0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 views4 pagesRadio Frequency Bands Guide
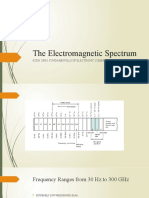
The document describes various radio frequency bands and their typical uses. It lists the frequency range and abbreviation for several bands including extremely low frequency (ELF), super low frequency (SLF), ultra low frequency (ULF) and others up to terahertz or tremendously high frequency (THz or THF). It also provides some example uses within each band such as communication with submarines in ELF/SLF, navigation and time signals in ULF/VLF, and experimental medical imaging and ultrafast molecular dynamics in the THz band.
Uploaded by
Ravindra KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 views4 pagesRadio Frequency Bands Guide
The document describes various radio frequency bands and their typical uses. It lists the frequency range and abbreviation for several bands including extremely low frequency (ELF), super low frequency (SLF), ultra low frequency (ULF) and others up to terahertz or tremendously high frequency (THz or THF). It also provides some example uses within each band such as communication with submarines in ELF/SLF, navigation and time signals in ULF/VLF, and experimental medical imaging and ultrafast molecular dynamics in the THz band.
Uploaded by
Ravindra KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd