Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer Protection Chapter 9: - Mangetizing Inrush Current - Overexcitation - CT Saturation
Uploaded by
Aakash Nawab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageTransformer Protection key points
Original Title
Chapter 9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTransformer Protection key points
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageTransformer Protection Chapter 9: - Mangetizing Inrush Current - Overexcitation - CT Saturation
Uploaded by
Aakash NawabTransformer Protection key points
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Transformer protection chapter 9
Transformer short circuit current
Reduce applied voltage at the primary side
1. Nominal voltage is applied at the primary in case of phase to phase fault in the field
2. Current full load divided by rated voltage gives us the percentage impedances
Net flux on the transformer remains constant.
Main objective of transformer protection is to provide ability to detect internal faults with high
sensitivities. It should only response to internal faults
Transformer are mostly overload and operates at the knee of characteristic of transformer
loading
When transformer is connected to generator if primary voltage at transformer increases it is
overexcitation.
1. Overload
2. Over excitation
3. through fault
Several methods to provide protection to transformer
Fault switch
Transfer trip
Limited fault- interrupting device
Factors affecting Differential protection
• Mangetizing inrush current
Initial current required to energize the transformer
• Overexcitation
• CT saturation
Differential voltage levels
Phase shifts in wye delta connected banks
Transformer taps for voltage control
Phase shift or voltage taps in regulating transformer
Taps are used for accommodating small changes in voltage we used tape changer.
False differential current:
Mangnetiziation inrush
When system voltage is applied to the transformer at normal conditions then a current transient
occurs know as magnetizing in rush current.
Residual flux
It is already present in the winding of the transformer
9.1 to 9.8 we have studied chapter 9
You might also like
- Distribution System Modeling and AnalysisDocument30 pagesDistribution System Modeling and AnalysisAakash Nawab0% (1)
- Transformer ProtectionDocument28 pagesTransformer ProtectionRajeev Lochan Swain71% (7)
- Overvoltage ProtectionDocument12 pagesOvervoltage Protection1453hNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter-4 Power System Apparatus ProtectionDocument26 pagesChapter-4 Power System Apparatus ProtectionKeneni AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 4Document4 pagesAssignment No 4NomanNo ratings yet
- 87T Protection SchemeDocument12 pages87T Protection Schemedskymaximus100% (1)
- Detection and Classification of Magnetizing Inrush and Interturn Fault Current in Transformer: Signal Processing ApproachDocument5 pagesDetection and Classification of Magnetizing Inrush and Interturn Fault Current in Transformer: Signal Processing ApproachIshwari KhaireNo ratings yet
- Protectionofpowertransformer 130727035128 Phpapp02 PDFDocument19 pagesProtectionofpowertransformer 130727035128 Phpapp02 PDFKarthik Kumar100% (1)
- Protection of Power TransformerDocument19 pagesProtection of Power TransformerRitesh Verma100% (2)
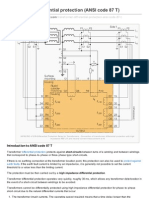
- Transformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87TDocument4 pagesTransformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87TBabar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Eet 308 SP2 V2Document14 pagesEet 308 SP2 V2RK KNo ratings yet
- Papers and Summaries On Stator Earth Fault ProtectionDocument3 pagesPapers and Summaries On Stator Earth Fault ProtectionMfundo NgobeseNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument11 pagesLab 1 Introduction To Power System Protectionsaud aliNo ratings yet
- Differential ProtectionDocument20 pagesDifferential ProtectionsherubdNo ratings yet
- Eel 3086 Switchgear and Protection Experiment 2 Differential Protection of A Three-Phase Transformer ObjectiveDocument15 pagesEel 3086 Switchgear and Protection Experiment 2 Differential Protection of A Three-Phase Transformer ObjectiveEngr Fahimuddin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii: Long-Duration Voltage VariationsDocument10 pagesUnit Iii: Long-Duration Voltage Variationslvb123No ratings yet
- Sizing of Instrument Transformer For 66 KV Ukai Left Branch Canal (LBC) Lift Irrigation SchemeDocument36 pagesSizing of Instrument Transformer For 66 KV Ukai Left Branch Canal (LBC) Lift Irrigation SchemeSumitNo ratings yet
- Transformer Differential ProtectionDocument5 pagesTransformer Differential ProtectionKarthick RathinasamyNo ratings yet
- Application of Over Voltage Protection To The Peruvian Power SystemDocument6 pagesApplication of Over Voltage Protection To The Peruvian Power Systemyofre24No ratings yet
- Generator Earthing and Stator Earth Fault ProtectionDocument9 pagesGenerator Earthing and Stator Earth Fault ProtectionYousif_AbdalhalimNo ratings yet
- Transformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TDocument4 pagesTransformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TFarooq KhanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Transformer FaultDocument4 pages3 - Transformer FaultJoseph FaresNo ratings yet
- KUET LAB SheetDocument49 pagesKUET LAB SheetchristopherNo ratings yet
- Transformer ProtectionDocument11 pagesTransformer ProtectionfirmanNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Inrush PDFDocument2 pagesSympathetic Inrush PDFAhmadNo ratings yet
- Chap-2-Transient Over VoltagesDocument68 pagesChap-2-Transient Over VoltageschalaNo ratings yet
- Impedance CalculationDocument1 pageImpedance Calculationamulya5No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Current TransformerDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Current TransformerVenkata Suresh MandavaNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent Relay Part 1Document5 pagesTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relay Part 1shobhit9tomarNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Magnetizing Inrush CurrentDocument7 pagesReduction of Magnetizing Inrush CurrentBruno MoraesNo ratings yet
- Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer Using Micro-ControllerDocument6 pagesAutomatic Load Sharing of Transformer Using Micro-ControllerSarang AbadagireNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection MethodsDocument22 pagesTransformer Protection Methodsmaneesh_03No ratings yet
- Introduction to Instrument TransformersDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Instrument TransformersVenkata Suresh MandavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7Ahmed Said GhonimyNo ratings yet
- Power System Lab Exp 3Document3 pagesPower System Lab Exp 3Riya PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 16Ee5T14 Electrical Measurements: Measuring InstrumentsDocument18 pages16Ee5T14 Electrical Measurements: Measuring InstrumentsJaya Prasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- 12 Steps For Designing Toroidal TransformersDocument9 pages12 Steps For Designing Toroidal TransformersFernando SotoNo ratings yet
- Differential Protection Explained - Principles, Design & ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesDifferential Protection Explained - Principles, Design & Considerationsjagadeesh_kumar_20No ratings yet
- Transformer PtotectionsDocument19 pagesTransformer Ptotectionsbiju singhNo ratings yet
- Application of Wavelet Transform in DiscDocument12 pagesApplication of Wavelet Transform in Discwaael abdulhassanNo ratings yet
- Lec5 Transformer ProtectionDocument48 pagesLec5 Transformer ProtectionEVTNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer ProtectionDocument27 pagesPower Transformer ProtectionrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Primary-Side Transformer ProtectionDocument15 pagesPrimary-Side Transformer ProtectionRicarno Sei'koNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformer: National Power Training Institute of NigeriaDocument34 pagesInstrument Transformer: National Power Training Institute of NigeriaMůąxxïęm à MøhďNo ratings yet
- Transformer-Protection 112511Document17 pagesTransformer-Protection 112511MileNo ratings yet
- Long Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load SheddingDocument4 pagesLong Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load Sheddingkrishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Inrush Current Detection & Harmonic Sharing in Differential Relay ProtectionDocument6 pagesPower Transformer Inrush Current Detection & Harmonic Sharing in Differential Relay ProtectionasrinivasareddyNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document9 pagesPaper 1Hana AliNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection 22-10-2020Document28 pagesTransformer Protection 22-10-2020abu sayedNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection - 2Document34 pagesTransformer Protection - 2Naveed RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Insem ReportDocument42 pagesInsem Reportsmartxdigital marketNo ratings yet
- An Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer Using Phase Locked Loop SynchronizationDocument4 pagesAn Automatic Load Sharing of Transformer Using Phase Locked Loop SynchronizationKudzai DubeNo ratings yet
- Over Current RelayDocument11 pagesOver Current RelayTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- Polyfuse Report MaterialDocument53 pagesPolyfuse Report Materialgauravpgi4567% (3)
- GeneratorDocument38 pagesGeneratorHari Krishna.M100% (1)
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent RelayDocument10 pagesTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relayhasbi fadliNo ratings yet
- EE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedDocument12 pagesEE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedarivurpNo ratings yet
- Rotor Earth Fault Protection-NewDocument16 pagesRotor Earth Fault Protection-NewssvasavaongcNo ratings yet
- ENG451 - 6 - Power System ProtectionDocument31 pagesENG451 - 6 - Power System ProtectionSM FerdousNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument19 pagesReportAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 2Document5 pagesMini Project 2Aakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument25 pagesTransmission LinesEricoVale100% (1)
- 1.2 Solved Problems Limits at Infinity - ENDocument24 pages1.2 Solved Problems Limits at Infinity - ENAdrian TandogNo ratings yet
- Poster@IcepeDocument1 pagePoster@IcepeAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementChapter 3Document103 pagesProject ManagementChapter 3Erica UyNo ratings yet
- 2 A2-Case-StudyDocument7 pages2 A2-Case-StudyAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - NewDocument1 pageQuiz 1 - NewAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Chap 03 Solutions Ex 3 1 Method PDFDocument18 pagesChap 03 Solutions Ex 3 1 Method PDFAnzaarNo ratings yet
- CH07sDocument13 pagesCH07sTricia DazaNo ratings yet
- PG Notes-1Document22 pagesPG Notes-1Aakash NawabNo ratings yet
- UET Taxila Admissions: Entry 2016Document4 pagesUET Taxila Admissions: Entry 2016Aakash NawabNo ratings yet
- 2017 10 08 Single Line DiagramDocument1 page2017 10 08 Single Line DiagramAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Chap 03 Solutions Ex 3 1 Method PDFDocument18 pagesChap 03 Solutions Ex 3 1 Method PDFAnzaarNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae de FahadDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae de FahadAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Chap 03 Solutions Ex 3 2 MethodDocument23 pagesChap 03 Solutions Ex 3 2 MethodAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Cvwritingslides 100301095539 Phpapp01Document14 pagesCvwritingslides 100301095539 Phpapp01Aakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills NotesDocument19 pagesCommunication Skills NotesAakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6.pdf Filename - UTF-8''Assignment#6Document3 pagesAssignment - 6.pdf Filename - UTF-8''Assignment#6Aakash NawabNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument7 pagesPart of SpeechAakash NawabNo ratings yet