when workloads arrive too
A well-designed network should limit quickly to handle)
the size of failure domains. EtherChannel is a form of link
A failure domain is the area of a aggregation that will allow the network
network that is impacted when a critical administrator to increase the amount of
device or network service experiences bandwidth (maximum rate of data
problems. transfer across a given path) between
The function of the devices that fail devices by creating one logical link out
will determine the impact of the failure of several physical links.
domain. EtherChannel uses existing switch
Use redundant links and reliable ports.
enterprise-class equipment to minimize The EtherChannel configuration
the disruption in a network. takes advantage of load balancing
Smaller failure domains reduce the between links that are part of the same
impact of a failure but also make EtherChannel.
troubleshooting easier.
1.6 Expanding the Access Layer
In the distribution layer (Hierarchical
design model) , network errors can Wireless connectivity is an important
be contained to a smaller area which aspect of extending access layer
will impact fewer users. connectivity.
When using Layer 3 devices at the The network must be designed to be
distribution layer, every router able to expand network access to
functions as a gateway for a limited individuals and devices, as needed.
number of access layer users.
Advantages of wireless connectivity 1. Campus LAN switches
include increased flexibility, reduced 2. Cloud-managed switches
cost, and the ability to adapt to changing 3. Data center switches
network and business requirements. 4. Service provider switches
End devices require a wireless NIC 5. Virtual networking
that incorporates a radio Various factors to consider when
transmitter/receiver, appropriate selecting switches include these:
software drivers, and also a wireless 1. Fixed vs. modular configuration
access point (AP) to connect to. 2. Stackable vs. nonstackable
3. Thickness of the switch (rack
1.6 Expanding the Access Layer
units)
Advanced routing protocols, such as 4. Cost, port density, power,
OSPF and EIGRP are used in large reliability
networks. 2.2 Port Density
Link-state routing protocols such as
OSPF works well for larger hierarchical The port density of a switch refers to
networks where fast convergence is the number of ports on a single switch.
important. Fixed configuration switches support
Single Area OSPF has one area – a variety of port density configurations:
Area 0 (Backbone). 1. Cisco Catalyst 3850 24 port and
Cisco’s proprietary distance vector 48 port switches
routing protocol, called EIGRP, is 2. The 48 port switch has an
another popular routing protocol. It is option for four additional ports
designed for larger networks using for pluggable SFP devices.
primarily Cisco routers. The modular Catalyst 6500 switch
Although the configuring EIGRP is can support over 1,000 switch ports.
simple, the underlying features and Modular switches are usually more
options of EIGRP are extensive and appropriate in large networks in order
robust. to reduce space and power issues.
OSPF supports a two-layer
2.3 Forwarding Rates
hierarchical design, referred to as
multiarea OSPF which requires an Area Entry-level switches have lower
0. forwarding rates than enterprise-level
Non-backbone areas must be switches.
directly connected to Area 0 Forwarding Rates are an important
factor when selecting a switch because
Selecting Network Devices
if the rate is too low, it will not be able
2.1 Switch Platforms to support full wire-speed
communication across all of its switch
Selecting the proper hardware to ports.
meet the current network requirements Access layer switches typically do
is critical when designing a network. not need to operate at full wire speed
There are five categories of switches because they are physically limited by
for enterprise networks: their uplinks to the distribution layer.
Higher performing switches are ASICs along with dedicated software
needed at the distribution and core can streamline the forwarding of IP
layers. packets independent of the CPU.
There is a trend in networking
toward a pure Layer 3 switched
2.3 Power over Ethernet (PoE)
environment.
PoE allows the switch to deliver
3.0 Router Requirements
power to a device over the existing
Ethernet cabling. Routing is required within the
This eliminates the need for a power distribution layer of an enterprise
cable to the networked device such an network. Without routing, packets could
IP phone or wireless access point. not leave the local network.
PoE allows more flexibility when Routers are critical networking
installing wireless access points and IP devices because they are responsible
phones by allowing them to be installed for:
anywhere that there is an Ethernet 1. Connecting businesses and
cable. homes to the Internet
The Cisco Catalyst 2960-C and 2. Interconnecting multiple sites
3560-C Series compact switches within an enterprise network
support PoE pass-through. 3. Connecting ISPs on the Internet
PoE pass-through devices can 4. Translating between different
power PoE devices as well as the switch media types and protocols
itself by drawing power from certain 5. Finding alternate paths if a link
upstream switches. or path goes down
Routers also serve other important
2.4 Multilayer Switching functions:
• Provide broadcast
Multilayer switches are typically containment by limiting
deployed in the core and distribution broadcasts to the local
layer. network
Multilayer switches can do the • Group users logically by
following: application or department
1. Build a routing table and • Provide enhanced security
support routing protocols through the use of access
2. Forward IP packets at a rate control lists in order to filter
close to that of Layer 2 unwanted traffic.
forwarding • Interconnect geographically
Multilayer switches often support separated locations.
specialized hardware called
application-specific integrated circuits
(ASICs).
2.5 Cisco Routers accommodate many different network
interface modules.
Selecting the proper router or
routers is an important task for the
network administrator in order to
2.7 Managing IOS Files and
accommodate a growing network.
Licensing
There are three categories of routers:
When selecting or upgrading a Cisco
1. Branch routers – Branch routers
IOS device, it is important to choose
optimize branch services on a
the proper IOS image with the
single platform while delivering
correct feature set and version.
an optimal application
IOS refers to the package of routing,
experience across branch and
switching, security, and other
WAN infrastructures.
internetworking technologies
2. Network edge routers –
integrated into a single multitasking
Network edge routers enable
operating system.
the network edge to deliver
high-performance, highly When a new device is shipped, it
secure, and reliable services comes preinstalled with the software
that unite campus, data center, image and corresponding permanent
and branch networks. licenses for the customer-specified
3. Service provider routers – packages and features.
Service provider routers 3.0 In-band versus Out-of-band
differentiate the service portfolio Management
and increase revenues by
delivering end-to-end scalable There are two methods for
solutions and subscriber-aware connecting a PC to a network device
services. for configuration and monitoring
tasks:
2.6 Router Hardware • Out-of-band management
through the use of the
Routers come in many forms: console or AUX port is used
1. They range in size from a small for the initial configuration or
desktop router to a rack- when a network connection
mounted or blade model router. is not available.
2. They can be categorized as
fixed configuration or modular. • In-band management is used
3. They come with a variety of to configure or monitor the
interfaces such as Fast device remotely through a
Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, network connection using
Serial, and fiber-optic. either SSH or HTTPs.
The Cisco 1941 router comes with • A reachable and
two Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45 interfaces operational network
built-in and two slots that can interface is required.
• For security reasons, learned, next hop, static
the use of Telnet and routes, and default routes
HTTP are not Interface Related:
recommended. 1. show interfaces – Displays
interfaces with line status,
3.1 Basic Router CLI Commands
bandwidth, delay, reliability,
encapsulation, duplex, and
A basic router configuration
I/O statistics
includes as follows:
1. Hostname for identification 3.3 Basic Switch Show Commands
2. Passwords for security
Switches make use of common IOS
3. Assignment of IP addresses
commands for configuration, to
to interfaces for connectivity
check for connectivity, and to display
4. Basic routing
current switch status. Here are
Verify and save configuration
some very useful commands:
changes with the copy running-
show port-security – Displays any
config startup-config command
ports with security activated. Include
To clear the router configuration, use
the interface ID to examine a
the erase startup-config and
specific interface.
reload commands.
show port-security address –
3.2 Basic Router Show Commands Displays all secure MAC addresses
configured on all switch interfaces.
The following are some of the most
show interfaces – Displays one or
common show commands:
all interfaces with line protocol
Routing Related:
status, bandwidth, delay, reliability,
1. show ip protocols –
encapsulation, duplex, and I/O
Displays information about
statistics.
the routing protocols
show mac-address-table –
configured
Displays all MAC addresses that the
2. show ip route – Displays
switch has learned, how they were
detailed routing table
learned, port number, and the VLAN
information including routing
assigned to the port.
codes, known networks,
Cisco switches also support the
administrative distance and
show cdp neighbors command.
metrics, how routes were
You might also like
- Part I - Antibiotics and The Human MicrobiomeDocument5 pagesPart I - Antibiotics and The Human MicrobiomeRejean Isip100% (3)
- Case Study 1Document11 pagesCase Study 1aliff imanNo ratings yet
- Textnow - Mon, 16 Nov 202logDocument10 pagesTextnow - Mon, 16 Nov 202logDejay GriffinNo ratings yet
- ENSA Module 11Document44 pagesENSA Module 11JohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scaling LANs Part1Document19 pagesChapter 1 Scaling LANs Part1amrlhql14No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: LAN Design: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0Document27 pagesChapter 3: LAN Design: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0Muhammad EmranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: LAN Design: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0Document32 pagesChapter 1: LAN Design: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0marwan khalilNo ratings yet
- WAN Design WAN DesignDocument26 pagesWAN Design WAN DesignHarsh BhorNo ratings yet
- CCNA3 CH 1Document18 pagesCCNA3 CH 1Mohammed ElaydiNo ratings yet
- Basic NetworkingDocument31 pagesBasic NetworkingVANI RAVINo ratings yet
- Week 1 - LAN Design Module PDFDocument24 pagesWeek 1 - LAN Design Module PDFJacob Satorious ExcaliburNo ratings yet
- Campus NetworkDocument8 pagesCampus NetworkRebeca García FrancoNo ratings yet
- PPT Sesión 01 2020 Redes Escalables (1940)Document30 pagesPPT Sesión 01 2020 Redes Escalables (1940)Luis NarvaezNo ratings yet
- LAN DesignDocument54 pagesLAN DesignRashed Al-GhwieenNo ratings yet
- Simulation of High Availability Internet Service Provider's NetworkDocument15 pagesSimulation of High Availability Internet Service Provider's NetworkAbi WiryawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Network Design PrinciplesDocument5 pagesLecture 2 - Network Design PrinciplesOge EstherNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 LAN DesignDocument116 pagesLesson-2 LAN Designdawit gebreyohansNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration 3 LAN Switching and Wireless - Chapter 1 ExamDocument5 pagesCCNA Exploration 3 LAN Switching and Wireless - Chapter 1 ExamAnwar SniedNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument10 pagesChapter Threemustefa endrisNo ratings yet
- Cisco 3 Chapter 1 QuizDocument8 pagesCisco 3 Chapter 1 QuiznmvalmoridaNo ratings yet
- Ccna4e Ch1 Study Guide KeyDocument11 pagesCcna4e Ch1 Study Guide Keyjdr114No ratings yet
- Take Assessment - Eswitching Chapter 1 - Ccna Exploration: Lan Switching and Wireless (Version 4.0)Document8 pagesTake Assessment - Eswitching Chapter 1 - Ccna Exploration: Lan Switching and Wireless (Version 4.0)Uros BrovcNo ratings yet
- Network Strategies CH#1 Introduction To Switched NetworkDocument44 pagesNetwork Strategies CH#1 Introduction To Switched NetworkArezo HalimiNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Network Performance of An Enterprises Network With VLANDocument12 pagesEnhancement of Network Performance of An Enterprises Network With VLANproftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 2 Network DesignDocument34 pagesChapter 1 Part 2 Network DesignEncik BurnNo ratings yet
- Network Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworksDocument41 pagesNetwork Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworkszizozoroNo ratings yet
- Network Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworksDocument41 pagesNetwork Design Fundamentals: CCNP SWITCH: Implementing Cisco IP Switched NetworksSulayman AlwabelNo ratings yet
- 9548 Exp 3Document4 pages9548 Exp 3Kakashi HatakeNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Network DesignDocument23 pagesEnterprise Network DesignUmer Aziz RanaNo ratings yet
- Practice WordDocument25 pagesPractice WordDasale DaposNo ratings yet
- Virtual Services Platform 4000 Series Data SheetDocument17 pagesVirtual Services Platform 4000 Series Data Sheet김경우No ratings yet
- Basic Networking Hardware: Kamal Harmoni Kamal AriffDocument22 pagesBasic Networking Hardware: Kamal Harmoni Kamal Ariffismail333100% (2)
- Chapter3.1 Designing A Network TopologyDocument49 pagesChapter3.1 Designing A Network Topologyquoc.dx.62cnttNo ratings yet
- 12.2 Scalable NetworksDocument7 pages12.2 Scalable NetworksSyifa FauziahNo ratings yet
- Exp3 AayushKumar 2022300025Document7 pagesExp3 AayushKumar 2022300025Aayush Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- Planning For Data Migrations:: Class Theoretical Address Range Binary Start Used For A B C D EDocument2 pagesPlanning For Data Migrations:: Class Theoretical Address Range Binary Start Used For A B C D EOliverNo ratings yet
- EN WPE0048 Switch-DifferencesDocument13 pagesEN WPE0048 Switch-DifferencesCarlos ChávezNo ratings yet
- Small Enterprise Design Profile (SEDP) - Network Foundation DesignDocument52 pagesSmall Enterprise Design Profile (SEDP) - Network Foundation DesignThinh Tien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - SwitchesDocument15 pagesWeek 1 - SwitchesDoreen AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Access, Distribution, and Core: Top of FormDocument7 pagesAccess, Distribution, and Core: Top of FormJudyrey P. MediavilloNo ratings yet
- Ccna3 Mod5 SwitchesDocument22 pagesCcna3 Mod5 SwitchesPrahallad RaoNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11-605488Document6 pagesWhite Paper c11-605488labguy2776No ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration 4.0 Module 3 Chapter 1 1Document6 pagesCCNA Exploration 4.0 Module 3 Chapter 1 1thequizzerNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Design GoalsDocument3 pagesFundamental Design Goalslilsoldier50% (2)
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1Maritza Alex Forero NietoNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 - SummaryDocument1 pageCCNA 3 - SummaryMouhamad BazziNo ratings yet
- Repeater - Current Wireless Network TechnologyDocument6 pagesRepeater - Current Wireless Network TechnologyGodwin OanesNo ratings yet
- Cisco Tutorial: The Cisco Three-Layered Hierarchical ..Document2 pagesCisco Tutorial: The Cisco Three-Layered Hierarchical ..Deepak RawatNo ratings yet
- 31 PDFscap4.Pub Distributed-SystemsDocument2 pages31 PDFscap4.Pub Distributed-SystemsLucas M. VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- Unidad4v1 4Document19 pagesUnidad4v1 4Andres SanchezNo ratings yet
- Divine Word University: 1.1 Chapter 1 - Introduction To Scaling NetworksDocument5 pagesDivine Word University: 1.1 Chapter 1 - Introduction To Scaling Networkseddie gonoNo ratings yet
- Services in A Converged WAN: Accessing The WAN - Chapter 1Document21 pagesServices in A Converged WAN: Accessing The WAN - Chapter 1Edgie AceNo ratings yet
- Deploying Pragmatic Techniques For Campus Network Design: Aditya Ahuja, Nikita Gupta, Kamal Dewan, Meenakshi SoodDocument6 pagesDeploying Pragmatic Techniques For Campus Network Design: Aditya Ahuja, Nikita Gupta, Kamal Dewan, Meenakshi SoodBaktiar HossainNo ratings yet
- CCNP (Cisco Certified Network Professional)Document8 pagesCCNP (Cisco Certified Network Professional)Liaqat Ali KashifNo ratings yet
- ITNE 3006 - AssignmentDocument13 pagesITNE 3006 - AssignmentSadia AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document30 pagesLecture 01Masoud magesaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- Project Report 1Document46 pagesProject Report 1archit garg100% (1)
- Lecture 11 Logical Network Design by Rab Nawaz JadoonDocument12 pagesLecture 11 Logical Network Design by Rab Nawaz Jadoonyasar khanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - LAN Design ModuleDocument27 pagesWeek 1 - LAN Design ModuleDean LevyNo ratings yet
- CCNA3 v4 0 Exam CH 1 LAN DesignDocument4 pagesCCNA3 v4 0 Exam CH 1 LAN DesignBrandon HarmonNo ratings yet
- HCI-130-148 SummarizedDocument11 pagesHCI-130-148 SummarizedRejean IsipNo ratings yet
- Summary of Pages 92-110: Human-Computer InteractionDocument7 pagesSummary of Pages 92-110: Human-Computer InteractionRejean IsipNo ratings yet
- INFO-MAN-ASSIGN AnswersDocument2 pagesINFO-MAN-ASSIGN AnswersRejean IsipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: STP: Network AdministrationDocument6 pagesChapter 3: STP: Network AdministrationRejean IsipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Dynamic Routing: Network AdministrationDocument5 pagesChapter 5-Dynamic Routing: Network AdministrationRejean IsipNo ratings yet
- Wireshark Assignment 3 DNSDocument7 pagesWireshark Assignment 3 DNSgeni1701dNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint CMD ListDocument12 pagesCheckpoint CMD ListKaushal KishorNo ratings yet
- UP 010 Manual PDFDocument41 pagesUP 010 Manual PDFIvan FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Lec 10Document15 pagesLec 10Surabhi KarandikarNo ratings yet
- Basic Notes On BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) - Sysnet NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Notes On BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) - Sysnet NotesRumi Sarmad PeerzadaNo ratings yet
- CommandsDocument12 pagesCommandsBeast BoyNo ratings yet
- Audiocodes Cpe & Access Gateway Products Mediant™ 500 MSBR: Multi-Service Business RouterDocument2 pagesAudiocodes Cpe & Access Gateway Products Mediant™ 500 MSBR: Multi-Service Business RouterRoberto InfantasNo ratings yet
- Topic: Course Name: Ethical HackingDocument39 pagesTopic: Course Name: Ethical HackingDaram Vishnu VishnuvardhanNo ratings yet
- EX - NO: Implementation of Address Resolution Protocol Date: AimDocument31 pagesEX - NO: Implementation of Address Resolution Protocol Date: AimMary JansiNo ratings yet
- XOS 9.5.4.0 Xos Configuration GuideDocument306 pagesXOS 9.5.4.0 Xos Configuration GuidemaxwellloweNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment #08 - Network & Host Detection ScansDocument3 pagesLab Experiment #08 - Network & Host Detection ScansAnoop DasNo ratings yet
- Gaoke Modo ApDocument2 pagesGaoke Modo ApJose CantilloNo ratings yet
- Routing Basic Interview Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesRouting Basic Interview Questions and AnswersLokesh ShanjeevNo ratings yet
- 28.1.3 Lab - Use The Netmiko Python Module To Configure A Router - ITExamAnswersDocument11 pages28.1.3 Lab - Use The Netmiko Python Module To Configure A Router - ITExamAnswersAndres Esteban AreasNo ratings yet
- Cisco VCEup - 350-401 15-June-2022 214qDocument90 pagesCisco VCEup - 350-401 15-June-2022 214qAbelNo ratings yet
- Volte Ims Architecture and Sip SignallingDocument60 pagesVolte Ims Architecture and Sip SignallingMauricio Lamiña100% (1)
- Cisco CDR LoggingDocument6 pagesCisco CDR LoggingmasriffaNo ratings yet
- S7600 Series Switches DatasheetDocument21 pagesS7600 Series Switches Datasheetmariadpg4No ratings yet
- MPLS-VRF Integration Forwarding CapabiliDocument6 pagesMPLS-VRF Integration Forwarding Capabilichandrashekar_ganesanNo ratings yet
- Performance and Scalability Numbers For All Switch Models: - Extreme Standby Router Protocol ™ (ESRP)Document5 pagesPerformance and Scalability Numbers For All Switch Models: - Extreme Standby Router Protocol ™ (ESRP)mkabanovNo ratings yet
- Report On HDLC and PPP ProtocolsDocument9 pagesReport On HDLC and PPP ProtocolsMUHAMMAD SHAHEERNo ratings yet
- Caja Blanca Yhn6enDocument101 pagesCaja Blanca Yhn6enAlan ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- IIB Admin and Development Useful CommandsDocument7 pagesIIB Admin and Development Useful Commandspradeep bvnNo ratings yet
- Maipu ROUTER SeriesDocument58 pagesMaipu ROUTER Seriessurender_snd1100% (1)
- Network Security v1.0 - Module 6Document81 pagesNetwork Security v1.0 - Module 6Ernesto Silverio FloresNo ratings yet
- TR 521Document70 pagesTR 521Óscar LealNo ratings yet
- 5516OLT V4.0 Provisioning and Maintenance CLIDocument28 pages5516OLT V4.0 Provisioning and Maintenance CLItest oneNo ratings yet
- FFRTC Log BakDocument2,800 pagesFFRTC Log BakSNEYDER ZABALANo ratings yet
- NMAP - Information GatheringDocument6 pagesNMAP - Information GatheringRockstar GmailNo ratings yet