Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P Waves (Lesson VII) : 4. Waveform Description
P Waves (Lesson VII) : 4. Waveform Description
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P Waves (Lesson VII) : 4. Waveform Description
P Waves (Lesson VII) : 4. Waveform Description
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson II - A "Method of ECG Interpretation
4. Waveform Description
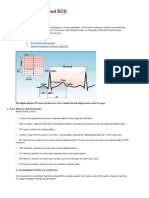
Carefully analyze the 12-lead ECG for abnormalities in each of the waveforms in the order
in which they appear: P-waves, QRS complexes, ST segments, T waves, and... Don't forget
the U waves.
P waves (lesson VII): are they too wide, too tall, look funny (i.e., are they
ectopic), etc.?
QRS complexes: look for pathologic Q waves (lesson IX), abnormal voltage
(lesson VIII), etc.
ST segments (lesson X): look for abnormal ST elevation and/or depression.
T waves (lesson XI): look for abnormally inverted T waves.
U waves (lesson XII): look for prominent or inverted U waves.
5. ECG Interpretation
This is the conclusion of the above analyses. Interpret the ECG as "Normal", or
"Abnormal". Occasionally the term "borderline"is used if unsure about the significance of
certain findings. List all abnormalities. Examples of "abnormal"statements are:
Inferior MI, probably acute
Old anteroseptal MI
Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB)
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)
Nonspecific ST-T wave abnormalities
Any rhythm abnormalities
Example:
http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/ecg/ecg_outline/Lesson2/index.html (3 of 4) [5/11/2006 9:39:36 AM]
You might also like
- Raza's ECGDocument45 pagesRaza's ECGcozmoxxxNo ratings yet
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- ECG Library PDFDocument98 pagesECG Library PDFJayden WaveNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument57 pagesEcgenii_ta100% (9)
- ECG QuizDocument25 pagesECG QuizBryan DorosanNo ratings yet
- II. Method of ECG InterpretationDocument3 pagesII. Method of ECG Interpretationapi-3769252100% (1)
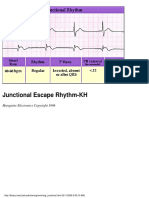
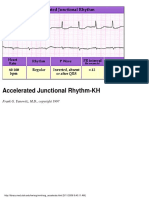
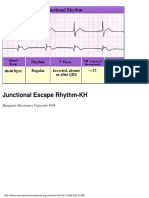
- Rhythm Analysis: "How To Determine Axis" ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)Document1 pageRhythm Analysis: "How To Determine Axis" ECG Measurement Abnormalities (Lesson IV)Lwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- NMTEC 211-ECG Lab InstructionsDocument4 pagesNMTEC 211-ECG Lab InstructionsRisleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0Document84 pagesIntroduction To EKG Interpretation v8.0TrickyRooNo ratings yet
- Ecg Reading Made EasyDocument59 pagesEcg Reading Made EasyAngealyn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Tutorial PDFDocument82 pagesEcg Tutorial PDFpacpacpac123No ratings yet
- Rythms in Als Course by JJJCDocument6 pagesRythms in Als Course by JJJCjasoncalderonsanNo ratings yet
- Ecg PDFDocument87 pagesEcg PDFSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- ECG EKG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG EKG InterpretationGunma AkagiNo ratings yet
- Lia TrapaidzeDocument32 pagesLia TrapaidzeShubham TanwarNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: (E.g., Lead II, III, V4-6)Document1 pageClick Here To View: (E.g., Lead II, III, V4-6)Lwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Lesson V (Cont) Introduction To ECG Rhythm AnalysisDocument1 pageLesson V (Cont) Introduction To ECG Rhythm AnalysisLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- EKGDocument31 pagesEKGJay JiangNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmia SDocument98 pagesNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmia SAdinda GupitaNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Document98 pagesNormal Ecg, Infarction & Arrhythmias: Iqbal Lahmadi Departement of Internal Medicine Sintang - 2013Maylisa ManurungNo ratings yet
- DR Kupe - ECGDocument14 pagesDR Kupe - ECGIrfan ZiadNo ratings yet
- A El Outline June 2007Document82 pagesA El Outline June 2007neysaonlineNo ratings yet
- ECG Waves and Intervals Spatial Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGDocument31 pagesECG Waves and Intervals Spatial Orientation of The 12 Lead ECGiah_18No ratings yet
- Introduction To Interpretation V10.0 (2017-2018)Document91 pagesIntroduction To Interpretation V10.0 (2017-2018)Muhammad AsrudinNo ratings yet
- Lesson V (Cont) Supraventricular ArrhythmiasDocument1 pageLesson V (Cont) Supraventricular ArrhythmiasLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 5 ECG Interpretation With AnswersDocument48 pages5 ECG Interpretation With AnswersQusai Ibraheem100% (1)
- 38 7-PDF EcDocument1 page38 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG Approach by DR SSSDocument51 pagesECG Approach by DR SSSAritro DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation EkgDocument6 pagesDissertation EkgBuyACollegePaperOnlineMilwaukee100% (1)
- XII. Nice Seeing "U" Again: Frank G. Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine University of Utah School of MedicineDocument1 pageXII. Nice Seeing "U" Again: Frank G. Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine University of Utah School of MedicineLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Criterii EKG Mayo ClinicDocument45 pagesCriterii EKG Mayo ClinicAnca LunguNo ratings yet
- An Approach To ECGDocument42 pagesAn Approach To ECGGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Clinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document24 pagesClinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)soniya josephNo ratings yet
- XI. T Wave Abnormalities: Frank G. Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine University of Utah School of MedicineDocument1 pageXI. T Wave Abnormalities: Frank G. Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine University of Utah School of MedicineLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Ecg Utah EduDocument87 pagesEcg Utah EduMos Viorel DanutNo ratings yet
- ECG TutorialDocument74 pagesECG TutorialIrina Triboi AmariiNo ratings yet
- (PDF.3) Management of Heart AttackDocument33 pages(PDF.3) Management of Heart AttackTheany Be SmilerNo ratings yet
- ECG Made EasyDocument82 pagesECG Made EasyBobby SodhiNo ratings yet
- ECG Master Class-2Document138 pagesECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Basic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALDocument16 pagesBasic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALCharlotte James100% (5)
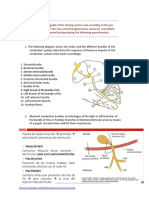
- Driving System Team 5Document3 pagesDriving System Team 5api-594276188No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular EKG's AtfDocument4 pagesCardiovascular EKG's AtfMariaNo ratings yet
- Syncope and Irregular HeartbeatDocument10 pagesSyncope and Irregular HeartbeathalesNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument11 pagesEcgRajneesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- ECG Laboratory Activit1Document9 pagesECG Laboratory Activit1Leiraset WuNo ratings yet
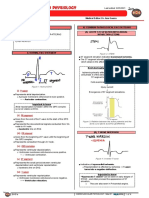
- 009 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular - EKG SDocument4 pages009 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular - EKG SSWATHIKA LNo ratings yet
- CCR 10 190Document12 pagesCCR 10 190Andrea BertoliniNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECG (Dr. MD Kalimuddin)Document53 pagesBasics of ECG (Dr. MD Kalimuddin)CloudySkyNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDocument76 pagesElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial CentreDocument90 pagesECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial Centrevaishali TayadeNo ratings yet
- Ecg 4Document18 pagesEcg 4api-3757039100% (3)
- I. The Standard 12 Lead ECGDocument2 pagesI. The Standard 12 Lead ECGapi-376925250% (2)
- Ecg PDFDocument70 pagesEcg PDFlauras3005No ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument48 pagesECG InterpretationKervayse St.ClairNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram NotesDocument23 pagesElectrocardiogram NotesSanjay RanaNo ratings yet
- Decoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonFrom EverandDecoding Cardiac Electrophysiology: Understanding the Techniques and Defining the JargonAfzal SohaibNo ratings yet
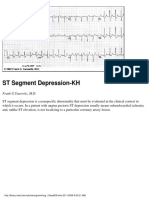
- ST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
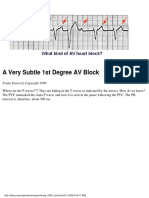
- A Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageA Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
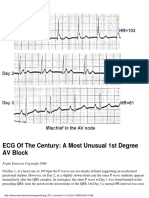
- ECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 142 7-PDF EcDocument1 page142 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 137 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page137 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
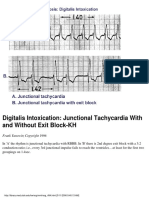
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
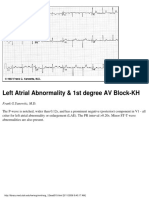
- Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageLeft Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
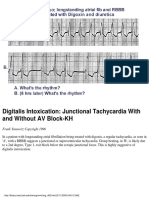
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 135 7-PDF EcDocument1 page135 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page129 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 130 7-PDF EcDocument1 page130 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF EcDocument1 page129 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 128 7-PDF EcDocument1 page128 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 126 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page126 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
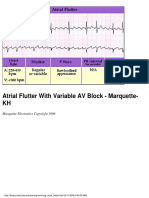
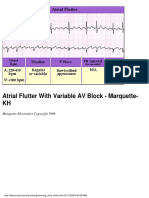
- Atrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet