Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
unkown user0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
142 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
142 views6 pagesNCP
Uploaded by
unkown userCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
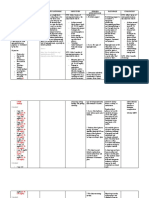
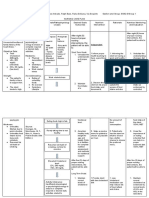
Date and Cues Need Nursing Objective of Nursing Intervention Evaluation
Time Diagnosis Care
S: P Imbalanced Short term: Independent: Short term:
Client’s son H nutrition: After 8 hours After 8 hours of
verbalized that client Y Less than of nursing -Discuss eating habits and encourage a nursing
was diagnosed with S body intervention, diabetic diet as prescribed. intervention, Goal
Diabetes Mellitus I requirements the client is R: To achieve health needs of the patient was partially met
Type II 15 years ago O related to expected to: with the proper food diet for her condition. as evidenced by:
L insulin
O: O deficiency as -Ingest -Observe signs of hypoglycemia: -Willingness to
Diagnostic test G evidenced appropriate changes in LOC, cold and clammy skin, cooperate of client
results: I by weakness amounts of rapid pulse, hunger, irritability, anxiety, is present during
C and FBS of calories and headache, lightheadedness, and health teaching,
FBS – 7mmol/L NEED 7mmol/L nutrients, shakiness.
HbA1C- 6.5% and HbA1C R: Hypoglycemia can occur once blood -Usual energy
Homeostasis of 6.5%. -Display usual glucose level is reduced and carbohydrate increased but not
energy levels, metabolism resumes and insulin is being back to usual
R: Type II and given. levels, and
Diabetes
occurs as -Demonstrate Dependent: -Client was
insulin stabilized cooperative in
production weight or gain -Administer Metformin 500mg/tab stabilizing her
continue to toward usual twice a day as ordered by physician. desire to reach
decrease as or desired R: Metformin decreases the hepatic glucose normal laboratory
body range with production which decreases the values.
resistance to normal gastrointestinal glucose absorption to
insulin laboratory increase cell insulin sensitivity.
increases after values.
an excess in Long term: Collaborative: Long term:
insulin After 2 to 3 After 3 days of
production in days of -Assist in minimal walking while nursing
the pancreas nursing avoiding the stairs as ordered. intervention, goal
fails to move intervention, R: Walking improves glucose control and was met as
glucose into the client exercise helps the muscle absorb blood sugar evidenced by:
the cells for manifests: while preventing glucose buildup in the
fuel. This bloodstream -FBS – 5.6mmol/L
leads to an -Prediabetes to
increase of normal FBS -HbA1C – 5.9%
glucose level values
in the body.
-Prediabetes to
-healthline, normal HbA1C
2017 values
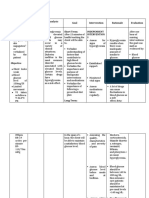
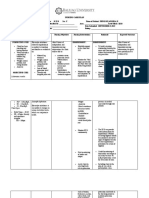
Date and Cues Need Nursing Objective of Nursing Intervention Evaluation
Time Diagnosis Care
S: P Fatigue Short term: Independent: Short term:
Report of non- H related to After 4 hours of After 4 hours of
productive cough, Y Class III nursing -Assess vital signs q4 hours. nursing
hypotension, and S heart failure intervention, R: To evaluate fluid status and intervention, Goal
tachycardia upon I as evidenced the client is cardiopulmonary response to activity was met as
admission. O by expected to evidenced by:
L cardiomegal participate in -Determine presence of degree of sleep.
O: O y with LR activities that R: Fatigue can be a consequence of sleep -Client was able to
Bipedal edema G ventricular reduce the deprivation participate in
I hypertrophy workload of activities that
VS: C the heart Dependent: reduce heart
RR – 23CPM NEED R: Heart workload and
failure is Long term: -Administer Digoxin 0.25μg once a day willing to apply
Diagnostic test Rest and described as After 2 to 3 as ordered by physician. health teachings.
results: Sleep the inability of days of nursing R: Digoxin increase the force of myocardial
BNP: 453pg/mL the heart to interventions, contraction which increases cardiac output Long term:
Troponin (+) support the the patient will and lowers heart rate. After 3 days of
Potassium – 2.9mEq organs and be able to nursing
Cardiomegaly with tissues for display Collaborative: intervention, goal
LR ventricular oxygen and stability in was met as
hypertrophy nutrients. hemodynamics -Administer oxygen @3Lpm via nasal evidenced by:
This leads to a . cannula.
decreased R: O2 administration improves -RR – 17CPM
cardiac output oxygenation of diseased myocardial tissue
which renders which prevents problems caused by low
the amount of oxygen such as damages to the heart and
blood that the the brain.
heart pumps
be inadequate
to circulate
the blood
returning to
the heart from
the body and
lungs. This
inadequacy of
oxygen and
nutrients then
causes
impaired
bodily
functions and
fatigue.
-MedicineNet,
2020
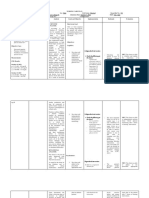
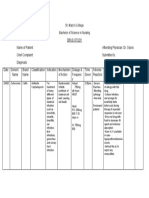
Date and Cues Need Nursing Objective of Nursing Intervention Evaluation
Time Diagnosis Care
S: P Excess fluid Short term: Independent: Short term:
Client’s son H volume After 4 hours of After 4 hours of
verbalized that client Y related to nursing -Monitor and calculate 24-hour intake nursing
was diagnosed with S reduced intervention, and output balance intervention, Goal
hypertension 6 years I glomerular the client is R: Diuretic therapy may result in sudden was met as
ago. O filtration expected to: increase in fluid loss even though edema or evidenced by:
L (decreased ascites remains.
O: O cardiac -Participate in -Client was
Presence of fluid in G output) as diet and fluid -Evaluate urine output in response to participative in
lower lung fields I evidenced by restrictions. diuretic therapy diet and fluid
Bipedal edema grade C presence of R: Focus is on monitoring the response to restrictions
2+ NEED fluid in lower Long term: the diuretics rather than the actual amount
lung fields After 1 week of voided Long term:
VS: Nutritio and bipedal nursing After 1 week of
RR – 23CPM n and edema. interventions, -Weigh daily on the same time of the nursing
Fluid the patient will day. intervention, goal
Diagnostic test R: Pulmonary be able to: R: A gain of 5lb represents approximately 2L was met as
results: edema occurs of fluid. Diuretics can also result in evidenced by:
BNP: 453pg/mL when the heart -Have reduced excessive fluid shifts and weight loss
Troponin (+) is not able to pitting on -Reduced pitting
Potassium – 2.9mEq pump bipedal edema of edema to grade
Cardiomegaly with efficiently 1
LR ventricular which causes a -Normalize
hypertrophy change of potassium level -Potassium level –
pressure in the between 3.5 3.7mEq/L
blood vessels and 5.5 mEq
and fluid is Dependent:
pushed into the
air spaces in the -Administer Furosemide 40mg tab twice
lungs. a day as ordered by physician.
R: Furosemide is a diuretic and it increases
Bipedal edema renal excretion of water, sodium chloride,
is caused by magnesium, potassium, and calcium.
excess fluid
trapped in the -Administer Digoxin 0.25μg once a day
body’s tissue as ordered by physician.
caused by R: Digoxin increases cardiac output
decreased therefore reducing edema by reducing the
cardiac output amount of blood backflow.
which causes
blood to Collaborative:
accumulate in
the legs, ankle, -Controlled low sodium with potassium
and feet. diet.
R: Sodium increases the risk of having edema
-MedlinePlus, as sodium attracts water, if accumulated on
2020 one spot, water follows which causes edema.
-Mayo Clinic,
2017 Potassium helps in the cardiac output of the
heart by increasing it.
You might also like
- Possible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionDocument12 pagesPossible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionClaire M. AuditorNo ratings yet
- Addison 'S Disease: A Nursing Care Plan OnDocument7 pagesAddison 'S Disease: A Nursing Care Plan OnKyla FronterasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Elevated Blood Glucose STO: After 4 Hours of Independent: STO: After 4 Hours ofDocument9 pagesSubjective: Elevated Blood Glucose STO: After 4 Hours of Independent: STO: After 4 Hours ofDacillo GailleNo ratings yet
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 pagesNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Nursing Analysis of HyperglycemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Analysis of HyperglycemiaDharylle Cariño100% (3)
- HYPOKALEMIADocument3 pagesHYPOKALEMIADienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1Andrea Marie SevillaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document7 pagesNCP 1Mark PabalanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument3 pagesNutrition Risk Assessment and ManagementSitty Aizah MangotaraNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1AGUSTIN PRECIOUS JOY CNo ratings yet
- Assignment Course Task Week15Document3 pagesAssignment Course Task Week15RAMIL GOPEZNo ratings yet
- Presentation TomorrowDocument8 pagesPresentation TomorrowRafik LakhdarNo ratings yet
- NCP GDMDocument10 pagesNCP GDMmishti94% (17)
- Clinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1Document11 pagesClinical Learning Log 3 Go Solo - Docx-1JezraleFame AntoyNo ratings yet
- NCP HomeworkDocument6 pagesNCP HomeworkAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes NCP SelDocument3 pagesGestational Diabetes NCP Selcherrymae mata100% (3)
- quizzes-NCM116Document10 pagesquizzes-NCM116mendozajanice0601No ratings yet
- NCPs (ABRIAN)Document23 pagesNCPs (ABRIAN)Rouie Björn ABrianNo ratings yet
- NCP Roldan OncoDocument6 pagesNCP Roldan OncoCeegi Arville RoldanNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body RequirementsDocument2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body RequirementsAngel Mae AlsuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Disease Condition:: Hyperemsis Gravidarum: DefinitionDocument4 pagesDisease Condition:: Hyperemsis Gravidarum: DefinitionPriyanka JohnNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Group 9Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan Group 9Joan Antonate MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan for Imbalanced NutritionDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan for Imbalanced Nutritionallkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaPuteri AzmanNo ratings yet
- Department of Nursing: Tarlac State University College of ScienceDocument11 pagesDepartment of Nursing: Tarlac State University College of ScienceDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCM116-RC Valdez Ati PDFDocument6 pagesNCM116-RC Valdez Ati PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient R.MDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Patient R.MAngela Mae DiestroNo ratings yet
- DM Care PlanDocument9 pagesDM Care PlanHarish Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPTin TinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationHanna La MadridNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesDiabetes Nursing Care PlanDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument4 pagesNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan for GI BleedingDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for GI BleedingIvy Villalobos100% (1)
- Hypovolemic Shock Sample NCPDocument14 pagesHypovolemic Shock Sample NCPRENEROSE TORRES100% (1)
- Managing Diabetes and RisksDocument8 pagesManaging Diabetes and RisksChristopher LontocNo ratings yet
- Case 1 - NCP NUTRI LAB 2Document6 pagesCase 1 - NCP NUTRI LAB 2Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal: IndependentasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- Week9 10Document2 pagesWeek9 10jutr ruyluNo ratings yet
- Pih-Ncp - BSN2D ZacalDocument3 pagesPih-Ncp - BSN2D ZacalIllaizah EdictoNo ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan On: Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument7 pagesA Nursing Care Plan On: Rheumatoid ArthritisBethany Paraguya100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- NCP T2DMDocument5 pagesNCP T2DMFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Angel Nieto PengsonNo ratings yet
- Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnDocument17 pagesType 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Discussion OnMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Atient Will Have Oxygen Saturation of Greater Than 95%.: Assess The Client's Ability To Cough Out SecretionsDocument8 pagesAtient Will Have Oxygen Saturation of Greater Than 95%.: Assess The Client's Ability To Cough Out Secretionsella retizaNo ratings yet
- XIX. NCP - Imbalanced NutritionDocument10 pagesXIX. NCP - Imbalanced NutritionTakeOne ForTheTeamNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPDocument4 pagesUncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info NCM 112 Rle Oxygenation PRDocument17 pagesToaz - Info NCM 112 Rle Oxygenation PRAndrea Elaine Joy TorrentoNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorderdepression 1Document11 pagesMood Disorderdepression 1Leslie Lagat PaguioNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Risks, Symptoms and Nursing CareDocument30 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus: Risks, Symptoms and Nursing CareWed LodNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Gastrointestinal BleedingMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument26 pagesDiabetesAlina Juliana MagopetNo ratings yet
- Practical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersFrom EverandPractical Insulin: A Handbook for Prescribing ProvidersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- DRUG STUDY TITLEDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY TITLEunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeunkown userNo ratings yet
- Adult:: Start With 50 MG Q.D., May Increase Slowly Up To 300 MG/D Given Q.H.S. or Divided B.I.DDocument4 pagesAdult:: Start With 50 MG Q.D., May Increase Slowly Up To 300 MG/D Given Q.H.S. or Divided B.I.Dunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetropololDocument3 pagesDrug Study Metropololunkown userNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone drug studyDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone drug studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- CombiventDocument2 pagesCombiventunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- HydrocortisoneDocument3 pagesHydrocortisoneunkown userNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeunkown userNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument1 pageKetorolacunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Initial Dose: 50 MG Orally Once A Day Maintenan Ce Dose: 50 To 200 MG Orally Once A DayDocument2 pagesInitial Dose: 50 MG Orally Once A Day Maintenan Ce Dose: 50 To 200 MG Orally Once A Dayunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: SaluronDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Saluronunkown userNo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol CalpolDocument1 pageParacetamol Calpolunkown userNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's College Bachelor of Science in Nursing Drug Study Salbutamol + IpratropiumDocument1 pageSt. Mary's College Bachelor of Science in Nursing Drug Study Salbutamol + Ipratropiumunkown userNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol + Ipratropium Q 6 HrsDocument1 pageSalbutamol + Ipratropium Q 6 Hrsunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Paroxetine Wsiness, Diz ZinessDocument3 pagesParoxetine Wsiness, Diz Zinessunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: SaluronDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Saluronunkown userNo ratings yet
- Harmful Effects Drugs AlcoholDocument4 pagesHarmful Effects Drugs AlcoholFlorie Fe Rosario OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Micro LectureDocument4 pagesMicro LectureJewel OlaezNo ratings yet
- Nisargastrikesmaharashtracoast: 2 Lac Flashpoints Are Not in List of Identified Areas Still ContestedDocument14 pagesNisargastrikesmaharashtracoast: 2 Lac Flashpoints Are Not in List of Identified Areas Still ContestedTomNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesmentDocument2 pagesRisk AssesmentChristopher Stewart0% (1)
- Statistical Analysis On Risk Factors of Prevalence of Malaria in Z/ Dugda Woreda, Oromia, East ArsiDocument31 pagesStatistical Analysis On Risk Factors of Prevalence of Malaria in Z/ Dugda Woreda, Oromia, East Arsitewodrosmolalign19No ratings yet
- Peritonitis and Abdominal Sepsis: Background, Anatomy, PathophysiologyDocument16 pagesPeritonitis and Abdominal Sepsis: Background, Anatomy, PathophysiologyTias SubagioNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL Assigmnent 1 PDFDocument12 pagesCLINICAL Assigmnent 1 PDFChelly ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Pir June 2015, Volume 36, Issue 6Document55 pagesPir June 2015, Volume 36, Issue 6Angie LuperdiNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJashtine JingcoNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis and HomoeopathyDocument18 pagesDermatitis and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- Managing Hypertension Through Diet and Lifestyle ChangesDocument1 pageManaging Hypertension Through Diet and Lifestyle ChangesChristian Daayata0% (1)
- Cardiac Surgery & Cardiology MCQsDocument18 pagesCardiac Surgery & Cardiology MCQssb medexNo ratings yet
- Research in Public Health by Prof DR Rwamakuba ZephanieDocument120 pagesResearch in Public Health by Prof DR Rwamakuba ZephanieDr Zephanie RwamakubaNo ratings yet
- Aaron Antonovsky - Unraveling The Mystery of Health - How People Manage Stress and Stay Well (JOSSEY BASS SOCIAL and BEHAVIORAL SCIENCE SERIES) - Jossey-Bass (1987)Document235 pagesAaron Antonovsky - Unraveling The Mystery of Health - How People Manage Stress and Stay Well (JOSSEY BASS SOCIAL and BEHAVIORAL SCIENCE SERIES) - Jossey-Bass (1987)Tom KuykenNo ratings yet
- Philippines HIV/AIDS Registry For September 2019Document8 pagesPhilippines HIV/AIDS Registry For September 2019Michael DavidNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1074761321003654 MainDocument35 pages1 s2.0 S1074761321003654 MainIoana BiticaNo ratings yet
- Final AnnouncementDocument14 pagesFinal AnnouncementAziz AndriyantoNo ratings yet
- Case Study On ManiaDocument30 pagesCase Study On ManiaIOM BNS75% (8)
- Oscillococcinum for InfluenzaDocument5 pagesOscillococcinum for InfluenzaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration CardDocument2 pagesHealth Declaration CardJasmin AngieNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: Diseases and Conditions: AppendicitisDocument6 pagesAppendicitis: Diseases and Conditions: AppendicitisWen RodsaNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinDocument35 pagesCephalosporinGavin BirlaNo ratings yet
- ABIS HSE L4 F 01 Risk Assessment FormDocument61 pagesABIS HSE L4 F 01 Risk Assessment FormOvais FarooqNo ratings yet
- K Park - Park's Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine-M - S BANARASIDAS BHANOT Publishers (2019)Document1,008 pagesK Park - Park's Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine-M - S BANARASIDAS BHANOT Publishers (2019)Labib Orcko100% (1)
- MEGALOBLASTIC ANAEMIA - pptxsdd.pptx.4Document30 pagesMEGALOBLASTIC ANAEMIA - pptxsdd.pptx.4Hiba MohammedNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form DOT AmendedDocument1 pageHealth Declaration Form DOT AmendedImee S. YuNo ratings yet
- 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America's Clinical Practice Guidelines For Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and MeningitisDocument32 pages2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America's Clinical Practice Guidelines For Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and MeningitisEugen TarnovschiNo ratings yet
- User Manual: (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound)Document11 pagesUser Manual: (High Intensity Focused Ultrasound)Agha SoroushNo ratings yet
- 00 Obs&Gyn Clerkship-1-1Document9 pages00 Obs&Gyn Clerkship-1-1samwel daniel100% (1)
- Uts 3Document26 pagesUts 3A.J. ChuaNo ratings yet