0% found this document useful (0 votes)
133 views30 pagesUnderstanding Ellipses: Definitions & Graphing
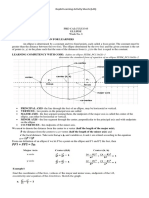
- An ellipse is defined as the locus of points where the sum of the distances to two fixed points (foci) is a constant.
- The standard forms of an ellipse equation depend on whether the major axis is horizontal or vertical.
- The key elements of an ellipse are its center, lengths of the major and minor axes (a and b), and foci.
Uploaded by
Mattheus Marcus ContrerasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
133 views30 pagesUnderstanding Ellipses: Definitions & Graphing
- An ellipse is defined as the locus of points where the sum of the distances to two fixed points (foci) is a constant.
- The standard forms of an ellipse equation depend on whether the major axis is horizontal or vertical.
- The key elements of an ellipse are its center, lengths of the major and minor axes (a and b), and foci.
Uploaded by
Mattheus Marcus ContrerasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd