Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value Biotin
Uploaded by
issaiahnicolle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views6 pagesThe document provides information on vitamins and minerals, including their functions, dietary sources, and daily value recommendations. It lists 15 vitamins (Biotin, Folate, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid, Riboflavin, Thiamin, Vitamins A, B6, B12, C, D, E, K) and 2 minerals (Calcium, Chloride), describing what each does in the body and examples of common foods where each can be found. The daily value recommendations aim to support overall health for Americans aged 4 and older.
Original Description:
Original Title
Vitamin_and_Mineral_Chart.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on vitamins and minerals, including their functions, dietary sources, and daily value recommendations. It lists 15 vitamins (Biotin, Folate, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid, Riboflavin, Thiamin, Vitamins A, B6, B12, C, D, E, K) and 2 minerals (Calcium, Chloride), describing what each does in the body and examples of common foods where each can be found. The daily value recommendations aim to support overall health for Americans aged 4 and older.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views6 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value Biotin
Uploaded by
issaiahnicolleThe document provides information on vitamins and minerals, including their functions, dietary sources, and daily value recommendations. It lists 15 vitamins (Biotin, Folate, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid, Riboflavin, Thiamin, Vitamins A, B6, B12, C, D, E, K) and 2 minerals (Calcium, Chloride), describing what each does in the body and examples of common foods where each can be found. The daily value recommendations aim to support overall health for Americans aged 4 and older.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Vitamins
VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES WHERE IS IT FOUND DAILY
VALUE*
Biotin • Energy storage • Avocados 300 mcg
• Protein, carbohydrate, • Cauliflower
and fat metabolism • Eggs
• Fruits (e.g., raspberries)
• Liver
• Pork
• Salmon
• Whole grains
Folate/Folic • Prevention of birth defects • Asparagus 400 mcg
Acid • Protein metabolism • Avocado
Important for • Red blood cell formation • Beans and peas
pregnant women and • Enriched grain products (e.g.,
bread, cereal, pasta, rice)
women capable of
becoming pregnant • Green leafy vegetables (e.g.,
spinach)
• Orange juice
Niacin • Cholesterol production • Beans 20 mg
• Conversion of food into • Beef
energy • Enriched grain products (e.g.,
• Digestion bread, cereal, pasta, rice)
• Nervous system function • Nuts
• Pork
• Poultry
• Seafood
• Whole grains
Pantothenic • Conversion of food into • Avocados 10 mg
Acid energy • Beans and peas
• Fat metabolism • Broccoli
• Hormone production • Eggs
• Nervous system function • Milk
• Red blood cell formation • Mushrooms
• Poultry
• Seafood
• Sweet potatoes
• Whole grains
• Yogurt
Riboflavin • Conversion of food into • Eggs 1.7 mg
energy • Enriched grain products (e.g.,
• Growth and development bread, cereal, pasta, rice)
• Red blood cell formation • Meats
• Milk
• Mushrooms
• Poultry
• Seafood (e.g., oysters)
• Spinach
Thiamin • Conversion of food into • Beans and peas 1.5 mg
energy • Enriched grain products (e.g.,
• Nervous system function bread, cereal, pasta, rice)
• Nuts
• Pork
• Sunflower seeds
• Whole grains
VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES WHERE IS IT FOUND DAILY
VALUE*
Vitamin A • Growth and • Cantaloupe 5,000 IU
development • Carrots
• Immune function • Dairy products
• Reproduction • Eggs
• Red blood cell • Fortified cereals
formation • Green leafy vegetables
• Skin and bone (e.g., spinach and broccoli)
formation • Pumpkin
• Vision • Red peppers
• Sweet potatoes
Vitamin B6 • Immune function • Chickpeas 2 mg
• Nervous system • Fruits (other than citrus)
function • Potatoes
• Protein, • Salmon
carbohydrate, and fat • Tuna
metabolism
• Red blood cell
formation
Vitamin B12 • Conversion of food into • Dairy products 6 mcg
energy • Eggs
• Nervous system • Fortified cereals
function • Meats
• Red blood cell • Poultry
formation • Seafood (e.g., clams, trout,
salmon, haddock, tuna)
Vitamin C • Antioxidant • Broccoli 60 mg
• Collagen and • Brussels sprouts
connective tissue • Cantaloupe
formation • Citrus fruits and juices (e.g.,
• Immune function oranges and grapefruit)
• Wound healing • Kiwifruit
• Peppers
• Strawberries
• Tomatoes and tomato juice
Vitamin D • Blood pressure • Eggs 400 IU
Nutrient of regulation • Fish (e.g., herring,
concern for most • Bone growth mackerel, salmon, trout, and
Americans • Calcium balance tuna)
• Hormone production • Fish liver oil
• Immune function • Fortified cereals
• Nervous system • Fortified dairy products
function • Fortified margarine
• Fortified orange juice
• Fortified soy beverages
(soymilk)
Vitamin E • Antioxidant • Fortified cereals and juices 30 IU
• Formation of blood • Green vegetables (e.g.,
vessels spinach and broccoli)
• Immune function • Nuts and seeds
• Peanuts and peanut butter
• Vegetable oils
Vitamin K • Blood clotting • Green vegetables (e.g., 80 mcg
• Strong bones broccoli, kale, spinach,
turnip greens, collards,
Swiss chard, mustard
greens)
* The Daily Values are the amounts of nutrients recommended per day for Americans 4 years of age or older.
Minerals
MINERAL WHAT IT DOES WHERE IS IT FOUND DAILY
VALUE*
Calcium • Blood clotting • Almond, rice, coconut, and 1,000 mg
Nutrient of • Bone and teeth hemp milks
concern for most formation • Canned seafood
Americans • Constriction and with bones (e.g.,
relaxation of blood salmon and
vessels sardines)
• Hormone secretion • Dairy products
• Muscle contraction • Fortified cereals and juices
• Nervous system • Fortified soy beverages
function (soymilk)
• Green vegetables (e.g.,
spinach, kale, broccoli, turnip
greens)
• Tofu (made with calcium sulfate)
Chloride • Acid-base balance • Celery 3,400 mg
• Conversion of food into • Lettuce
energy • Olives
• Digestion • Rye
• Fluid balance • Salt substitutes
• Nervous system • Seaweeds (e.g., dulse and kelp)
function • Table salt and sea salt
• Tomatoes
Chromium • Insulin function • Broccoli 120 mcg
• Protein, • Fruits (e.g., apple and banana)
carbohydrate, and fat • Grape and orange juice
metabolism • Meats
• Spices (e.g., garlic and basil)
• Turkey
• Whole grains
Copper • Antioxidant • Chocolate and cocoa 2 mg
• Bone formation • Crustaceans and shellfish
• Collagen and • Lentils
connective tissue • Nuts and seeds
formation • Organ meats (e.g., liver)
• Energy production • Whole grains
• Iron metabolism
• Nervous system
function
Iodine • Growth and • Breads and cereals 150 mcg
development • Dairy products
• Metabolism • Iodized salt
• Reproduction • Potatoes
• Thyroid hormone • Seafood
production • Seaweed
• Turkey
Iron • Energy production • Beans and peas 18 mg
Nutrient of concern • Growth and • Dark green vegetables
for young children, development • Meats
pregnant women, • Immune function • Poultry
and women • Red blood cell • Prunes and prune juice
capable of formation • Raisins
becoming • Reproduction • Seafood
pregnant • Wound healing • Whole grain, enriched,
and fortified cereals and
breads
MINERAL WHAT IT DOES WHERE IS IT FOUND DAILY
VALUE*
Magnesium • Blood pressure • Avocados 400 mg
regulation • Bananas
• Blood sugar regulation • Beans and peas
• Bone formation • Dairy products
• Energy production • Green leafy vegetables (e.g.,
• Hormone secretion spinach)
• Immune function • Nuts and pumpkin seeds
• Muscle contraction • Potatoes
• Nervous system • Raisins
function • Wheat bran
• Normal heart rhythm • Whole grains
• Protein formation
Manganese • Carbohydrate, • Beans 2 mg
protein, and • Nuts
cholesterol • Pineapple
metabolism • Spinach
• Cartilage and bone • Sweet potato
formation • Whole grains
• Wound healing
Molybdenum • Enzyme production • Beans and peas 75 mcg
• Nuts
• Whole grains
Phosphorus • Acid-base balance • Beans and peas 1,000 mg
• Bone formation • Dairy products
• Energy production and • Meats
storage • Nuts and seeds
• Hormone activation • Poultry
• Seafood
• Whole grain, enriched,
and fortified cereals and
breads
Potassium • Blood pressure • Bananas 3,500 mg
Nutrient of regulation • Beet greens
concern for most • Carbohydrate • Juices (e.g., carrot,
Americans metabolism pomegranate, prune, orange,
• Fluid balance and tomato)
• Growth and • Milk
development • Oranges and orange juice
• Heart function • Potatoes and sweet potatoes
• Muscle contraction • Prunes and prune juice
• Nervous system • Spinach
function • Tomatoes and tomato products
• Protein formation • White beans
• Yogurt
Selenium • Antioxidant • Eggs 70 mcg
• Immune function • Enriched pasta and rice
• Reproduction • Meats
• Thyroid function • Nuts (e.g., Brazil nuts) and
seeds
• Poultry
• Seafood
• Whole grains
Minerals
MINERAL WHAT IT DOES WHERE IS IT FOUND DAILY
VALUE*
Sodium Acid-base balance Breads and rolls 2,400 mg
Nutrient to get less Blood pressure regulation Cheese (natural and processed)
of Fluid balance Cold cuts and cured meats (e.g.,
Muscle contraction deli or packaged ham or turkey)
Nervous system function Mixed meat dishes (e.g., beef stew,
chili, and meat loaf)
Mixed pasta dishes (e.g., lasagna,
pasta salad, and spaghetti with
meat sauce)
Pizza
Poultry (fresh and processed)
Sandwiches (e.g., hamburgers, hot
dogs, and submarine sandwiches)
Savory snacks (e.g., chips,
crackers, popcorn, and pretzels)
Soups
Table salt
Zinc Growth and development Beans and peas 15 mg
Immune function Beef
Nervous system function Dairy products
Protein formation Fortified cereals
Reproduction Nuts
Taste and smell Poultry
Wound healing Seafood (e.g., clams, crabs,
lobsters, oysters)
Whole grains
* The Daily Values are the amounts of nutrients recommended per day for Americans 4 years of age or older.
You might also like
- NCLEX-RN Test Study GuideDocument199 pagesNCLEX-RN Test Study GuidebtheresakNo ratings yet
- Plymouth Hospitals Guide to Nasogastric and Gastrostomy FeedingDocument45 pagesPlymouth Hospitals Guide to Nasogastric and Gastrostomy FeedingbandarascbNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNDocument36 pagesAcid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNkatrinasdNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersDocument4 pagesMed Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersMaxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease: Thoracic Conference Frank Nami, M.DDocument49 pagesCongenital Heart Disease: Thoracic Conference Frank Nami, M.DMarie CrystallineNo ratings yet
- Review On Peripheral IV FluidsDocument37 pagesReview On Peripheral IV FluidsWoot RootNo ratings yet
- Endocrine MedicationsDocument47 pagesEndocrine MedicationsAamir AzizNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Mrs. Hogan AsthmaDocument4 pagesCase Study 1 Mrs. Hogan Asthmaissaiahnicolle100% (2)
- NUR217a IV Flow Rate CalculationDocument8 pagesNUR217a IV Flow Rate CalculationMikeNo ratings yet
- PAMANTASAN NG CABUYAO Diagnostic Exam for Community Health Nursing 2 & Psychiatric NursingDocument19 pagesPAMANTASAN NG CABUYAO Diagnostic Exam for Community Health Nursing 2 & Psychiatric Nursingissaiahnicolle100% (2)
- METABOLISM AND NUTRITIONDocument46 pagesMETABOLISM AND NUTRITIONMICHELLE FACTONo ratings yet
- UWORLDNCLEXreview2021 Watermarked PDFDocument100 pagesUWORLDNCLEXreview2021 Watermarked PDFashley100% (1)
- Constipation: Stools ExplainedDocument4 pagesConstipation: Stools ExplainedArun MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Midterm 1Document26 pagesNCM 106 Midterm 1JULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Diet TherapyDocument140 pagesDiet Therapyraghadalesawi51No ratings yet
- University Students' Self-Efficacy in Online Learning Due To COVID-19Document7 pagesUniversity Students' Self-Efficacy in Online Learning Due To COVID-19issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Prof. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument5 pagesProf. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: Katrina Saludar Jimenez, R. NDocument42 pagesHepatobiliary Disorders: Katrina Saludar Jimenez, R. NKatrinaJimenezNo ratings yet
- Pharm WorksheetsDocument29 pagesPharm Worksheetsj.siemens1dNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Note TakingDocument3 pagesFundamentals Note TakingJero BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Calories ValueDocument103 pagesCalories ValueJ.n. AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsDocument16 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Function of G I System: The Primary Digestive Functions Are Break Down Food Particles "Document113 pagesFunction of G I System: The Primary Digestive Functions Are Break Down Food Particles "cherryann_12100% (1)
- Anti-Infectives: Antiviral, Antitubercular DrugsDocument38 pagesAnti-Infectives: Antiviral, Antitubercular Drugsapril jholynna garroNo ratings yet
- Assocham Knowledge Report On Nutracuticals Released at 3rd National Symposium 6Document111 pagesAssocham Knowledge Report On Nutracuticals Released at 3rd National Symposium 6Syed Osama Ali100% (1)
- Project Report On MillDocument13 pagesProject Report On MillAashish KuNo ratings yet
- NLN nutrition practice exam study guideDocument3 pagesNLN nutrition practice exam study guideKaren HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Completed Concept MapDocument4 pagesCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848No ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part IDocument17 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part Iɹǝʍdןnos97% (64)
- Pamantasan NG Cabuyao: College of NursingDocument78 pagesPamantasan NG Cabuyao: College of NursingissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancyDocument6 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancykirbsNo ratings yet
- NCP AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP Asthmaissaiahnicolle0% (1)
- Jamjam Chap 1 5Document56 pagesJamjam Chap 1 5Pau AbuenaNo ratings yet
- TPNDocument43 pagesTPNMuhammad Arif Nur SyahidNo ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Anjani.S.Kamal 1 Year MSC (N)Document23 pagesPresented By: Anjani.S.Kamal 1 Year MSC (N)shubham vermaNo ratings yet
- Description Size Weight (Grams) Energy (Calories) Carbs (Grams) Protein (Grams) Cholesterol (Milligms) Fat (Grams) Saturated Fat (Grams)Document45 pagesDescription Size Weight (Grams) Energy (Calories) Carbs (Grams) Protein (Grams) Cholesterol (Milligms) Fat (Grams) Saturated Fat (Grams)api-138100148No ratings yet
- Brain Dump NUR 213 FINALDocument37 pagesBrain Dump NUR 213 FINALkelsey jackson100% (1)
- Flashcards for Admin ConsiderationsDocument1 pageFlashcards for Admin ConsiderationsAntonette Joy SolinapNo ratings yet
- 60 Most Common DrugsDocument1 page60 Most Common DrugsNikkaLim100% (1)
- Maternal Ob NotesDocument103 pagesMaternal Ob NotesBoris OrbetaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Ch. 36 - UrinaryDocument27 pagesWeek 11 - Ch. 36 - UrinaryMary SingletonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Aki Presentation EportfolioDocument32 pagesClinical Case Aki Presentation Eportfolioapi-463444835No ratings yet
- CH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and PancreasDocument28 pagesCH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and Pancreasjrflores1284No ratings yet
- Sinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementDocument4 pagesSinus Bradycardia: I. Sinus Dysrhythmias Description ManagementMargueretti Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- ATI Med Template Vitamin DDocument1 pageATI Med Template Vitamin DHeather MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Analysis ProjectDocument7 pagesNutrition Analysis Projectapi-268293649No ratings yet
- En CalculationsDocument12 pagesEn Calculationsapi-402549057No ratings yet
- Guide To Diabetes MedicationsDocument2 pagesGuide To Diabetes MedicationsJianhua ShiNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: Perioperative OverviewDocument24 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: Perioperative OverviewSheena Ann L. LLarenasNo ratings yet
- ULCERATIVE COLITIS-doneDocument6 pagesULCERATIVE COLITIS-donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- Nutri - RVWR - Water Soluble VitaminsDocument4 pagesNutri - RVWR - Water Soluble VitaminsDon Nikko Lemuel OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Portillo Health Assessment VocabularyDocument9 pagesJennifer Portillo Health Assessment VocabularyJennifer PortilloNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument13 pagesIneffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsLester MooreNo ratings yet
- Diabetes WorksheetDocument2 pagesDiabetes WorksheetAstrid TelloNo ratings yet
- Potassium and Sodium Level Imbalances: Hyperkalemia, Hypokalemia, Hypernatremia, HyponatremiaDocument5 pagesPotassium and Sodium Level Imbalances: Hyperkalemia, Hypokalemia, Hypernatremia, HyponatremiaChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Diagnosis Schizophrenia 2Document1 pageDiagnosis Schizophrenia 2Bukola OgunnaikeNo ratings yet
- Blood PanelsDocument7 pagesBlood Panelslisalov100% (1)
- Mds 3Document3 pagesMds 3api-434982019No ratings yet
- Nursing 212 Final Exam Review - Fall 2017Document12 pagesNursing 212 Final Exam Review - Fall 2017Marc LaBarbera100% (1)
- Quizlet EndoDocument17 pagesQuizlet EndoemmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PathophysiologyDocument125 pagesIntroduction To PathophysiologyJes CmtNo ratings yet
- Rvrtv5tgt5Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument4 pagesRvrtv5tgt5Abnormal Uterine BleedingChethranNo ratings yet
- 3 Fluids and Electrolytes PPDocument112 pages3 Fluids and Electrolytes PPjcodoyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate - Modified Diets For Malabsorption SyndromesDocument51 pagesCarbohydrate - Modified Diets For Malabsorption SyndromesJustKath OneseventwoNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentsDocument76 pagesHealth AssessmentsAtashia Rain GaguiNo ratings yet
- Comfort, rest, and sleep through pain managementDocument17 pagesComfort, rest, and sleep through pain managementDyna TumbokonNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDDocument48 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDGabriel Carlo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Self Efficacy 4 PDFDocument39 pagesSelf Efficacy 4 PDFCiara Mae PrincesNo ratings yet
- CECILIA-Act 2Document3 pagesCECILIA-Act 2issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- SalerioDocument28 pagesSalerioRizqaFebrilianyNo ratings yet
- Self-Efficacy and Clinical Competence of Fourth-Year Nursing Students: A Self-Reported StudyDocument7 pagesSelf-Efficacy and Clinical Competence of Fourth-Year Nursing Students: A Self-Reported StudyissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Nurse Education in Practice: Melodie Rowbotham, Rachel M. OwenDocument6 pagesNurse Education in Practice: Melodie Rowbotham, Rachel M. OwenissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Self-Efficacy and Clinical Reasoning of UnderDocument98 pagesThe Relationship of Self-Efficacy and Clinical Reasoning of UnderissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument24 pagesPreviewissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Article5 1Document6 pagesArticle5 1issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Progression of Clinical Self-Efficacy Among Baccalaureate NursingDocument109 pagesProgression of Clinical Self-Efficacy Among Baccalaureate NursingissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- PrayerDocument1 pagePrayerissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Relationship between self-efficacy, problem solving, communication of Korean nursesDocument7 pagesRelationship between self-efficacy, problem solving, communication of Korean nursesissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Google Meet LinksDocument1 pageGoogle Meet LinksissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- SimsDocument1 pageSimsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- FullDocument1 pageFullissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Patient InformationDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Patient InformationissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCP FormDocument2 pagesNCP FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing PatternissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCP - Cellular AberrationDocument1 pageNCP - Cellular Aberrationissaiahnicolle100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Bronchial Asthma PatientDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Bronchial Asthma PatientissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Senn Retractors (2) : Instrumentation 1. Av Shunt TrayDocument8 pagesSenn Retractors (2) : Instrumentation 1. Av Shunt TrayissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- CHN Practice Without AnswerDocument19 pagesCHN Practice Without AnswerissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Equipment SuppliesDocument5 pagesEquipment SuppliesissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
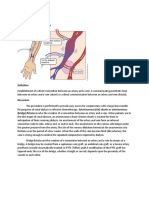
- Arteriovenous Shunt or Arteriovenous (Bridge) FistulaDocument1 pageArteriovenous Shunt or Arteriovenous (Bridge) FistulaissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Anton-Paduraru Dieta Vegetariana La Copil Pedia - Nr-4 - 2014 - Art-1Document10 pagesAnton-Paduraru Dieta Vegetariana La Copil Pedia - Nr-4 - 2014 - Art-1o0209No ratings yet
- Lkfo 6Document39 pagesLkfo 6JUAN MANCILLANo ratings yet
- WFP (Indonesia) Fortified BiscuitsDocument3 pagesWFP (Indonesia) Fortified BiscuitsPham Thi Cam TuNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Exam 1: FortifiedDocument8 pagesNutrition Exam 1: FortifiedNicholas LimNo ratings yet
- Fortifications in Ice-Cream With Enhanced FunctionDocument9 pagesFortifications in Ice-Cream With Enhanced FunctionRosalin nathNo ratings yet
- Diet and NutritionDocument92 pagesDiet and NutritionSheeba AnilNo ratings yet
- Tugas WindaDocument11 pagesTugas Windawinda sari wahyuniNo ratings yet
- Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies Bengaluru CampusDocument11 pagesNarsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies Bengaluru CampusSaurabh Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- Vitamins, Minerals, Antioxidants, Phytonutrients, Functional FoodsDocument32 pagesVitamins, Minerals, Antioxidants, Phytonutrients, Functional Foodssatrijo salokoNo ratings yet
- Calcium Lactate Gluconate Aug02Document3 pagesCalcium Lactate Gluconate Aug02tarekscribdNo ratings yet
- WHO - Guidelines - Implementing Effective Actions For Improving Adolescent NutritionDocument68 pagesWHO - Guidelines - Implementing Effective Actions For Improving Adolescent NutritionDaysi RocioNo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 110 - Articles - 75606 - Submission - Proof - 75606 1309 172008 1 10 20120413Document18 pagesAjol File Journals - 110 - Articles - 75606 - Submission - Proof - 75606 1309 172008 1 10 20120413Md UmerNo ratings yet
- A Study of Village Kudapi, Hatgamharia, W.singhbhum JharkhandDocument23 pagesA Study of Village Kudapi, Hatgamharia, W.singhbhum JharkhandArun D PaulNo ratings yet
- SCRAPBOOKDocument18 pagesSCRAPBOOKKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Sunlight Robbery Vitamin D 0liver GillieDocument19 pagesSunlight Robbery Vitamin D 0liver Gillieashlei32No ratings yet
- Food Sources of 31 Essential Vitamins and MineralsDocument18 pagesFood Sources of 31 Essential Vitamins and Mineralssampath pambalaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document10 pagesVitamin B12entomaNo ratings yet
- Fortified rice: An opportunity to address micronutrient deficienciesDocument19 pagesFortified rice: An opportunity to address micronutrient deficiencieslalit keswaniNo ratings yet
- Dietary Reference Intakes For Vitamins - NCBI BookshelfDocument2 pagesDietary Reference Intakes For Vitamins - NCBI Bookshelfmuthu kumarNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For DFS Production For The Salt ProcessorsDocument115 pagesTraining Manual For DFS Production For The Salt ProcessorsSyed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Safe Upper Levels For Vitamins and Minerals (FSA)Document360 pagesSafe Upper Levels For Vitamins and Minerals (FSA)jcpchin2No ratings yet
- The Flour Treatment Agent and Fortificant That May Compromise The Halalan Syafiqullah Bin Lukman (1180869) Group 3 INSTRUCTOR: Assoc. Prof DR Alina Abdul Rahim Faculty of Science & TechnologyDocument9 pagesThe Flour Treatment Agent and Fortificant That May Compromise The Halalan Syafiqullah Bin Lukman (1180869) Group 3 INSTRUCTOR: Assoc. Prof DR Alina Abdul Rahim Faculty of Science & TechnologySyafiqullahNo ratings yet
- Vitamins To CLEAN Your FATTY LIVERDocument5 pagesVitamins To CLEAN Your FATTY LIVERNiloufar GholamipourNo ratings yet
- Legal Mandates Related To Nutrition and Diet Therapy ReportDocument41 pagesLegal Mandates Related To Nutrition and Diet Therapy ReportSceneryNo ratings yet
- pdf15 Total Dairy BrochureDocument12 pagespdf15 Total Dairy BrochurefreelimcomNo ratings yet