Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rhythm Analysis: "How To Determine Axis" ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)
Rhythm Analysis: "How To Determine Axis" ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rhythm Analysis: "How To Determine Axis" ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)
Rhythm Analysis: "How To Determine Axis" ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson II - A "Method of ECG Interpretation
QT interval (from beginning of QRS to end of T)
QRS axis in frontal plane (go to: "How To Determine Axis")
Go to: ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)for description of normal and abnormal
measurements
2. Rhythm Analysis
State basic rhythm (e.g., "normal sinus rhythm", "atrial fibrillation", etc.)
Identify additional rhythm events if present (e.g., "PVC's", "PAC's", etc)
Consider all rhythm events from atria, AV junction, and ventricles
Go to: ECG Rhythm Abnormalities (Lesson V)for description of arrhythmias
3. Conduction Analysis
"Normal"conduction implies normal sino-atrial (SA), atrio-ventricular (AV), and
intraventricular (IV) conduction.
The diagram
illustrates the
normal cardiac
conduction
Click to view
system.
The following conduction abnormalities are to be identified if present:
SA block (lesson VI): 2nd degree (type I vs. type II)
AV block (lesson VI): 1st, 2nd (type I vs. type II), and 3rd degree
IV blocks (lesson VI): bundle branch, fascicular, and nonspecific blocks
Exit blocks: blocks just distal to ectopic pacemaker site
(Go to ECG Conduction Abnormalities (Lesson VI) for a description of
conduction abnormalities)
http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/ecg/ecg_outline/Lesson2/index.html (2 of 4) [5/11/2006 9:39:36 AM]
You might also like
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationFrom EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument1 pageECG InterpretationCecil-An DalanonNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument57 pagesEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- II. Method of ECG InterpretationDocument3 pagesII. Method of ECG Interpretationapi-3769252100% (1)
- Ecg Reading Made EasyDocument59 pagesEcg Reading Made EasyAngealyn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Tutorial PDFDocument82 pagesEcg Tutorial PDFpacpacpac123No ratings yet
- Ebook Ecgs Made Easy 5Th Edition Aehlert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesEbook Ecgs Made Easy 5Th Edition Aehlert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFquynhagneskrv100% (11)
- Ebook Ecgs Made Easy 6Th Edition Aehlert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument40 pagesEbook Ecgs Made Easy 6Th Edition Aehlert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFquynhagneskrv100% (11)
- Ecgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert Test BankDocument18 pagesEcgs Made Easy 5th Edition Aehlert Test Bankhaodienb6qj100% (30)
- ECG Waves and Intervals Spatial Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGDocument31 pagesECG Waves and Intervals Spatial Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGiah_18No ratings yet
- Introduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0Document84 pagesIntroduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0TrickyRooNo ratings yet
- Syncope and Irregular HeartbeatDocument10 pagesSyncope and Irregular HeartbeathalesNo ratings yet
- 5 ECG Interpretation With AnswersDocument48 pages5 ECG Interpretation With AnswersQusai Ibraheem100% (1)
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Dr. Mohamed Hassan MBBS, Mmed (Pediatric), PHDDocument33 pagesElectrocardiogram (Ecg) : Dr. Mohamed Hassan MBBS, Mmed (Pediatric), PHDMohamed Hassan MohamudNo ratings yet
- Lesson V (Cont) Introduction To ECG Rhythm AnalysisDocument1 pageLesson V (Cont) Introduction To ECG Rhythm AnalysisLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- EKGDocument31 pagesEKGJay JiangNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument24 pagesHow To Read An ECGredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Interpretation V10.0 (2017-2018)Document91 pagesIntroduction To Interpretation V10.0 (2017-2018)Muhammad AsrudinNo ratings yet
- 12 - Lead ECG-A Web Brain For Easy InterpretationDocument54 pages12 - Lead ECG-A Web Brain For Easy Interpretatione-kino3692100% (1)
- Ecg PDFDocument87 pagesEcg PDFSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Hotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PDocument145 pagesHotel Dpalma, Bandung 16 Maret 2018: Dr. Benny Prasetya PkangheriNo ratings yet
- BCS EkgDocument55 pagesBCS Ekggita suariyaniNo ratings yet
- 23 Interpreting - ECGs - An - Integrative - ApproachDocument7 pages23 Interpreting - ECGs - An - Integrative - ApproachkrunalNo ratings yet
- Basic ECGDocument14 pagesBasic ECGDexter TurlaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGDocument39 pagesIntroduction To ECGSingey LhendupNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument21 pagesHow To Read An ECGSlychenkoNo ratings yet
- Ecg PDFDocument70 pagesEcg PDFlauras3005No ratings yet
- (PDF.3) Management of Heart AttackDocument33 pages(PDF.3) Management of Heart AttackTheany Be SmilerNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared byDocument16 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared bypipoahmed51No ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGSarah RonquilloNo ratings yet
- ECG Laboratory Activit1Document9 pagesECG Laboratory Activit1Leiraset WuNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers Cardiac External Invasive Electrodes TransvenousDocument6 pagesPacemakers Cardiac External Invasive Electrodes TransvenousEduardoNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsRinothja RajaratnamNo ratings yet
- Practical 2: Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : by - Mohamad Azmir Bin Azizan Medical Lab Technologist Faculty of Medicine UitmDocument19 pagesPractical 2: Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : by - Mohamad Azmir Bin Azizan Medical Lab Technologist Faculty of Medicine UitmraburtonNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGcharlyn206No ratings yet
- P Waves (Lesson VII) : 4. Waveform DescriptionDocument1 pageP Waves (Lesson VII) : 4. Waveform DescriptionLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EkgDocument8 pages12 Lead EkgKarla LopezNo ratings yet
- Final Q Bank CVS Upto Cardiac Output (13-01-2017)Document2 pagesFinal Q Bank CVS Upto Cardiac Output (13-01-2017)faris babuNo ratings yet
- An Approach To ECGDocument42 pagesAn Approach To ECGGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Clinical Relevance of ECGDocument4 pagesClinical Relevance of ECGdrfelixNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Document98 pagesNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Maylisa ManurungNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition by AehlertDocument16 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition by Aehlertpamelachavezbawyoemckf100% (28)
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmia SDocument98 pagesNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmia SAdinda GupitaNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering: EENG424L-Medical Instrumentation I LabDocument8 pagesSchool of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering: EENG424L-Medical Instrumentation I LabMahdi BraitehNo ratings yet
- 8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsDocument76 pages8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Utah EduDocument87 pagesEcg Utah EduMos Viorel DanutNo ratings yet
- 11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFDocument16 pages11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFBìnhNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Flash Cards (EKG in A Nut Shell)Document62 pagesCardiology Flash Cards (EKG in A Nut Shell)Nabeel Kouka, MD, DO, MBA, MPHNo ratings yet
- NMTEC 211-ECG Lab InstructionsDocument4 pagesNMTEC 211-ECG Lab InstructionsRisleNo ratings yet
- ECG in Acute Coronary Syndrome: DR Awadhesh Kumar Sharma Deptt of CardiologyDocument47 pagesECG in Acute Coronary Syndrome: DR Awadhesh Kumar Sharma Deptt of CardiologyIndomedikgramNo ratings yet
- KP 1.3.1.8 Interpretasi Ekg 2014Document27 pagesKP 1.3.1.8 Interpretasi Ekg 2014Try MutiaraNo ratings yet
- Decoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonFrom EverandDecoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonAfzal SohaibNo ratings yet
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachFrom EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
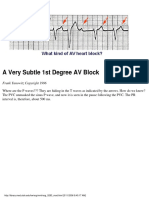
- A Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageA Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 142 7-PDF EcDocument1 page142 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
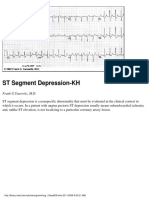
- ST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageLeft Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page129 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
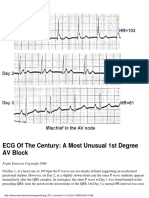
- ECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 126 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page126 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
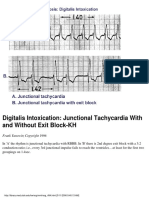
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 137 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page137 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
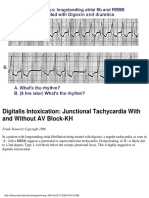
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 135 7-PDF EcDocument1 page135 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 130 7-PDF EcDocument1 page130 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF EcDocument1 page129 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 128 7-PDF EcDocument1 page128 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
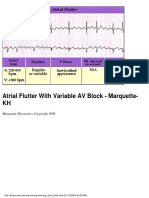
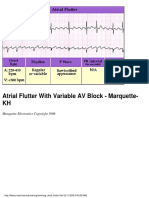
- Atrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet