Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eng4u4a4traditional Vs Structural Linguistics 1
Uploaded by
api-272459379Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eng4u4a4traditional Vs Structural Linguistics 1
Uploaded by
api-272459379Copyright:
Available Formats
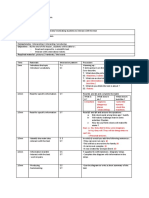
Traditional Linguistics Structural (functional) Linguistics
8 classifications/parts of speech 12 morphological classifications
Deals with/emphasizes written English Deals with/emphasizes spoken English
Is prescriptive (“prescribes”/tells the Is descriptive (describes the way people
correct way of speaking) *clear rules* talk)
● Auxiliaries are classified as verbs ● The analysis begins with word forms
● Determiners are classified as & works back toward meaning
adjectives ● Makes generalizations about English
● Interrogatives overlap with pronouns rather than formulates specific rules
& adverbs (may view tradition grammar as
● Primarily concerned with having “archaic” rules)
morphology (relationship of one part ● Emphasis placed on grammatical
of a word to another part of a word) meaning rather than semantic
& syntax (relationships among ● Define word class according to
words; the way words make patterns syntax (relationships among words;
to form sentences) the way words make patterns to
● Traditional functional grammar is form sentences) & morphology
essential to clear writing. The reader (relationship of one part of a word to
is absent & cannot ask the writer to another part of a word)
clarify the ideas; must be clear to be ● Also, concerned with the study of
understood. sounds
● Doesn’t let you write like you talk. ● Emphasis on phonemes, stress,
● Doesn’t let you end a sentence in a pitch, & juncture (pauses)
preposition.
● Doesn’t let you start a sentence with ● Shares same names with Traditional
“And.” Linguistics for
○ Nouns
● The 8 parts of speech: ○ Verbs
○ Nouns ○ Adjectives
○ Verbs ○ Adverbs
○ Adjectives ● Other 8 are called function words
○ Adverbs ○ Auxiliares
○ Pronoun ○ Prepositions
○ Interjection ○ Determiners
○ Preposition ○ Conjunctions
○ Conjunction ○ Pronouns
○ Interrogatives
○ Intensives
○ “Empty” words
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- An Introduction To French PronunciationDocument185 pagesAn Introduction To French Pronunciationbycsx100% (3)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lesson One: Phonology and phonetics overviewDocument110 pagesLesson One: Phonology and phonetics overviewhafid100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Difference Between Context and Content ExplainedDocument6 pagesDifference Between Context and Content ExplainedMelissa Kayla Maniulit100% (1)
- Answering Important Conversational Questions in SpanishDocument4 pagesAnswering Important Conversational Questions in Spanishapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Eng4 Elements of Poetry of The Romantic RevolutionDocument2 pagesEng4 Elements of Poetry of The Romantic Revolutionapi-272459379No ratings yet
- E4u4a5generative TransformationalgrammarDocument3 pagesE4u4a5generative Transformationalgrammarapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Eng 4 Unit 1 1Document4 pagesEng 4 Unit 1 1api-272459379No ratings yet
- Eng 4 TinternabbeyDocument1 pageEng 4 Tinternabbeyapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Eng 3 U 3 A 7 Pronounproblem 2Document4 pagesEng 3 U 3 A 7 Pronounproblem 2api-272459379No ratings yet
- Spelling Study TipsDocument2 pagesSpelling Study Tipsapi-272459379No ratings yet
- The Novelisteng2unit7a6Document3 pagesThe Novelisteng2unit7a6api-272459379No ratings yet
- ObjectpronounschartDocument1 pageObjectpronounschartapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Spanishpillarsofresearchspanish Speaking Country Pillars of ResearchDocument1 pageSpanishpillarsofresearchspanish Speaking Country Pillars of Researchapi-272459379No ratings yet
- NovelistbeselectiveDocument1 pageNovelistbeselectiveapi-272459379No ratings yet
- FivemajorwayslanguagecanchangevarietiesofenglishDocument2 pagesFivemajorwayslanguagecanchangevarietiesofenglishapi-272459379No ratings yet
- SaberconocerDocument2 pagesSaberconocerapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Types of NovelsDocument2 pagesTypes of Novelsapi-272459379No ratings yet
- English Ivunit 8wordsworth ByronDocument1 pageEnglish Ivunit 8wordsworth Byronapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Pronouncasee 3 U 3 A 5Document4 pagesPronouncasee 3 U 3 A 5api-272459379No ratings yet
- Spelling Practice Ways To Study Your Spelling WordsDocument1 pageSpelling Practice Ways To Study Your Spelling Wordsapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Preterit VsimperfectnotesDocument2 pagesPreterit Vsimperfectnotesapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Ar VerbsDocument1 pageAr Verbsapi-272459379No ratings yet
- PinotesDocument2 pagesPinotesapi-272459379No ratings yet
- SpanishstudytipsseaDocument1 pageSpanishstudytipsseaapi-272459379No ratings yet
- FromjoshuatoruthDocument3 pagesFromjoshuatoruthapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Commands Babysitting Your NeighborDocument1 pageCommands Babysitting Your Neighborapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Aj ShireysoccerrecommendationDocument1 pageAj Shireysoccerrecommendationapi-272459379No ratings yet
- UsingestarcorrectlyDocument1 pageUsingestarcorrectlyapi-272459379No ratings yet
- What Is A Thesis StatementDocument1 pageWhat Is A Thesis Statementapi-272459379No ratings yet
- Psalms Categoriesbible700unit6Document4 pagesPsalms Categoriesbible700unit6api-272459379No ratings yet
- FromcreationtomosesDocument2 pagesFromcreationtomosesapi-272459379No ratings yet
- A J Letter 3Document1 pageA J Letter 3api-272459379No ratings yet
- Project BasedDocument10 pagesProject BasedNancy CervantesNo ratings yet
- Collaborative LearningDocument24 pagesCollaborative LearningJamilah VzqzNo ratings yet
- The Great Eskimo Vocabulary Hoax: Chapter NineteenDocument8 pagesThe Great Eskimo Vocabulary Hoax: Chapter NineteenKirbyWadNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Causes of Grammatical Errors For Esl TeachersDocument4 pagesRevisiting Causes of Grammatical Errors For Esl TeachersEvanessa VillacrusisNo ratings yet
- Lexemes, Lexicons and Paraphrases DefinedDocument4 pagesLexemes, Lexicons and Paraphrases DefinedMarissa Swanda TupamahuNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Place & Manner of Articulation (Consonants)Document19 pagesWeek 2 Place & Manner of Articulation (Consonants)yulisyafaNo ratings yet
- English FAL P3 Grade 11 Nov 2019.pdf RDocument8 pagesEnglish FAL P3 Grade 11 Nov 2019.pdf Rmmatliphuti08No ratings yet
- Parallel Structure with Paired ConjunctionsDocument6 pagesParallel Structure with Paired ConjunctionsDing DongNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument16 pagesChapter IiTitilayomi EhireNo ratings yet
- In-Depth Interviews - Definition and How To Conduct Them - QuestionProDocument5 pagesIn-Depth Interviews - Definition and How To Conduct Them - QuestionProJyka Shayne LimNo ratings yet
- Social SciencesDocument13 pagesSocial SciencesHải Đoàn NamNo ratings yet
- Thestoriesofciroandbeba PDFDocument8 pagesThestoriesofciroandbeba PDFjulzcatNo ratings yet
- Diversity Lesson Plan-I Am MixedDocument5 pagesDiversity Lesson Plan-I Am Mixedapi-297649375No ratings yet
- Sách giáo trình Tiếng Anh 2.1Document41 pagesSách giáo trình Tiếng Anh 2.1Thiên PhúcNo ratings yet
- G.5 - Learning Burden PPT REVDocument38 pagesG.5 - Learning Burden PPT REVandri jupanoNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm M3Document33 pagesOral Comm M3Ednel Fritz P. MadridondoNo ratings yet
- Name of Presenter: - Oral Presentation Rubric Criteria Distinguished (4) Proficient (3) Basic (2) UnacceptableDocument2 pagesName of Presenter: - Oral Presentation Rubric Criteria Distinguished (4) Proficient (3) Basic (2) UnacceptableCNSC IFMS BSFi 3A manilaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 5 - Q1 - W1Document5 pagesDLL - Math 5 - Q1 - W1marivic dyNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ENGL - Learning Actvity 001Document5 pagesGrade 11 ENGL - Learning Actvity 001Christopher CamiloNo ratings yet
- UNIDAD 4 SUCCESSFUL INTERVIEW PREPARATIONDocument5 pagesUNIDAD 4 SUCCESSFUL INTERVIEW PREPARATIONcharlyNo ratings yet
- Philippine English Exam Table of SpecificationsDocument4 pagesPhilippine English Exam Table of SpecificationsMatet GenerosaNo ratings yet
- Mobile MarketingDocument8 pagesMobile Marketinglekid57996No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlannounaNo ratings yet
- 5 Myths About English Language Learners (ELLs) and Special Education Colorín ColoradoDocument10 pages5 Myths About English Language Learners (ELLs) and Special Education Colorín ColoradoEdgar De La MoraNo ratings yet
- Using the 'New Cutting Edge' at Indonesian High SchoolsDocument9 pagesUsing the 'New Cutting Edge' at Indonesian High SchoolsAhmed Ra'efNo ratings yet
- 13-Precise Praise Feedback SheetDocument1 page13-Precise Praise Feedback Sheetapi-331619242No ratings yet
- Making Type 1 Fonts For VietnameseDocument6 pagesMaking Type 1 Fonts For VietnameseMihaiLeonteNo ratings yet