Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDF
Uploaded by
Manila NandaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDF
Uploaded by
Manila NandaCopyright:
Available Formats
ndlle
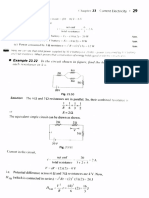
INTRODUCTORY E
distributed
on
a
the centre of mass f the dis
c e n t r e
r
t h r o u g h
disc.
the
p a s s i n g
u n i f o r m l y
axis of
is m o m e n t
q an
ant-
(angular mome
charge about
. A w m a g n e t i c
moment=
speed
Oert
M a g n e t i c
a n g u l a r the
Find distribution:
plane.
to its
charge o of
20A
cm
Forany of 8.0
aivent
loop is giveniby 0.60i-080
Hint: radius
having
a o f the
Mof
M 0i
of wire
loop of Wie
a
dipole
moment
m o m e n t
(O.25 T) i + (0.30 .30 T)k find,
circular
by B
circular =
the
2. A parallel
to
given
and field
ength magnetic
uniform
ocated in and
loop loop.
on the of the
the torgue energy
that if t
the wire is formed
wire is formed nto a crola
(8) potential
when the
Show
(6) the
magnetic
current i. the coil has
of wire
carries a
magnetic
field is
developed
one tur
3. A lengthL
torque
in a given t =L I B / 4 T .
maximum magnitude
has the
is oriented initially with ts
initially
maximum
torque
1.45 A-m the change mary
4. A coil with
magnetic
uniform
moment
0.835
Tmagnetic
field. Whati
moment
parallel
otential
o l eene
the ffielc
is parallel to the
antiparallel to
a magnetic
that its
rotated 180° so
when it is wwww. ****"
wwwww**************
Law
5.7 Biot Savartarticles, discussed the
magnetic force
exerted on a
a
magnetic field. To
we
In the preceding conductor n a
and current carrying the next article
charged particle interaction, this and
magnetic
complete the description of the field. As in electrostatics,
there are two
deals with the origin of the magnetic
One is Coulomb's law
the electric field at some point.
methods of calculating and the another is Gauss's
which gives the electric field due to point charge
a
law which is useful in calculating the electric
field ofa highly symmetric
configuration of charge. Similarly, in magnetics, there are basically two
methods ofcalculating magnetic field at some point. One is Biot Savart law
Fi
which gives the magnetic field due to an infinitesimally small current
carrying wire at some point and the another is Ampere's law, which is useful ino
magnetic field of a highly symmetric configuration carrying a steady current.
We begin by showing how to the law of Biot and Savart to calculate the magnene-
use
at some point in
space by a small current element. Using this formalism and
superposition, we then calculate the total magnetic field due to various current listril-
From their u
experimental results, Biot and Savart arrived at a "essior
magnetic field at some point in space in mathematical Th=
terms of the current that
baseda on the folowing experimental observations for the produces the
with length element dl of a wire magnetic field dB a aP
carrying a steady current i.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Snell's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesSnell's Law WorksheetCamille Rose Basbas100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07 Nov 2020Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07 Nov 2020Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDFDocument1 pageAdobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDFManila NandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07 Nov 2020Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDFDocument1 pageAdobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDFManila NandaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyDocument2 pagesChemistry Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyManila NandaNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyDocument2 pagesMaths Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyManila NandaNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyDocument2 pagesMaths Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyManila NandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPhysics Paper 1. JEE (Advanced) 2020. Tentative Answer Key. Section 1 Question No. Answer KeyManila NandaNo ratings yet
- A) Academic AchievementDocument4 pagesA) Academic AchievementManila Nanda100% (1)
- Questions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Document12 pagesQuestions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Document11 pagesQuestions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- A Thing of Beauty: Literary DevicesDocument5 pagesA Thing of Beauty: Literary DevicesManila NandaNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF PHYSICS PORTION OF JEE (MAIN) 2020 (2nd September Morning)Document3 pagesANALYSIS OF PHYSICS PORTION OF JEE (MAIN) 2020 (2nd September Morning)Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Document12 pagesQuestions & Answers: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Document19 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2020 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- By: Eng. SPARS Jayathilaka Senior Lecturer UnivotecDocument29 pagesBy: Eng. SPARS Jayathilaka Senior Lecturer Univotecandrew smithNo ratings yet
- TL1838 Infrared Receiver Datasheet: 1. FeaturesDocument4 pagesTL1838 Infrared Receiver Datasheet: 1. FeaturesAndy DanteNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Field Paper 1Document5 pagesElectric Charges and Field Paper 1KabilanNo ratings yet
- MT Procedure AsmeDocument4 pagesMT Procedure AsmeMartinNo ratings yet
- NDT Eddy CurrentsDocument13 pagesNDT Eddy Currentsyashwant verma100% (1)
- EE 405 LectureNotes 1Document16 pagesEE 405 LectureNotes 1Maaz AwanNo ratings yet
- Moog Servo Valves CatalogueDocument20 pagesMoog Servo Valves Cataloguemt.sasongkoNo ratings yet
- Motwane - Oil BDVDocument34 pagesMotwane - Oil BDVvikash kumarNo ratings yet
- 8 Static ElectricityDocument11 pages8 Static ElectricityHasan CosalevNo ratings yet
- Class-D LC Filter Design: Application ReportDocument20 pagesClass-D LC Filter Design: Application ReportAung Khaing PhyoNo ratings yet
- Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems: Unit 5Document30 pagesTransducers and Data Acquisition Systems: Unit 5Vineela ThonduriNo ratings yet
- MIL-HDBK-225A Synchros Description and OperationDocument236 pagesMIL-HDBK-225A Synchros Description and OperationBob MatreciNo ratings yet
- CH 28Document63 pagesCH 28mariamNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5 Capacitive Circuit ObjectivesDocument4 pagesActivity No. 5 Capacitive Circuit ObjectivesJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- KamDocument4 pagesKamRoyyan Hasmi FadhillahNo ratings yet
- To Understand The Working of PotentiostatDocument5 pagesTo Understand The Working of PotentiostatRaza AliNo ratings yet
- KILOVAC Current Sensing (KCS) Contactors From TE - 2386 - KCS01 - Bro - R1 PDFDocument8 pagesKILOVAC Current Sensing (KCS) Contactors From TE - 2386 - KCS01 - Bro - R1 PDFDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Power Systems Page-5Document3 pagesMultiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Power Systems Page-5RitNo ratings yet
- Ali Imran (FA17-BCS-047) A03Document6 pagesAli Imran (FA17-BCS-047) A03Ali ImranNo ratings yet
- A Four-Port MIMO Antenna Using Concentric Square-Ring Patches Loaded With CSRR For High IsolationDocument4 pagesA Four-Port MIMO Antenna Using Concentric Square-Ring Patches Loaded With CSRR For High IsolationcgakalyaNo ratings yet
- Laser Doppler and Phase Doppler Measurement TechniquesDocument2 pagesLaser Doppler and Phase Doppler Measurement TechniquesFemurNo ratings yet
- The Production of WaterDocument6 pagesThe Production of Waterlyn amianitNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - 1Document2 pagesHome Assignment - 1chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- 5824 3181 PDFDocument2 pages5824 3181 PDFMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Acces Point - Ee Refresher 1Document13 pagesAcces Point - Ee Refresher 1christinesarah0925No ratings yet
- Iec 60282 - 2 - 2008 - en - 19Document19 pagesIec 60282 - 2 - 2008 - en - 19Lee HeonbeomNo ratings yet
- Electricity Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocument6 pagesElectricity Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Sciencepdthedon007No ratings yet
- Service Manual: TA-E9000ESDocument130 pagesService Manual: TA-E9000ESНиколай СорокинNo ratings yet
- Home Depot Inventory Form Sept. 2020Document38 pagesHome Depot Inventory Form Sept. 2020Salvador G. YadaoNo ratings yet